Notation to describe Domain and Range - SPA
advertisement

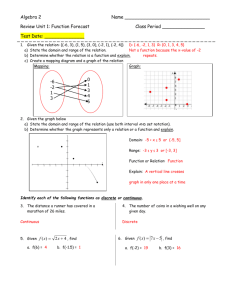
Pre Calculus 10 Lesson Domain and Range: Let’s use proper notation State the Domain and Range Ways to write this: the old way Interpret the meaning Let’s begin to use the Set Notation (curly brackets are used for this, or if there is no restriction on the domain or range we simply say x and read “x belongs to all real numbers” or “the domain is all real numbers). Task: Match each relation with its domain and range Identify what type of notation is being used to describe domain and range: words, inequalities, interval notation, number line, set notation. Choose one of the relations and express its domain and range using as many notation as you can (words, inequalities, interval notation, number line, set notation) Your turn to play #1 Express the domain (all permissible values of independent variable) and range (all permissible values of dependent variable) using the SET NOTATION. Your turn to play #2 Express the domain (all permissible values of independent variable) and range (all permissible values of dependent variable) using the INTERVAL NOTATION. Your turn to play #3 Express the domain (all permissible values of independent variable) and range (all permissible values of dependent variable) using the NUMBER LINE NOTATION. Your turn to play #4 Express the domain (all permissible values of independent variable) and range (all permissible values of dependent variable) using the INEQUALITIES NOTATION. Your turn to play #5 Express the domain (all permissible values of independent variable) and range (all permissible values of dependent variable) using the INEQUALITIES NOTATION. Your turn to play #6 Express the domain (all permissible values of independent variable) and range (all permissible values of dependent variable) using the NUMBER LINES NOTATION Note: This relation has a non permissible value. So far, all the relations involved CONTINUOUS DATA. We could have DISCRETE DATA too. In such case it is best to use SET NOTATION to describe domain and range (permissible values of input and output variables) Give some examples of CONTINUOUS quantities and some examples of DISCRETE quantities. Your turn to play #7 Given a function, there could be a need to set the domain arbitrarily (based on the context) Graph y 2 x for each of the specified domains. Solution Your turn to play