File
advertisement

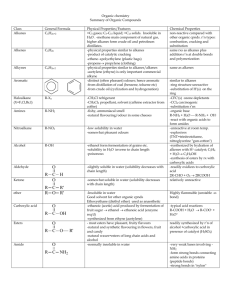
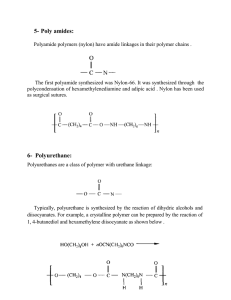
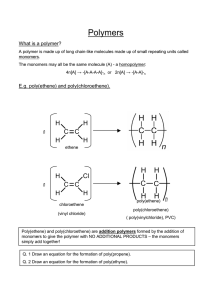
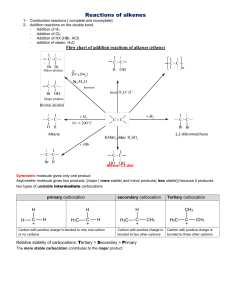
ORGANIC CHEMISTRY- SUMMARY IGCSE 620 Hydrocarbons • 1. Alkanes; Saturated compounds (single bond); Used as fuels; Substitution Reactions (light as the catalyst ); Methane, Ethane etc • 2. Alkenes; Unsaturated compounds (double bonds); Highly reactive; Addition Reactions; Ethene, Propene etc • (Addition of Hydrogen, Halogen, Hydrogen halide, Steam) • Test for unsaturated compounds: Using Bromine water: turns red-brown to colourless • Hydrocarbons burn to produce CO2 and H2O • When incomplete combustion occurs, the products are CO, C and H2O Petroleum • Fractional Distillation based on Boiling points. Fractions include- Petroleum Gas, Petrol, Naphtha, Kerosene, Diesel, lubricating oil, Bitumen • Cracking: Meaning and need; Alkene is one product. • Alcohol: Methanol, Ethanol, Propanol • Manufacture of Ethanol by Batch process(Yeast) and continuous process(from ethene) ; • Advantages and disadvantages of the two methods. • Homologous Series: alkanes, Alkenes, Alcohols, Carboxylic acids etc as examples; • Properties of homologous series • Formula: Writing molecular formula and structural formula of organic compounds • Functional groups: double bond; -OH and –COOH groups • Esterification reaction: Carboxylic acid + Alcohol Ester + water. • Naming esters. Use of esters. • Isomerism: Meaning and writing isomers of simple alkanes (straight and branched forms) Polymerisation • Meaning; two kinds of polymerisations (Addition and Condensation Polymerisation). • How to write the polymer structure from the structure of the monomer; Repeating unit • Identifying the structure of monomers from the polymer. • Examples of Addition Polymerisation: Poly ethene, Poly propene, Poly chloroethene, Poly tetrafluoroethene • Examples of condensation polymers: Poly ester (Terylene) and Poly amide (Nylon) • Natural polymers: Starch (from glucose); Proteins (from amino acids); Lipids (from glycerol and fatty acids) • Hydrolysis of macro molecules (digestion) by digestive enzymes. END