Transitions to Democracy
advertisement
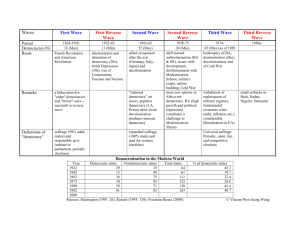
Transitions to Democracy The world circa 1960: B • 20-25 stable liberal democracies, • some newly independent countries trying liberal democracy • 80-90 countries either under or tending toward some form authoritarianism located primarily in • Western Europe, • North America, • & the white commonwealth: – Australian – New Zealand – Canada Latin America: alternated between shaky polyarchies and military government, e.g. • Argentina • Brazil • Peru • Mexico • Paraguay….. Communist party-state systems: • • • • • • USSR Poland Czechoslovakia Hungary Bulgaria Romania • Yugoslavia • People’s Republic of China • North Korea • North Viet Nam • Albania The three waves of democratization • 1rst wave: 1870-1910 • 2nd wave: – interwar period • followed by a reverse wave – post world war II: re-democratization of • Italy • West Germany (Federal Republic of Germany) • Japan • 3rd wave -- from 1970… to present? 1970s • Greece (military dictatorship, 1967-74) • Portugal 1974 – end of Salazar-Caeteno regime (from 1931) • Spain (1975) – end of Franco regime (from 1939) 1980s • collapse of military regimes in Latin America – – – – – Argentina, 1982 Brazil (opening 1977-85) Uruguay Paraguay Bolivia... 1989and beyond • fall of Berlin Wall • collapse of ‘satellite’ Communist regimes in east central Europe • break-up of the Soviet Union • Chile • Republic of South Africa • South Korea • Taiwan Transitional vs. consolidated democracies • Transitional democracies -- newly launched or re-democratized liberal democracies • Consolidated democracies: – no significant challenges to regime – “the only game in town” • Some questions: – How do we know a regime is consolidated? – How do regimes become consolidated? Categories, scales, classificatory schemes: • levels of measurement • classifying democracies – liberal democracy v. non-democracy.. – More democratic v. less democratic – more stable v. less stable • degrees of consolidation: more consolidated v. less consolidated Levels of measurement • nominal (discrete categories) • ordinal (a scale: positions on it are either: more or less, higher or lower • interval (a scale on which positions reflect measured differencesb What do we expect to find in a democracy? • Inclusiveness – all or almost all of the adult population entitled to vote • Elections – free and fair elections -- elections with choice • competition Countries and where they fit: Dimensions of liberal democracy: Mexico before 2000: – – – – – constitution some restrictions on political rights some competition elections, but not entirely free and fair elections dominance of the PRI (Party of Institutional Revolution) Nigeria: • First Republic: parliamentary system, 1961-1966 • civil war blocking Biafran secession, 1966-1969 • military rule: – General Gowan, 19691975General – Obasanjo, 1975/6-1979 • Second Republic: presidential system from 1979-1983 • Military governments from 1983-1993 – General Babangida – General Abacha • Redemocratization in 1993 under Obasanjo