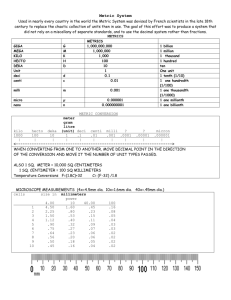
COMP3470 IS33 People-Centred Information Systems Development
advertisement

School of Computing FACULTY OF Engineering COMP3470 IS33 People-Centred Information Systems Development Week 5 : Lecture 1 Failure Case Study – Denver International Airport Weeks 5(1) 2008 IS33 DIA 1 The Denver International Airport Case Study Why study this? Any recent escalating IT project? Search for ‘NHS IT project over budget’ - In Google - In BBC News 12th Oct 2004 – http://news.bbc.co.uk/1/hi/health/3734504.stm GP worries http://news.bbc.co.uk/1/hi/health/3750474.stm - An update May 2007 http://www.computerweekly.com/Articles/2007/05/17/218050/nhs-nationalprogramme-for-it-in-the-spotlight.htm Does it ring a bell? See NAO’s value for money report on the National Programme for IT in the NHS published in June 2006. – CW2! Weeks 5(1) 2008 IS33 DIA 2 The Denver International Airport Case study Why study this? - Appreciate the range of issues in developing complex system - Introduce the concept of de-escalation - Appreciate the roles of people in complex projects Weeks 5(1) 2008 IS33 DIA 3 Sources of information Montealegre R & Keil M, De-escalating Information Technology Projects: Lessons from the Denver International Airport, MIS Quarterly, Vol 24, No. 3, Sept 2000, pp.417-447 Donaldson A.J.M., Narrative Case Study of the Denver Airport Baggage Handling System, SFC TR 2001-02, May 2002 access via http://www.cs.mdx.ac.uk/research/SFC/Reports/TR2002-01.pdf Weeks 5(1) 2008 IS33 DIA 4 Business drivers (i) Early 80s, City of Denver would like a ‘state-of-the art’ modern airport to act as a hub for major American airlines – a project for job and trade creation Sept 89, $60m was authorised to build DIA with target opening date in Oct 93 Feb 90 & Dec 91, Continental and United Airlines sent their commitment to use DIA as hub (hence they have a concourse each, A & B) Weeks 5(1) 2008 IS33 DIA 5 Business drivers (ii) Traditionally, major airlines would look after their own system for handling baggage. UA commissioned BAE to build an automated baggage handling system for their concourse. Tug-&-cart was a common baggage handling system in those days. In 92, DIA project management team began to see the benefits of an airport-wide automated baggage handling system, as “the friendliness of an airport is measured in time”. Apr 92, BAE was awarded the contract to build the system (despite BAE originally turned down the opportunity because the project was overambitious) and UA’s requirements became part of the project. Weeks 5(1) 2008 IS33 DIA 6 What happened (i) May 92, head of DIA project resigned Aug 92- Jan 93, numerous changes to requirements (from UA and Continental) Oct 92, Chief Airport Engineer (strong proponent of the baggage system) died Feb 93, Mayor delayed opening to Dec 93 and then to Mar 94. Summer 93, cars were running but programming not completed (BAE controlled) Weeks 5(1) 2008 IS33 DIA 7 What happened (ii) Sept 93, BAE negotiated maintenance contract with City of Denver and lost the contract (intended to pay £12 per hr for jobs that the union wanted £20 per hr) – occasioned a 2-day strike of millwrights and electricians Sept 93, opening delayed until May 94, and then 7 times over the next few months Jan 94, UA requested alterations to odd-size baggage inputs Weeks 5(1) 2008 IS33 DIA 8 What happened (iii) Mar 94, still dealing with ‘unclean’ electricity supply and needed additional equipment that took months to arrive Apr 94, City of Denver invited reporters to observe the first test of the baggage system without notifying BAE – reporters saw piles of damaged clothes and personal items lying beneath the Telecar’s tracks May 94, Mayor hired the German firm ‘Logplan’ to assess the state of the baggage handling system ….beginning of the ‘deescalation’ Weeks 5(1) 2008 IS33 DIA 9 The solution at the end DIA opened on 28 Feb 95 with 5 runways 99 gates Cost of $5.2 billion 3 different baggage handling systems: UA with an automated system Continental with a tug-and-cart system Others with a very conventional, highly labour intensive system Weeks 5(1) 2008 IS33 DIA 10 Concept of de-escalation The MIS Quarterly paper tried to articulate a process to get out of a troubled escalating project (they acknowledged the limitation of drawing conclusion from one case) see table 4 on p.438 Problem recognition Re-examination of prior course of action Search for alternative course of action Implementing an exit strategy Weeks 5(1) 2008 IS33 DIA 11 People issues Who were the stakeholders? And their relationships? Project management teams Inadequate skills set Poor communications Leading figures Weeks 5(1) 2008 IS33 DIA 12




![ecet- 462 [laboratory 12] - Purdue University Calumet](http://s3.studylib.net/store/data/008173019_1-0dac381f4a6d06f77c60ad52a4e53595-300x300.png)