Topic 8

Topic 8
Economic Concepts
Topic 8: Economic Concepts
• Learning Objectives
– Apply the following economic concepts and measures in making financial planning recommendations
1) Supply and demand
2) National Income Accounts (including GDP)
3) Business cycles (unemployment, recession, fiscal and monetary policy)
4) Interest rates (including its term structure and the yield curve) and inflation
5) Exchange rates
Topic 8: Economic Concepts
• Supply and demand
• Fiscal policy
• Monetary policy
• Economic indicators
• Business cycles
• Inflation, deflation and stagflation
• Yield curve
Topic 8: Supply and Demand
• Supply
– The amount of a good or service that producers are willing to sell
• Normally, the higher the price of the item, the greater will be the quantity supplied
• Demand
– The amount of a good or service that buyers are willing to purchase
• Normally, the lower the price of the item, the greater will be the quantity demanded
Topic 8: Fiscal Policy
• Government actions by Congress and the
President to influence the level of economic activity
– Restrict the money supply (tighten)
• Decrease government spending
• Increase taxes
– Stimulate the money supply (loosen)
• Increase government spending
• Decrease taxes
Topic 8: Monetary Policy
• Federal Reserve actions to increase or decrease the size of the nation’s money supply
– Tighten money supply
• Raise reserve requirement
• Raise discount rate
• Sell government securities
– Loosen money supply
• Lower reserve requirement
• Lower discount rate
• Buy government securities
Topic 8: Economic Indicators –
Leading Indicators
• Tend to give early signals of the future direction of the economy
– The average weekly hours of manufacturing production workers
– The average weekly new claims for unemployment compensation
– Building permits for new private housing units
– Stock prices
– Size of the money supply
Topic 8: Business Cycles
• The business cycle is the name economists give to the expansion and contraction of economic activity
– The beginning is said to be a trough of the wave, and expansion continues until economic activity reaches a peak and economic activity turns down
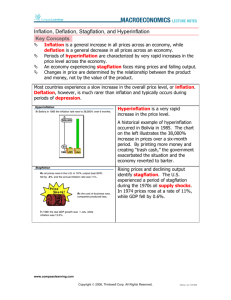
Topic 8: Inflation, Deflation and
Stagflation
• Inflation
– Increase in the general level of prices
• Deflation
– Decrease in the general level of prices
• Stagflation
– Prices will be increasing at a high inflation rate, coupled with an economic recession or high unemployment
Topic 8: Yield Curve
• A diagram that plots yield to maturity against term to maturity for similar securities
– Usually, the yield curve is upward-sloping, indicating higher interest rates for longer time until maturity of a security
Topic 8: Yield Curve
• Three theories
– Market Segmentation theory
• Investors have preferred habitat and short-term securities are not good substitutes for long-term securities
– Expectations theory
• Return on long-term security equals accumulated return on multiple short-term securities
– Liquidity Preference theory
• Long-term securities are less liquid and investors demand a premium for illiquidity