The Blood Notes
advertisement

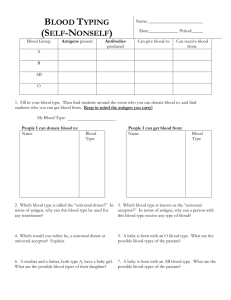
Blood & Circulation Unit 10 Introduction Blood is the primary transportation fluid of the body. Two of its most important functions are transportation and protection. Blood Composition Blood is a fluid tissue that has many chemicals dissolved in it and millions upon millions of cells floating in it. Blood Composition Blood – Mostly made of water. The body’s cells depend on food, oxygen & salt delivered through the circulatory system for survival. Blood Composition Blood – The average adults has approximately 6 liters of blood in their body. (7%-9% of total body wt.) Blood Composition Blood is made of two components: 1.Plasma – liquid part 2.Formed Elements – cells & cell fragments Blood Composition Plasma - Plasma Proteins Albumins – thickens blood Globulins – protects us from infections Fibrinogen – needed for blood to clot Blood Composition Plasma - Serum Contains antibodies which can be used to treat patients with specific antigens. Blood Composition Plasma - Serum Antibody – substance that destroys or deactivates a foreign matter (antigen) that attacks the body Blood Composition Formed Elements – 3 Kinds Red Blood Cells – RBC (erythrocytes) White Blood Cells – WBC (leukocytes) Platelets - Thrombocytes Blood Composition Formed Elements – Red Blood Cells – RBC Functions: 1.Transports CO2 from cells to lungs. 2.Transports O2 from lungs to cells. Blood Composition Oxygen – carried in red blood cells as oxyhemoglobin. Wastes - dissolved in the blood and carried to excretory organs. Blood Composition Every second there are approximately 2 million RBC’s produced by the body. How happy are they Jimmy? Happier than an oxygenated red blood cell! Blood Composition Formed Elements – White Blood Cells – WBC Function: 1.Defend body from microorganisms that invade tissues or bloodstream Blood Composition Formed Elements – White Blood Cells – WBC 2.Phagocytosis – process by which phagocytes ingest and digest foreign matter attacking cells/tissues Blood Composition Formed Elements – White Blood Cells – WBC 3.Provide immunity from certain infections/diseases (antibodies) Blood Composition Formed Elements – White Blood Cells – WBC Types: 1.Granular – granules in their cytoplasm 2.Nongrannular – no granules in cytoplasm Blood Composition Formed Elements – Platelets – Thrombocytes Function: 1.Essential for blood clotting Platelet Blood Composition Formed Elements – Platelets – Thrombocytes Vitamin K stimulates liver cells to produce prothrombin (blood protein) which causes faster clotting. Blood Composition Formed Elements – Platelets – Thrombocytes Vitamin K Food Sources: fruits, vegetables Blood Composition Formed Elements – Platelets – Thrombocytes Clot Formation Platelets turn sticky to start forming clot, fibrinogen (plasma protein) is combined with thrombin (protein) forming fibrin Blood Composition Formed Elements – Platelets – Thrombocytes Fibrin A fibrous gel made of what appears to be a tangle of fine threads. RBC’s are in the tangle. Fibrin Blood Composition Normal Values (per cubic mm) RBC’s - 4.2-5.8 Million WBC’s – 5-9 Thousand Platelets – 250-400 Thousand Blood Types ABO System Four different blood types: Type A Type B Type AB Type O Blood Types ABO System Blood types are determined by the antigen present in the RBC’s of the person’s blood at birth. The person can only accept blood with compatible antigen. Blood Types Blood Type Antigen Type A “A” Antigen Type B “B” Antigen Type AB “A” & “B” Antigens Type O No Antigens Blood Types ABO System Type O Universal Donor Type AB Universal Recipient Blood Types Rh System Rh Positive – RBC’s contain additional antigen called Rh (First discovered in Rhesus monkeys) Rh Negative – Rh Antigen does not exist Blood Types Blood Type Antigen A+ “A” Antigen Rh Antigen A- “A” Antigen B+ “B” Antigen Rh Antigen B- “B” Antigen Blood Types Blood Type Antigen AB+ “AB” Antigen Rh Antigen AB- “AB” Antigen O+ No Antigens Rh Antigen O- No Antigens Blood Types ABO System Type O- Universal Donor Type AB+ Universal Recipient Blood Disorders Erythroblastosis Fetalis Baby from Rh Positive father and Rh Negative mother inherits the Rh Positive antigen from father. Mother’s body creates antibodies against baby’s Rh+ blood. Blood Disorders Erythroblastosis Fetalis The FIRST baby born is not affected. This condition is a danger to future pregnancies if the mother is not treated upon delivering the first baby. Blood Disorders Erythroblastosis Fetalis Treatment – RhoGam Blood protein given by way of injection to mother upon delivery of first baby. Blood Disorders Erythroblastosis Fetalis Treatment – RhoGam Stops the mother’s body from forming anti-Rh antibodies preventing harm to next Rh positive baby. Blood Disorders Anemia The inability of blood to carry sufficient oxygen to the body cells due to decreased RBC’s. Causes: Trauma, Ulcers, Radiation, Infection Blood Disorders Polycythemia The thickening of blood caused by an overproduction of RBC’s in bone marrow. Can actually be too thick to flow properly. Blood Disorders Sickle Cell Anemia Severe, sometimes fatal hereditary disease. When O2 is low in these patients, crystals form causing RBC’s to become deformed. Blood Disorders Sickle Cell Anemia A drug called hydroxyurea has been shown to help reduce symptoms and even prevent sickle cell crisis. Blood Disorders Leukopenia Abnormally low WBC count. (under 5000/cubic mm) AIDS is one example of a cause of leukopenia Blood Composition Normal Values (per cubic mm) RBC’s - 4.2-5.8 Million WBC’s – 5-9 Thousand Platelets – 250-400 Thousand Blood Disorders Leukocytosis Abnormally high WBC count. (over 10,000/cubic mm) More common than leukopenia and usually associated with infections. Blood Disorders Leukemia Malignant high WBC count. (can be > 30,000/cubic mm) “Blood Cancer” The WBC’s do not function properly. Body not able to effectively defend self. Blood Disorders Thrombus Stationary blood clot. Blood Disorders Embolus Clot which moves throughout bloodstream. Blood Disorders Hemophelia Inherited disorder. Failure of the body to form clotting factors VIII, IX or XI Blood Disorders Hemophelia Treatment: Extraction of these factors from donated blood. (purified to decrease chances of transmitting viral diseases – HIV) End Of Lecture