Nuclear Chemistry
advertisement

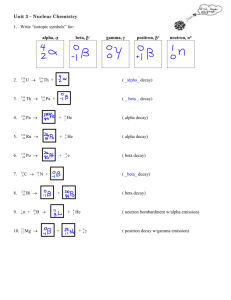
Chapter 18 Mass # Symbol Element Parts Name or symbol – Mass # of a Reaction Reactants Products Alpha emission or decay (a) –helium atom 238 U 4 He + 234 Th 92 2 90 Beta emission or decay (b)– 234 Th 234 Pa + 0 e 90 91 -1 0 -1e Gamma emission or decay (g) 238 U 4 He + 234 Th + 0 g 92 2 90 0 4 2He in the products 0 0g Positron emission or decay 22 Na 0 e + 22 Ne 11 +1 10 +1e Electron capture – beta particle in the reactants 201 Hg + 0 e + 201 Au 80 -1 79 Neutron emission or decay– 209 Po 1 n + 200 Po 84 0 84 Proton – 0 1 1H or 1 1p 1 0n Mass # and the atomic # totals must be the same for reactants and the products. 3919K 35 17Cl + ___ -1e + ___ 20682Pb 23894Pu + ___ 0 4 2He + 235 92U Alpha decay of Cu-68 Gamma emission of Thorium-235 Positron emission of P-18 Astatine-210 releasing 3 neutrons Electron capture of Ti-45 Radioactive isotopes or nuclides all decay because they are unstable, some just breakdown much faster than others Half-life – amount of time for half of the original sample to decay For two samples of the same isotope, regardless of the sample size, after one halflife, only half of the original amount of sample remains. Isotopes Carbon – 14 Sodium – 24 Bismuth – 212 Polonium – 215 Thorium – 230 Thorium – 234 Uranium – 235 Uranium – 238 Half-Live 5730 years 15 hours 60.5 seconds 0.0018 seconds 75400 years 24.1 days 7.0 x 108 years 4.46 x 109 years Barium – 139 has a half-life of 86 minutes. If you originally have a 10 gram sample of Barium-139, how much will be left after 258 minutes? How many days will it take 50 grams of Radon – 222 (half-life of 3.82 days) to decay to 3.125 grams? If a sample of Cesium-135 decays from 10 grams to 2.5 grams over a period of 84 days, what is the half-life of Cesium-135? Fusion – combining two smaller nuclei into one heavier, more stable nucleus. 3 He + 1 H 4 He + 0 e 2 1 2 1 Fission – splitting a large unstable nucleus into two nuclei with smaller mass numbers. 209 Po 125 Te + 84 Ge 84 52 32