1. course plan ECO
advertisement
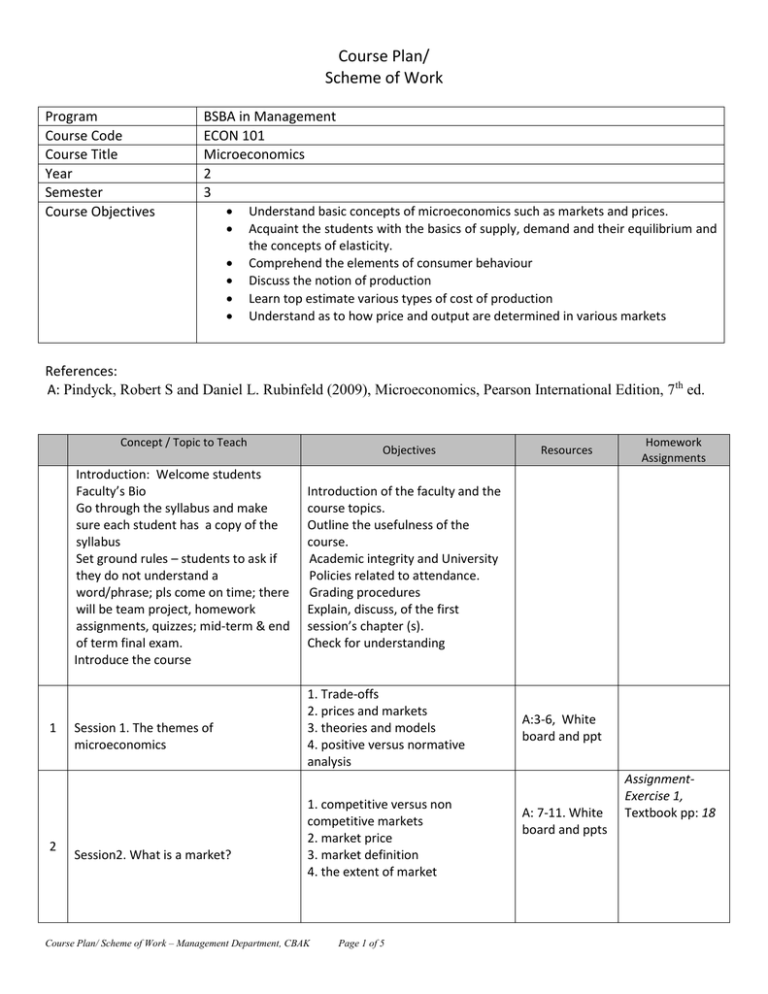
Course Plan/ Scheme of Work Program Course Code Course Title Year Semester Course Objectives BSBA in Management ECON 101 Microeconomics 2 3 Understand basic concepts of microeconomics such as markets and prices. Acquaint the students with the basics of supply, demand and their equilibrium and the concepts of elasticity. Comprehend the elements of consumer behaviour Discuss the notion of production Learn top estimate various types of cost of production Understand as to how price and output are determined in various markets References: A: Pindyck, Robert S and Daniel L. Rubinfeld (2009), Microeconomics, Pearson International Edition, 7th ed. Concept / Topic to Teach Introduction: Welcome students Faculty’s Bio Go through the syllabus and make sure each student has a copy of the syllabus Set ground rules – students to ask if they do not understand a word/phrase; pls come on time; there will be team project, homework assignments, quizzes; mid-term & end of term final exam. Introduce the course 1 2 Session 1. The themes of microeconomics Session2. What is a market? Objectives Resources Homework Assignments Introduction of the faculty and the course topics. Outline the usefulness of the course. Academic integrity and University Policies related to attendance. Grading procedures Explain, discuss, of the first session’s chapter (s). Check for understanding 1. Trade-offs 2. prices and markets 3. theories and models 4. positive versus normative analysis 1. competitive versus non competitive markets 2. market price 3. market definition 4. the extent of market Course Plan/ Scheme of Work – Management Department, CBAK Page 1 of 5 A:3-6, White board and ppt A: 7-11. White board and ppts AssignmentExercise 1, Textbook pp: 18 Concept / Topic to Teach 3 4 5 6 Session 3. Real versus nominal prices, Why study microeconomics? Session4. Supply and demand Session5. The market mechanism, changes in market equilibrium Session6. Elasticities of supply and demand Objectives Resources 1. real price 2. nominal price A: 12-18. White board and ppts 1. the supply curve 2. the demand curve 1. interaction of supply and demand 2. Changes in market equilibrium 1. point elasticity of supply 2. arc elasticity of supply 3. point elasticity of damand 4. arc elasticity of demand A: 22-24, White board and ppts 1. Demand elasticities 2. supply elasticities A: 34-39. White board and ppts 7 8 Session8. Understanding and predicting the effects of changing market condition Mathematical approaches A: 49-57, White board and ppts 9 Session9. Effects of government intervention 1. price controls A: 58-61 White board and ppts 10 MID TERM EXAM I 11 12 13 Session10. Consumer Behaviour Session11. Indifference curves Session 12. Consumer choice 1. Indifference maps 2. shape of indifference curves 3. Marginal rate of substitution 4. perfect substitutes and complements 5. budget line 1. effects of change in income and prices 2. marginal benefit & marginal cost 3. corner solutions and marginal utility Course Plan/ Scheme of Work – Management Department, CBAK Page 2 of 5 Quiz I A: 25-33, White board and ppts Session7. Short run versus long run elasticities of demand 1. consumer preferences 2. Market baskets 3. Basic assumptions 4. indifference curves Homework Assignments A: 40-48, White board and ppts A: 67-72 White board and ppts A: 72-84 White board and ppts A: 85-100 White board and ppts AssignmentExercise 1, Textbook pp: 62 Quiz II Concept / Topic to Teach 14 Session13. Individual demand 15 session 14: Individual demand (continued) 16 session 15: Income and substitution effect 17 Session 16: Market demand 18 Session17. Consumer surplus 19 Session18. Network externalities 20 Session19. production 21 Session20. Production with one variable input 22 Session21. Production with one variable input (continued) 23 Session22. Isoquants 24 Session23. Production with two variable input Objectives 1. price change 2. individual demand curve 3. Income changes 4. normal versus inferior good 1. normal versus inferior good 2. Engel curves 3. substitutes and complements 1. Income effect 2. substitution effect 3. giffen good 1.from individual to market demand 2. elasticity of demand To learn the topic 1. Bandwagon effect 2. the snob effect 1. technology of production 2. production function 3. short run versus long run 1. average and marginal products 2. slopes of the product curves 3. average product of labor curve 4. marginal product of labor curve 5. Labor productivity A: 112-115. White board and ppts A: 115-119 White board and ppts A:120-125 White board and ppts A: 125-131 White board and ppts A: 132-135. White board and ppts A: 136-139. White board and ppts Homework Assignments AssignmentExercise 2, Textbook pp: 107 Quiz III AssignmentExercise 1, Textbook pp: 146 A: 195-197. White board and ppts A: 198-202. White board and ppts A: 202-206 Law of diminishing marginal returns White board and ppts 1. Assumptions A: 207-209. 