Study Guide - Mrs. Alvarez History Home
advertisement

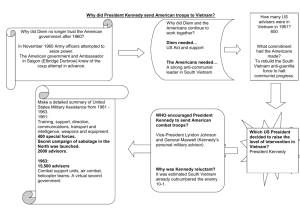
Study Guide US II Q4 MCA 1. The Supreme Court decision in Brown v. Board of Education ended __________. • the “separate but equal” doctrine. 2. Martin Luther King Jr., influenced by Gandhi, believed in ____________. • nonviolent protest. 3. The Student Nonviolent Coordinating Committee (SNCC) decided to entrust decisions about priorities and tactics to ________. • young activists. 4. Civil Rights leaders targeted Birmingham in 1963 because the city ___________. • was highly segregated. 5. The brutality against African Americans in Birmingham prompted Kennedy to ___________. • propose a strong civil rights bill. 6. Television was a major factor in the election of 1960 because during the campaign _______. • the candidates faced each other in the nation’s first televised debates. 7. Kennedy’s New Frontier included efforts to ______. • improve the space program. 8. The Warren Commission decided that the Kennedy assassination was ______. • the act of a single man. 9. As a member of Congress, Lyndon Johnson was known for his _______. • great skill as a legislator. 10. Johnson called his plan for improving the nation the ______. • Great Society. 11. Medicare and Medicaid were programs designed to help people afford _____. • health care. 12. During the 1960s, the Supreme Court made several decisions which _____. • protected the rights of people accused of crimes. 13. The goal of the Bay of Pigs invasion was to ______. • force Fidel Castro from power. 14. Why did the Soviets build the Berlin Wall? • To stop people from escaping from East Germany. 15. The Cuban Missile Crisis ended when… • the Soviets removed their missiles from Cuba. 16. President Kennedy’s policy in Vietnam was to ____________. • increase the number of American military advisers. 17. What did the United States fear would happen if it did not get involved in Vietnam? • Communists would take over the country. 18. What congressional action gave President Johnson that authority to escalate the Vietnam War? • the Gulf of Tonkin Resolution 19. Television coverage of the Vietnam War… • brought the brutality of the war into homes. 20. Which of the following best describes the philosophy of the counterculture? • question traditions and experiment with new ways of living 21. How did the Vietnam War finally end in 1975? • with North Vietnam gaining control of all of Vietnam 22. Why did President Kennedy support the government of Ngo Dinh Diem? • Kennedy feared that Communists would take over South Vietnam. 23. What was the name of the 1954 meeting to discuss conflict in Vietnam? • Geneva Conference 24. What was the name of the major attack by Viet Cong and North Vietnamese? • Tet Offensive 25. What was Ho Chi Min’s main strategy? • Aggressively attack South Vietnam and American forces utilizing guerilla warfare Essay Questions Identify and explain two causes and two effects of the Cuban Missile Crisis. Causes • Communism in Cuba (90 miles from USA) • Bay Of Pigs Invasion • Kennedy’s aggressive foreign policy: (Cuban Missile Crisis) – NATO nuclear missiles in Turkey – Missile gap: JFK started new arms race • • • • Effects Limited Test Ban Treaty (1963) Red Phone Hotline b/w Soviets & Whitehouse (1963) *Back off of bombs Krushchev took bombs out of Cuba – U.S. took bombs out of Turkey – Both realized world was closer than ever to nuclear war Identify & explain two causes and two effects of United States involvement in the Vietnam War. • • • • Causes Domino Theory & Containment Geneva Conference (US Took Responsibility of Vietnam from France) Kennedy & Johnson sending increased number of military advisers to Vietnam Gulf of Tonkin Resolution • • • • • • Effects Anti-war protests divided US society 58,000 US dead, 300,000 wounded US War Veterans PTSD Countless Vietnamese civilians killed/maimed Herbicides cause health problems Cambodia & Laos destabilized, fell to Communists – 1.5 - 2,000,000 Cambodians killed in Khmer Rouge genocides Compare and contrast the countercultures of the 1950s and the 1960s. Identify and explain a minimum of one example of each. Different: • 50s: Beats were small group of poets & writers Similar: – Black clothes • Importance of Music – Jazz music • Opposed social norms & – Marijuana cultural conformity – Apolitical – hip vs. square • Youth-based / youthdriven • Wore different clothing as a form of rebellion • Mysticism / spirituality • Drug Use • Sexual Revolution – known for "playing it cool" (keeping a low profile) • 60s: Hippies were more numerous – – – – Colorful clothes Folk / Electric Rock music Psychedelics (LSD) Active in Civil Rights / Anti-war Protest Movements – became known for "being cool" (displaying their individuality)