Competitive Forces (9)
advertisement

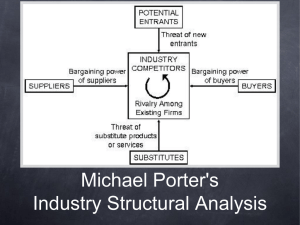
Chapter 2 Strategic Advantage 5 Competitive Forces Why Study Strategic IT? • Technology is no longer an afterthought in forming business strategy, but the actual cause and driver. • IT can change the way businesses compete. Strategic View of IS • Information systems are vital competitive networks. • Information systems are a means of organizational renewal. • An IS can enable a businesses to reengineer or reinvent itself in order to survive and succeed. Porter’s Competitive Forces To survive and succeed, a business must develop and implement strategies to effectively counter the: 1. Rivalry of competitors within its industry 2. Threat of new entrants into an industry and its markets 3. Threat posed by substitute products which might capture market share 4. Bargaining power of customers 5. Bargaining power of suppliers Rivalry of competitors • Online-shopping, price comparison tools (Froogle, Shopzilla, etc.) increase rivalry. • Industries with high rivalry – Automotive – Cell Phone – Retail Clothing – Fast Food • Industries with low rivalry? Threat of new entrants • Internet/E-commerce enables a business to emerge overnight • Almost any medium-sized retail store can become a global ecommerce competitor at little cost. It costs a lot to become a global donut competitor Substitute Products • Internet makes substitutes easier to find. – Can’t afford to fly...take a train. – Ipod not available...buy a Dell DJ – Thomas the Tank Engine costs too much...consider Imaginarium. Bargaining power Customer: • Suppliers: • Here is where the Internet has empowered the customer • Home Depot, Walmart, etc. can persuade suppliers to lock-out the little guys – Ebay – Lending Tree – Reverse auctions – By forcing suppliers into investing in SCM software Competitive Strategies 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Cost Leadership Differentiation Innovation Growth Alliance Cost Leadership Strategy • Becoming a low-cost producer of products and services • Finding ways to help suppliers and customers reduce their costs • Increase costs of competitors Differentiation Strategy • Developing ways to differentiate a firm’s products and services from its competitors’ Innovation Strategy • Development of unique products and services • Entry into unique markets or market niches • Making radical changes that alter the fundamental structure of an industry Growth Strategy • Significantly expanding capacity to produce goods and services – Expanding into global markets • Diversifying into new products and services • Integrating into related products and services Example of Bad Diversification: Dr. B.’s great new business idea: The Quick-Lube, Dentist, Movie Theater Alliance Strategy • Establishing new business linkages and alliances with – – – – customers, suppliers, competitors, consultants, etc. • Great advantages from linking Information Systems of different companies. Examples Cost Leadership: • Priceline.com • Bidding • Buyer set pricing Examples Innovation: E-trade Online discount stock trading Market leader, then problems... Examples Growth: Walmart Beer, diapers, discount beef jerky, country music CD’s, NASCAR merchandise, cheap plastic furniture, and every ingredient you need to make napalm (all at low prices). Market leadership Examples Differentiation: • Moen • Online customer design • Increase in market share Examples Alliance: Walmart & Proctor N’ Gamble Beer, diapers, discount beef jerky, country music CD’s, NASCAR merchandise, cheap plastic furniture, every ingredient you need to make napalm, and oxycontin (all at low prices). Even more Market leadership Other Competitive Strategies • Locking in customers or suppliers by building valuable new relationships with them. • Building switching costs so a firm’s customers or suppliers are reluctant to pay the costs in time, money, effort, and inconvenience that it would take to switch to a company’s competitors. Other Competitive Strategies • Raising barriers to entry that would discourage or delay other companies from entering a market. • Leveraging investment in information technology by developing new products and services that would not be possible without a strong IT capability. Advantage vs. Necessity • Competitive Advantage – developing products, services, processes, or capabilities that give a company a superior business position relative to its competitors and other competitive forces • Competitive Necessity – products, services, processes, or capabilities that are necessary simply to compete and do business in an industry Customer-Focused Business A business that: • can anticipate customers’ future needs. • responds to customer concerns. • provides top-quality customer service. Value Chain Definition: • View of a firm as a series, chain, or network of basic activities that add value to its products and services, • and thus add a margin of value both to the firm and its customers.