careers in food service - Fort Thomas Independent Schools
advertisement

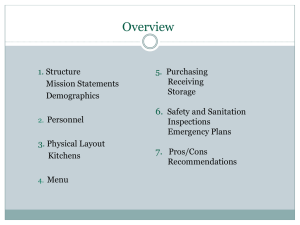
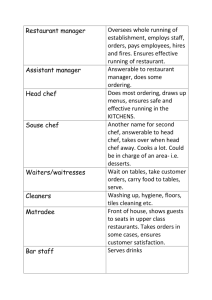
According to the NRA (National Restaurant Association) there are 13.1 million people in the US working the food service industry. one of the largest employment segments in the US Most of these perform a service Wide array of career ops 2 General types of foodservice jobs a. Working with the customers – service staff b. Working with the food prep – production staff Service staff must be able to relate to all kinds of customers 4 types of Service opportunities are Host, cashier, server, and buser Use the kitchen brigade – first established by Chef Escoffier Some restaurants use cross-training: employees gain experience in different tasks. Reduces labor cost Fast service Line cook/station cooks work on food production line work is usually divided into stations – grill, fry Sous chef under chef supervises assists other chefs fills in for executive chef Pastry chef baked items (rolls and breads, desserts) often start very early in the a.m. Prep cook prepares the ingredients used by the line cooks. May wash the vegetables that will be cooked that evening Garde Mange – pantry chef prepares cold food items Salads, cold meats, appetizers, garnishes Executive Chef manages all the kitchen operations orders supplies creates work schedules develops menus Manage food prep and service Works with the restaurant manager and dining room supervisor as a team Research chef Hired by large food manufacturers to work in lab or test kitchens Hired by restaurant chains Works with food scientist to develop new products Write nutrition info on packaging Culinary Scientist Combines culinary arts and food science Develops new technologies Creates new food products Food service director Manages the banquet operations of hotels and banquet halls Hospitals, universities, nursing homes, schools Catering director Reports to the foodservice director Coordinates the food for all the functions that may be occurring at the same time Coordinates servers, bartenders, and food Kitchen manager Often in chain restaurants Orders ingredients Oversees food production Manages employees May not have the power to decide on foods to be served and style of service Dining room supervisor For large restaurants Coordinates and supervisors dining room activities Restaurant manager Manages dining room supervisor and kitchen manager Over the entire restaurant May also be used for cooking etc. if a smaller restaurant Purchaser Buys food and supplies Needs to search for best prices and quality Stay current with inventory Sales rep Helps chef to select food and equipment to meet their needs Works for vendor Food researcher Food writer Food scientist Food stylist Food marketer Menu developer Recipe developer Foodservice trainer Registered dietitians or nutritionist Grocery and deli managers The more education and training you have, the faster you will advance The training program should fit your career goals Experience is key Excellent opportunities for hands on learners Fast paced, ever changing May work nights and weekends, classes geared to those hours Usually require work experience, course work, and a test Includes pastry, baking, culinary arts, etc Servsafe certification Need to research employability Usually fast paced and short term Usually take 2 years Usually include hands on practice May include on the job experience Need to evaluate expenses May need to extend learning Usually 4 year programs In-depth training in more than one area Hands on training in many type of food prep techniques Management Marketing Business Cooperative education