ssentials Program
advertisement
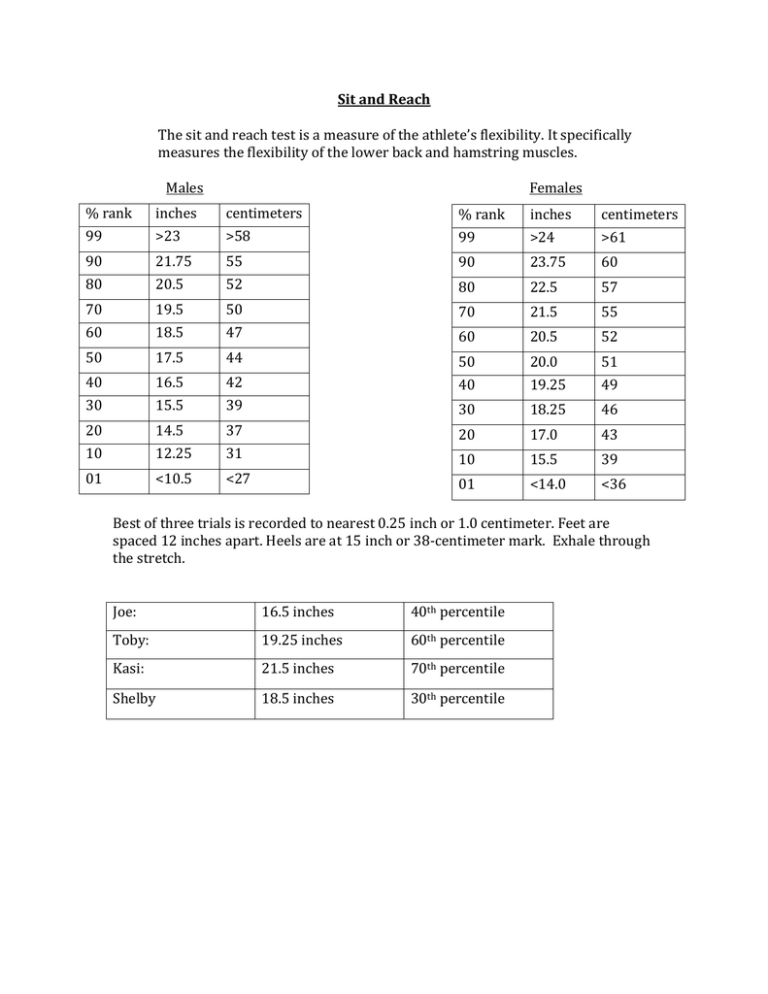
Sit and Reach The sit and reach test is a measure of the athlete’s flexibility. It specifically measures the flexibility of the lower back and hamstring muscles. Males Females % rank inches centimeters % rank inches centimeters 99 >23 >58 99 >24 >61 90 21.75 55 90 23.75 60 80 20.5 52 80 22.5 57 70 19.5 50 70 21.5 55 60 18.5 47 60 20.5 52 50 17.5 44 50 20.0 51 40 16.5 42 40 19.25 49 30 15.5 39 30 18.25 46 20 14.5 37 20 17.0 43 10 12.25 31 10 15.5 39 01 <10.5 <27 01 <14.0 <36 Best of three trials is recorded to nearest 0.25 inch or 1.0 centimeter. Feet are spaced 12 inches apart. Heels are at 15 inch or 38-centimeter mark. Exhale through the stretch. Joe: 16.5 inches 40th percentile Toby: 19.25 inches 60th percentile Kasi: 21.5 inches 70th percentile Shelby 18.5 inches 30th percentile T-test The T-test is used to assess an athlete’s speed at direction changes (agility) Three cones are set 5 yards apart in a straight line. A fourth cone is placed 10 yards from the middle cone to form a “T”. Technique Start at the cone at the base of the “T” When the athlete is ready, they will sprint towards the middle of the three cones. On the first signal of movement the timer starts the stopwatch The athlete runs to the middle cone and touches the base of the cone The athlete then shuffles 5 yards to the left cone and touches the base The athlete then shuffles 10 yards to the far right cone and touches the base The athlete then shuffles 5 yards back to the middle cone and touches the base The athlete then backpedals 10 yards to the base of the “T” or through the starting line The timer then stops the stopwatch and records the time Record times to the nearest 0.1 second. Must face forward the entire test. Must touch all cones. Best time of two trials is recorded. Sport Time (s) Trial 1 (sec) Trial 2 (sec) College basketball 8.9 Excellent <9.5 <10.5 (men) Good 9.6- 10.5 10.6- 11.5 College basketball 9.9 (women) Average 10.6- 11.5 11.6- 12.5 Competitive college 10.0 athletes (men) Poor >11.6 >12.6 Competitive college 10.8 athletes (women) Resource: Top End Sports Recreational 10.5 college athletes (men) Recreational 12.5 college athletes Trial 1 Trial 2 Trial 3 (women) Joe: 10.3 10.3 Good College tennis 9.4 seconds seconds (men) Toby: 10.9 11.1 Average Resource: Athletic Body in Balance, pg. seconds seconds 138. Kasi: 13.7 13.4 Poor Shelby: seconds 12.4 seconds seconds 12.1 seconds Average Standing Long Jump The standing long jump (broad jump) tests explosive leg power. Technique The athlete stands behind a line marked on the ground with feet shoulder width apart When the athlete is ready, he/she bends the legs at the knees, pulls the arms back and gets ready to use a great amount of force to jump as far as possible After the athlete jumps and is in the air, he/she must land on both feet without falling backwards or forwards The back foot is then marked and scored Must land on both feet to be scored. Best of three trials is recorded. Record to nearest 0.5 inch or 1 cm. Males Females % rank inches centimeters % rank inches centimeters 90 148 375 90 124 315 80 133 339 80 115 293 70 122 309 70 110 279 60 116 294 60 104 264 50 110 279 50 98 249 40 104 264 40 92 234 30 98 249 30 86 219 20 92 234 20 80 204 10 86 219 10 74 189 Attempt 1 Attempt 