16
35
Extending the Analysis of Aggregate
Supply
McGraw-Hill/Irwin
Copyright © 2012 by The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved.
From Short Run to Long Run
• Short run
• Wages and other input prices don’t
•
LO1
change.
• Upsloping aggregate supply
Long run
• Wages and other input prices fully
flexible
• Vertical aggregate supply.
35-2
From Short Run to Long Run
• Production above potential output:
• Price level increases.
• Nominal wages eventually rise to
maintain real wages (purchasing power).
• Other input prices rise
• Short run aggregate supply shifts left
because costs are higher.
• Return to potential output at a higher
price level.
LO1
35-3
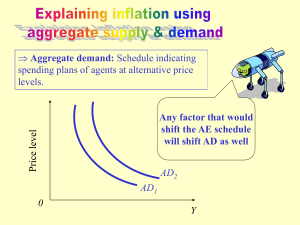
Extended AD-AS Model
Increased Demand -- Short
Long Run
Price Level
LRAS
b
P2
P1
AS1
a
AD2
AD1
Qf Q2
Real Domestic Output
LO2
35-4
Perfectly Competitive Firm in Long-run Equilibrium
Price ($)
MC
Pe
D = P = MR
Qe
Q2
QUANTITY
Extended AD-AS Model
Increased Demand -- Short
Long Run
Price Level
LRAS AS2 AS
1
P3
c
b
P2
P1
a
AD2
AD1
Qf Q2
Real Domestic Output
LO2
35-6
Extended AD-AS Model
Long Run
Run
Decreased Demand - Short
Price Level
LRAS AS1
a
P1
P2
AS2
b
AD1
AD2
Q1 Qf
Real Domestic Output
LO2
35-9
Perfectly Competitive Firm in Long-run Equilibrium
Price ($)
MC
Pe
D = P = MR
Q2
Qe
QUANTITY
Extended AD-AS Model
Long Run
Run
Decreased Demand - Short
Price Level
LRAS AS1
a
P1
P2
P3
AS2
b
c
AD1
AD2
Q1 Qf
Real Domestic Output
LO2
35-11
From Short Run to Long Run
So what is it about full employment that
keeps bringing everything back here?
Price Level
ASLR
AS1
a
P1
AD1
Qf
Real Domestic Output
LO1
35-12
From Short Run to Long Run
It’s the level of employment at which there is neither
upward nor downward pressure on wages and input
prices.
Price Level
ASLR
AS1
a
P1
AD1
Qf
Real Domestic Output
LO1
35-13
Extended AD-AS Model
Demand-Pull Inflation
Price Level
ASLR
P3
AS1
c
b
P2
P1
AS2
a
AD2
AD1
Qf Q2
Real Domestic Output
LO2
35-14
Extended AD-AS Model
Cost-Push Inflation
Price Level
ASLR
AS1
c
P3
P2
AS2
b
a
P1
AD2
AD1
Q2 Q f
Real Domestic Output
LO2
35-15
Extended AD-AS Model
Recession
Price Level
ASLR
P3
AS2
a
P1
P2
AS1
b
c
AD1
AD2
Q1 Qf
Real Domestic Output
LO2
35-16
Inflation and Unemployment
• Low inflation and unemployment
• Fed’s two major goals
• Compatible or conflicting?
• Short-run tradeoff between inflation
•
•
LO3
and unemployment
Supply shocks cause both rates to
rise
No long-run tradeoff
35-20
The Phillips Curve
• Demonstrates short-run tradeoff between
inflation and unemployment
Concept
Empirical Data
7
6
5
4
3
2
1
0
0
1
2
3
4
5
6
Unemployment Rate (Percent)
LO3
7
Annual Rate of Inflation (Percent)
Annual Rate of Inflation (Percent)
Data for the 1960s
7
69
6
5
68
4
66
67
3
65
2
1
64
63
62
61
0
0
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
Unemployment Rate (Percent)
35-22
The Phillips Curve
Annual rate of inflation (percent)
14
13
12
11
10
9
8
7
6
5
4
3
2
1
Unemployment rate (percent)
LO4
35-23
The Long-Run Phillips Curve
PCLR
Annual Rate of Inflation (Percent)
15
PC3
12
b3
PC2
9
a3
b2
PC1
6
c3
a1
c2
b1
3
0
a2
3
4
5
6
Unemployment Rate (Percent)
LO4
35-24
The Phillips Curve
• No long-run tradeoff between inflation
and unemployment
• Short-run Phillips curve
• Role of expected inflation
• Long-run vertical Phillips curve
• Disinflation
LO4
35-26