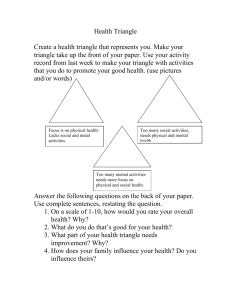
Health Intro
advertisement

9/2/14 PLEASE GRAB JOURNAL AND GET PREPARED FOR CLASS. -PENCILS SHARPENED -SITTING QUIETLY READY TO LEARN JOURNAL SET UP TABLE OF CONTENTS W-E-L-L W- warm-up E- exercise L- Linking L- Leaving Note 9/2/14 TOC: Health Triangle W- In your own words define what you think the meaning of health is. E- Health Health is the combination of physical, mental, emotional, and social well being. The word health comes from an Old English word meaning “to make sound, whole, or well.” (same root as heal) The Health Triangle Being healthy means having a balanced health triangle. Physical Health-keeping your body strong and healthy. Balanced Diet Sleep Daily Exercise Managing Weight Avoiding Diseases & Drugs Social Health Social health involves getting along with others. parents, siblings, friends, teachers…, making and keeping friends, giving and receiving support when needed and being a good citizen. Mental Health Mental health is the state of liking and accepting yourself. Learning, Coping, Stress Management Short? Tall? Skinny? Chubby? Dark skin? Light skin? How do you feel about yourself? Why? Love yourself! You are very special! Emotional Health The ability to show emotions in a healthy & accepted manner. expressing emotions, facing problems, dealing with pressure & stress, and staying positive. Express emotions Positive? Negative? Handle Responsibilities Learn new skills? Set goals? Resilient? Eating Habits Exercise? Sleep? Doctors check ups? Avoid Drugs/Alcohol Avoid Risk Support people? Friendly? Careful with what you say? Loyal, Truthful, dependable? Able to give feedback Doesn’t put people down E- Foldable Set-up Materials: -Blue Text book pg 3 -Craft box -2White Printer Paper Label the Front: “My Health Triangle” Label each page Physical Health, Social Health, Mental/Emotional Health L- Foldable directions You are going to fill out the foldable specific to you…. For example: Physical Health: Social: Mental/Emo: Express emotions Positive? Negative? Handle Responsibilities Learn new skills? Set goals? Resilient? L- VOCABULARY CH 1 Write the word down and leave space. Go to glossary pg. 447 and define! DEFINE: 1. Self-Assessment 2. Wellness 3. Heredity 4. Environment 5. Culture 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. 12. 13. 14. Media Evaluate Risk Behavior Consequences Cumulative Risk Subjective Objective Prevention Abstinence Express emotions Positive? Negative? Handle Responsibilities Learn new skills? Set goals? Resilient? Eating Habits Exercise? Sleep? Doctors check ups? Avoid Drugs/Alcohol Avoid Risk Support people? Friendly? Careful with what you say? Loyal, Truthful, dependable? Able to give feedback Doesn’t put people down E- Health in Past vs. Today Infectious diseases were the most significant health problems in the past. Health problems today are caused in part by unhealthy lifestyles. EX: Diabetes, heart disease, and cancer are examples of lifestyle diseases. Health in Past Infectious diseases Cholera- Some affected individuals have copious amounts of diarrhea and develop dehydration so severe it can lead to death. Yellow fever is an acute viral infectious disease that is transmitted to humans through the bite of infected mosquitoes. Yellow fever is thought to have originated in Africa and was likely brought to the Americas on ships during the slave trade Health in Past Infectious diseases Tuberculosis (TB) is an infection, primarily in the lungs caused by bacteria called Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Smallpox is an infectious disease of the past that was eliminated by vaccination. The disease was caused by the variola virus, which spread from person to person. Affected people became very ill with a high fever and a characteristic rash. Up to one-third of people with smallpox died. Health in Past Health Today Heart Disease- Is the leading cause of death in the United States for men and women. Coronary heart disease (CHD) is a narrowing of the small blood vessels that supply blood and oxygen to the heart. Fatty material and other substances form a plaque build-up on the walls of your coronary arteries. The coronary arteries bring blood and oxygen to your heart. This buildup causes the arteries to get narrow. As a result, blood flow to the heart can slow down or stop. Health Today Skin Cancer Excessive exposure to sunlight is the main cause of skin cancer. Sunlight contains ultraviolet (UV) rays that can alter the genetic material in skin cells, causing mutations. Sunlamps, tanning booths, and X-rays also generate UV rays that can damage skin and cause malignant cell mutations. Risk Factors and Your Health A risk factor is anything that increases the likelihood of injury, disease, or other health problems. Controllable Risk Factors- risk factors you can control by some choices. Uncontrollable Risk Factors- risk factors you cannot control including age, race, gender, and heredity. You can protect your health by focusing on controllable risk factors. Know the leading causes of death for people in your age group. Be aware of the leading causes of death for people of all ages. Six Health Risk Behaviors 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. Sedentary Lifestyle Alcohol and Other Drug Use Sexual Activity Behaviors That Cause Injury Tobacco Use Poor Eating Habits What risk factors do you think are the most common at your school? L&L What could be risky behaviors for your health? Name at least 3 What can you do to change these factors? L What did you find interesting about todays lesson? Any questions you still have? Answer in a complete sentence! **Use 5 vocabulary words we learned from yesterday. 1/28/15 TOC: Triangle Analysis W- After completing or thinking about your health triangle do you think you are balanced? Balanced: Physically, Mentally/Emotionally, and Socially Explain your answer E- Healthy Living Video Physical Health Mental/Emotional Social - Health Health LWhy is having a balance health triangle important? And why is it important to start early? LTomorrow we will begin talking about goals. You saw in the video teens setting different goals, what kinds of strategies did they use?