2 Attempt 3 Joe: 96 inches 97 inches 100.5 inches 30th percentile Toby 97 inches 97 inches 98.5 inches 30th percentile Kasi: 61 inches 60.5 inches 59.5 inches <10th percentile Shelby: 73 inches 68 inches 64.5 inches <10th percentile Squat Test The squat test is used to measure local muscular endurance of the legs. Technique Stand in front of plyometric box, facing away, feet shoulder-width apart Squat down and lightly touch the backside on the box Immediately stand back up Repeat this until the athlete is fatigued or cannot keep up with the metronome Record the number of squats completed Athlete cannot sit on the box but must rather lightly touch the box with backside. Squat must be performed with thighs traveling below parallel to the floor. Only one attempt is allowed. Ages 18-25 Excellent Males Females >49 >43 Good 44-48 37-43 Above Average 39-43 33-36 Average 35-38 29-32 Below Average 31-34 25-28 Poor 25-30 18-24 Very Poor <25 <18 Resource: National Register of Personal Trainers Joe: 39 Above Average Toby: 51 Excellent Kasi: 16 Very Poor Shelby: 52 Excellent Test Order: 1. Sit and Reach – flexibility 2. T-test- agility 3. Standing Long Jump- max power 4. Squat Test- local muscular endurance References: Baechle, T.R., & Earle, R. W. (Eds.). (2008). Essentials of strength training and conditioning (3rd ed.). Champaign, IL: Human Kinetics. Cook, Gray. (2003). Athletic Body in Balance, Champaign, IL: Human Kinetics. (National Register of Personal Trainers (NRPT), 2013). (Top End Sports (2013). Sport Specific Testing. Retrieved from http://www.topendsports.com/testing/sportspecific.htm. Resistance Training Program Basketball is a total-body sport that involves, sprinting, changes of direction, jumping, and shuffling. A resistance-training program should have such details incorporated. 4-week off-season: Sport practice-low, resistance training-high. Resistance training goal: Hypertrophy Lower Body Workout (Monday and Thursday) Exercise Load Reps Sets Rest Barbell Single Leg Squat Lunge 80% of 1RM 8 4 30-90 seconds 10-12 RM 10-12 3 30-90 seconds Leg Press 80% of 1RM 8 4 30-90 seconds Romanian Deadlift (RDL) Leg Extension 10-12 RM 10-12 3 30-90 seconds 10-12 RM 10-12 3 30-90 seconds Standing Calf Raise Seated Calf Raise 12-15 RM 12-15 3 30 seconds 12-15 RM 12-15 3 30 seconds Abdominal Crunch - 12-20 3 30 seconds Upper Body Workout (Tuesday and Friday) Exercise Load Reps Sets Rest Barbell Bench Press Lat Pulldown 75% of 1RM 10 4 30-90 seconds 10-12 RM 10-12 3 30-90 seconds Incline Bench 75% of 1RM 10 4 30-90 seconds Bent over Row 10-12 RM 10-12 3 30-90 seconds Dumbbell Shoulder Press Dumbbell Pullover Biceps Curl 75% of 1RM 10 4 30-90 seconds 10-12 RM 10-12 3 30-90 seconds 10-12 RM 10-12 3 30-90 seconds Triceps Pushdown Hanging Leg Raise 10-12 RM 10-12 3 30-90 seconds - 12-20 3 30 seconds Plyometric Workout (offseason) This plyometric workout can be done two times per week to increase vertical and speed. Remember to land softly, maintain athletic posture, and to fully recover between sets. Jump Rope (two feet)- 3 x 30 seconds with 45 second rest Jump Rope (side-to-side)- 3 x 30 seconds with 45 second rest Forward Skip-1x half court Backward Skip- 1x half court Split-Squat Jumps- 2-3 x 30 seconds with 45 second rest Ice Skaters- 2-3 x 30 seconds with 45 second rest Burpees- 2-3 x 30 seconds