2. properties White board 3. isoquant map and handouts 1. input flexibility 2. diminishing marginal returns 3. substitution among inputs To learn the topic 25 Resources Session24. Returns to scale Course Plan/ Scheme of Work – Management Department, CBAK Page 3 of 5 A:209-214 White board and ppts A: 215-218 White board and ppts AssignmentExercise 2, Textbook pp: 219 Quiz IV Concept / Topic to Teach Objectives 26 Session25: Cost of production 1. economic cost versus accounting cost 2. opportunity cost 3. sunk cost 4. fixed cost versus variable cost 5. marginal and average cost 27 Session26. Cost in the short run 1. determinants of short run costs 2. Shapes of cost curves 28 Session27. Costs in the long run 29 Session28. Long run versus short run cost curves 30 Session29. Production with two outputs 31 Session30. Dynamic changes in cost 32 MID TERM II 33 Session31. Perfect competition 34 Session32. Short run equilibrium under Perfect competition 1. user cost of capital 2. cost minimizing input choice 3. isocost line 4. choosing inputs Cost minimization with varying output levels 4. expansion path and long run costs 1. inflexibility of short run production 2. long run average cost 3. economies and diseconomies of scale 4. relationship between short run and long run costs 1. economies of scope 2. product transformation curves 3. economies and diseconomies of scope 4. The degree of economies of scope 1. the learning curve 2. graphing the learning curve 3. learning versus economies of scale 1. perfectly competitive markets 2. profit maximization 3. marginal revenue 4. marginal cost 1. choosing output in short run 2. short run supply curve 3. short run market supply curve Resources A: 221-227 White board and ppts A: 228-233 White board and ppts Homework Assignments A: 234-242, White board and ppts A: 243-247 White board and ppts A: 248-250. White board and ppts Quiz V AssignmentExercise 4, Textbook pp: 261 A: 251-255. White board and ppts A:271-279 White board and ppts AssignmentExercise 4, Textbook pp: 306 A: 279-291. White board and ppts Quiz VI 35 Session33. Long run equilibrium under Perfect competition 1. output in long run 2. industry long run supply curve Course Plan/ Scheme of Work – Management Department, CBAK Page 4 of 5 A: 292-303 White board and ppts Concept / Topic to Teach 36 Session34. Monopoly 37 Session35. Monopoly power 38 Session36. Pricing with market power 39 Session37. Monopolistic competition 40 Session38. Monopolistic competition (continued) 41 42 Session39. Oligopoly Session40. Oligopoly(continued) 43 Session41. Oligopoly(continued) 44 Session42. Oligopoly(continued) Objectives Resources 1. average revenue 2. marginal revenue 3. output decision A: 350-360. White board and ppts 1. measuring monopoly power 2. sources of monopoly power 3. social cost of monopoly power 1. Capturing consumer surplus 2. first degree price discrimination 3. second degree price discrimination 4. third degree price discrimination A: 361-372. White board and ppts equilibrium in short run equilibrium in long run A: 444-446 White board and ppts A: 446-447 White board and ppts Economic efficiency 1. equilibrium in oligopoly market 2. Cournot model 3. Stackelberg model 1. price competition with homogeneous products 2. price competition with heterogeneous products 1.competetion versus collusion 2. Prisoner’s dilemma 3. price rigidity 4. price signalling 5. price leadership Cartels FINAL EXAMINATIONS Course Plan/ Scheme of Work – Management Department, CBAK Page 5 of 5 Homework Assignments AssignmentExercise 4, Textbook pp: 388 A: 391-428. White board and ppts A: 449-456 White board and ppts Quiz VII AssignmentExercise 3, Textbook pp: 476 A:456-459 White board and ppts A: 461-469 White board and ppts A: 469-475 White board and ppts Quiz VIII