Circulatory system
advertisement

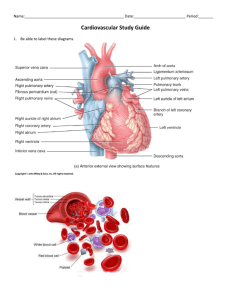
Circulatory system Department of Histology & Embryology Sichuan University I. The components of the Circulatory system Cardiovascular System Lymphatic vascular system Arteries Heart Capillaries Tissues Veins Lymphatic Lymphatic Thoracic duct ← ← Right lymphatic duct vessels capillaries function: transport nutrient,oxygen,carbon dioxide and waste metabolic product II. General Structure of the Blood Vessels tunica intima tunica media tunica adventitia III. Arteries Large artery Medium-sized artery Small artery Arteriole Medium-sized artery Muscular A. Medium-sized artery Muscular A. Structural characters 1. Very much (10~40 layers) smooth muscle cells intermingled with collagenous F., elastic F. 2. Very evident internal and external elastic lamina 3. Very defined 3 layers Function regulate blood flow to various organs Large artery elastic A. Large artery elastic A. Structural characters 1. tunica media consists of elastic membranes mainly abundant (40~70 layers) elastic laminas and a few smooth muscle cells in media 2. internal and external elastic membranes are not prominent 3. three layers are not distinguished Functions of large A. 1.transport blood from heart 2.store blood during ventricle contraction 3.elastic recoil keep continuous blood flow Small artery and arteriole muscular A. Structural characters 1.Diameter<1mm 2. Present internal elastic lamina 3. A few layers of smooth muscle F. 4. No external elastic lamina 5.Arteriole: diameter < 0.3mm 1~2layers of smooth muscle F. Functions 1. regulate blood flow to organs and tissues 2. regulate blood pressure Comparison LA MA SA Internal elastic lamina not evident evident present media elastic laminas S.M.F. S.M.F. external elastic lamina not evident evident another name function elastic A. absent muscular A. Capillary A diffuse network of thin tubules between A. and V. the main place for substance interchange Characters 1. distribution (everywhere) -----very wide total length (60,000 km) ------very long total area(6000 m2 )------------very large 2. lumen (6~8μm) ------------very narrow 3. blood current-----------------very slow ? 4. wall ---------------------------very thin Structure of the wall -Endothelium -Basal membrane -Pericyte周细胞 3 Types Of Capillaries in EM Continuous capillary 连续性毛细血管 Fenestrated capillary有孔毛细血管 Sinusoid血窦 endothelium basal membrane cell junction Continuous capillary connective T.,muscle T.,nervous T. Fenestrated capillary kidney, intestine, endocrine gland Sinusoid liver, spleen, bone marrow Continuous capillary Fenestrated capillary Sinusoid Heart endocardium—L. C.T. endothelium: simple squamous epi. subendothelium: L.C.T. subendocardium: L.C.T. Purkinje fiber myocardium-- the thickest layer abundant cardiac muscle cells Epicardium--L. C.T. coronary blood vessels, nerves mesothelium ( visceral layer of the pericardium) En endothelium M muscle fibers SEn subendocardial layer P conducting (Purkinje) fibers Mes mesothelium N autonomic nerves CT loose connective tissue Ep epicardium M myocardium F fat Development of Cardiovascular System It derives from mesoderm 中胚层 Establishment of the early blood circulation Development of the heart * Congenital malformation * 1. Establishment of the early blood circulation (3rd week) blood islands endothelium blood stem cell extraembryonic embryonic blood stem cells these capillaries differentiate to: arteries, veins & capillaries 2. Development of the heart★ • formation of endocardial heart tubes • change of location of heart tube • establishment of heart’s shape • partition of the heart • the congenital malformations (1) Formation of endocardial heart tubes cardiogenic area 生心区 *endocardial heart tubes *paired tubes fuse into single *heart tube link up with blood vessels (embryo, connecting stalk, chorion & yolk sac) -primitive cardiovascular system (2) Change of location of heart tube *ventral to the foregut 前肠 *caudal to the oropharyngeal membrane (3) Establishment of heart’s shape ① elongation ② dilatation bulbus cordis 心球 Ventricle 心室 Atrium心房 sinus venosus 静脉窦 bulbus cordis - truncus arteriosus 动脉干 sinus venosus - veins truncus arteriosus bulbus cordis ventricle atrium sinus venosus veins ③ curvature formation bulboventricular loop 球室袢 ( U-shaped ) bulbus cordis *atrium foregut ④ narrowing atrium – ventricle atrioventricular canal 房室管 (4) Partition of the heart * primitive heart:one atrium one ventricle atrioventricular canal partition of atrium ventricle bulbus cordis ① partition of the atrioventricular canal 房室管 dorsal endocardial cushion 心内膜垫 ventral endocardial cushion ② partition of the primitive atrium septum primum 第一房间隔(原发隔) foramen primum 第一房间孔(原发孔) foramen secundum 第二房间孔(继发孔) septum secundum 第二房间隔(继发隔) foramen ovale 卵圆孔 * thin membrane from dorsocranial wall * caudal free edge & the endocardial cushion septum primum foramen primum * foramen secundum appears in the cranial part of the septum primum * foramen primum is closed foramen secundum septum secundum foramen ovale *ventrocranial wall 腹颅侧壁 *thick membrane *on the right side *covers the foramen secundum from the right side 心脏模型 foramen primum septum primum : (thin membrane) (disappear) foramen secundum (cranial part) septum secundum : foramen ovale (thick membrane) (caudal part) Before birth blood in right atrium foramen ovale left atrium After birth pulmonary blood circulation starts to work - pressure in left atrium increase foramen ovale - close - by valve valve fuses with the septum secundum - interatrial septum ③ Partition of the primitive ventricle interventricular septum 室间隔 muscular interventricular septum membranous interventricular septum muscular interventricular septum endocardial cushions interventricular foramen 室间孔 apex membranous interventricular septum bulbar ridges 球嵴 (left & right) muscular interventricular septum endocardial cushions ④ Partition of the bulbus cordis 心球 & the truncus arteriosus 动脉干 two large arteries: aorta pulmonary trunk two ridges - in the walls of the bulbus cordis & truncus arteriosus -bulbar ridges ( left & right ) aorta pulmonary trunk two ridges grow & fuse together - aorticopulmonary septum 主肺动脉隔 ascending aorta & pulmonary trunk twist around each other aorticopulmonary septum is not coronal but in spiral or sagittal orientation (5) The congenital malformations ① atrial septal defects 房间隔缺损 normally § The septum primum is absorbed excessively § The septum secundum developed poorly § The septum primum is fenestrated * The septum primum can’t cover the foramen ovale completely * interatrial shunting of blood blood left → right pulmonary circulation↑ body circulation↓ infection development ② ventricular septal defects 室间隔缺损 muscular *membranous septal defects ③ Tetralogy of Follot 法乐四联症 a combination of four cardiac defects: *pulmonary stenosis 肺动脉狭窄 *membranous ventricular septal defect 室间隔膜部缺损 *overriding aorta 主动脉骑跨 *hypertrophy of the right ventricle 右心室肥大 This malformation results from the right of bulbus cordis partition (aorticopulmonary septum) right → left blood diversion Clinical symptom: * Cyanosis of the lips and fingernails “blue baby” * Short of oxygen, easy to be tired. * Poor growth and development The end