with 60 second rest 4-week pre-season: Sport practice-medium, resistance training-medium. Resistance training goal: Strength/Hypertrophy Monday: Heavy day- 100% of calculated loads in Core Exercises Exercises Power Clean Set 1 Load 90% of 1RM 4 90% of 1RM 4 Load 82% of 1RM 82% of 1RM 82% of 1RM 82% of 1RM Reps 6 6 6 6 80% of 1RM 8 85% of 1RM 6 85% of 1RM 6 90% of 1RM 4 Load 80% of 1RM 85% of 1RM 85% of 1RM 90% of 1RM Reps 8 6 6 4 Front Squat Load Reps Incline Bench Press Seated Row Load 8-10RM 8-10RM 8-10RM Reps 8-10 Alternating Dumbbell curl Load 8-10RM 8-10RM 8-10RM Reps 8-10 Triceps Pushdown Load 8-10RM 8-10RM 8-10RM Reps 8-10 8-10 8-10 Reps 15-20 15-20 15-20 Abdominal Crunch Set 4 90% of 1 RM 4 Reps Push Jerk Load/Reps Set 2 Set 3 8-10 8-10 Set 5 Rest 2 minutes 2 minutes 90% of 1RM 4 2 minutes 2 minutes 30-90 seconds 8-10 30-90 seconds 8-10 30-90 seconds 30 seconds Wednesday: Light day- 80% of calculated loads in Core Exercises Exercises Load/Reps Set 2 Set 3 Set 4 85% of 1 RM 6 85% of 1RM 6 85% of 1RM 6 85% of 1RM 6 2 minutes Load 80% of 1RM 80% of 1RM 80% of 1RM 80% of 1RM 1-2 minutes Reps 8 8 8 8 Load 80% of 1RM 8 80% of 1RM 8 85% of 1RM 6 85% of 1RM 6 2 minutes Load 80% of 1RM 80% of 1RM 85% of 1RM 85% of 1RM 2 minutes Reps 8 8 6 6 Load 8-10RM 8-10RM 8-10RM Reps 8-10 8-10 Alternating Hammer curl Load 8-10RM 8-10RM 8-10RM Reps 8-10 8-10 One armed Triceps Extension Load 8-10RM 8-10RM 8-10RM Reps 8-10 8-10 8-10 Hanging Leg Raise Reps 15-20 15-20 15-20 Hang Clean Set 1 Load Reps Push Jerk Back Squat Reps Incline Dumbbell Press Bent over Row Set 5 Rest 30-90 seconds 8-10 30-90 seconds 8-10 30-90 seconds 30 seconds Friday: Medium day- 90% of calculated loads in Core Exercises Exercises Power Clean Set 1 Load 90% of 1RM 4 90% of 1RM 4 Load 80% of 1RM 80% of 1RM 82% of 1RM 82% of 1RM Reps 8 8 6 6 85% of 1RM 6 85% of 1RM 6 87% of 1RM 5 90% of 1RM 4 Load 85% of 1RM 85% of 1RM 87% of 1RM 90% of 1RM Reps 6 6 5 4 Load 8-10RM 8-10RM 8-10RM Reps 8-10 Load 8-10RM 8-10RM 8-10RM Reps 8-10 Load 8-10RM 8-10RM 8-10RM Reps 8-10 8-10 8-10 Reps 15-20 15-20 15-20 Front Squat Load Reps Incline Bench Press One Armed Row Barbell Curl Triceps Kickbacks Abdominal Crunch Set 4 90% of 1 RM 4 Reps Push Jerk Load/Reps Set 2 Set 3 8-10 8-10 Set 5 Rest 2 minutes 1-2 minutes 90% of 1RM 4 2 minutes 2 minutes 30-90 seconds 8-10 30-90 seconds 8-10 30-90 seconds 30 seconds Plyometric Workout (offseason) Plyometrics, should follow after a good warm up and stretching. Should be done two days per week before resistance training. 45-second rest between sets Alternate bounding- 3 sets of 10 reps at 75% intensity Alternating push off- 3 sets of 10 reps at 90% intensity (using 6-inch box) Underhand medicine ball throw- 3 sets of 10 reps at 90% intensity Squat jump- 3 sets of 10 reps at 90% intensity 2-week competitive in-season: Sport practice-high, resistance training-low Resistance training goal: Maintenance of Strength/Hypertrophy Never lift legs the day before a game. This can cause fatigue and negatively affect court performance. Always try to leave two days for recovery. Exercise Dumbbell Bench Press One armed Dumbbell Row Lunges Military Press Neutral-Grip Chin-Ups Box Step-Ups Back Extension Abdominal Crunch Maintenance (Wednesday) Load Sets Reps 67%,75%,80% 3 12,10,8 Rest 30-90 seconds 8-10RM 8-10 30-90 seconds 67%,75%,80% 3 8-10RM 3 10-12RM 3 12,10,8 8-10 10-12 30-90 seconds 30-90 seconds 60-90 seconds 10-12RM - 3 3 10-12 15-20 60-90 seconds 30 seconds - 3 15-20 30 seconds 3 Maintenance (Saturday) Exercise Barbell Single Leg Squat Dumbbell Incline Press Dumbbell Upright Row Lunges Load 67%,75%,80%,85% Sets 4 Reps 12,10,8,6 Rest 30-120 seconds. 67%,75%,80% 3 12,10,8 8-10RM 3 8-10 67%,75%,80% 3 12,10,8 Bar Dips 10-12RM 3 10-12 Pull-ups 10-12RM 3 10-12 Good mornings Hanging Leg Raise 12-15RM 3 12-15 - 3 12-20 30-90 seconds 30-90 seconds 30-90 seconds 30-90 seconds 60-90 seconds 30-60 seconds 30 seconds Focus Training on Maximal Tension Achieving maximal tension on targeted muscle fibers can occur in two ways. One way is to lift heavy loads (70%-80% of max) for 8-12 reps or to lift a lighter load in a fatigued state. Lifting in a fatigued state makes lighter weight feel heavier and force the muscles to work harder. Putting a maximum effort in trying to strain muscles to move the weight will ensure optimal muscle growth. Under such tension, muscles become damaged and repair themselves by becoming bigger. Limit Isolation Lifts/ Encourage Compound Lifts Compound lifts are multi-joint movements that involve coordinated actions of several muscle groups to move a certain weight. The more ligaments, muscles, and tendons used through the motion, the more compound the lift is. Bench press, squat, and deadlift are the three core compound lifts that incorporate several muscle groups and encourage growth. Olympic or power lifts are more constructive to the body than isolation exercises. Full range multiple joint movements engage various muscles within the body which work simultaneously. This enhances coordination and balance and can train small stabilizer muscles. Examples of power lifts include full snatch, power clean, and power jerk. Cardiovascular Endurance Cardiovascular work is best done in the morning. This ensures that metabolism is raised throughout the day, which can burn more calories and promote faster muscle growth. Slow steady cardio may result in muscle loss while sprints or HIIT workouts allow preservation of muscle. A basic sprint workout includes seven 20-second sprints followed by a 60-90 second rest in-between. Train the Muscle Do not think about how much weight is being moved for a particular workout. What is heavy to one individual may be light to another and vice versa. Rather, focus on the muscle being worked to ensure optimal growth. Just because someone can curl 135 pounds does not mean they will have a better physique or are more athletic than someone who can only curl 30 pounds. While pushing oneself beyond their comfort zone is key to becoming stronger, technique should remain the highest priority. Switch It Up To achieve maximum tension on muscles, either work with heavy lifts or work with lighter weight in a fatigued state. This means, for one particular day, work the legs with heavy squats, front squats, and lunges for four sets each with reps ranging from eight to twelve. The next day, incorporate a series of different light kettlebell exercises and pushups with high repetitions. Doing a series of different forms of exercise will ensure a slower adaptation from the muscles. Athletic Performance Test and Program Design Essentials of Strength Training and Conditioning Jordan Knoepfel