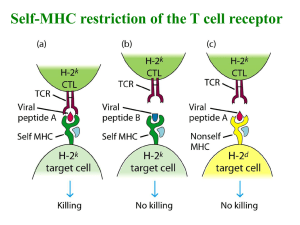
TCR
advertisement

FOR A GIVEN SPECIES(?)/MHC/ORGAN SPECIFIC AUTOIMMUNE DISEASE • One Critical Protein • One Critical Peptide • One Critical Register • ? Germline Encoded Critical TCR Segment THUS: Targeting Trimolecular Complex Possible for Prevention THE NOD EXAMPLE TCR rearrangement Vα Vβ Jα Dβ Jβ Antigen Presenting Cell Peptide V V D J Chr. 14 J Chr. 6 T cell Recognition of Antigen on an APC Antigen Endocytosis CD4+ T cell T Cell Receptor APC Peptide MHC II Trimolecular Complex The Trimolecular Complex NOD MOUSE TCR MHC PEPTIDE INS B:9-23 MHC B:9-23 TCR TCR Liu et al Diabetes 2012 Zhang et al, J. Diabetes 2011 Michels et al, J. Immunol 2011 MHC B:9-23 MHC TCR B:9-23 Deletion of T cells expressing specific TCR alpha or TCR beta genes Antibody binds to MHC/peptide complex and blocks it from interacting with TCR Small molecule prevents from binding/dislodges the B:9-23 peptide from MHC Interfering with formation of the trimolecular recognition complex * “Stages” in Development of Type 1A Diabetes (?Precipitating Event) Beta cell mass Genetic Predisposition Overt immunologic abnormalities Normal insulin release Progressive loss insulin release Glucose normal Overt diabetes C-peptide present Minimal C-peptide Age (years) Eisenbarth, 2012 nPOD 6052-02 Tail: 12 yo 1 year diabetes -Lobular Pseudoatrophic Islets Glucagon/anti-CD3 Insulin and Ki67 Type 1 diabetes Anti-insulin: health • No cure; therapy is insulin for life; physiologic glycaemic control never achieved Anti-insulin: disease •Excess morbidity and mortality •Incidence increasing by ~5% every 5 years; costs ~£1 billion of UK NHS budget Peakman Type 1 diabetes is T cell mediated •Infiltrating CD4+, CD8+ T cells •Anti-T cell therapies are effective •Islet cell autoantibodies disease CD4 T-cell CD8 T-cell CD4 Treg TCR Epitope HLA II HLA I APC Peakman Islet autoantigen The Immune System Acquired (Adaptive) Innate • Rapid Microbial Defense • Long-lived Microbial Defense • Adaptive Immune • Neoplasm surveillance System Activation • Autoimmunity, Transplantation Rejection & Atopy BDC The Innate Immune System • Antimicrobial Peptides (e.g., Defensins, Cathelicidins) • Phagocytes (Macrophages, Neutrophils, Monocytes, Dendritic Cells) • Pattern Recognition Receptors • Alternative Complement System • NK Cells • B1B Cells* * Aspects of both the innate and adaptive immune system BDC Selected Pattern Recognition Receptors: Toll-like Receptors TLR: Selected Ligands: TLR1 PGN, Zymosan, Antifungal & Lipoproteins Antibacterial TLR2 Role in Immunity: TLR6 TLR4 LPS Antibacterial TLR5 Flagellin TLR11 ? TLR9 CpG Antibacterial & Antiviral TLR3 dsRNA Antiviral TLR7 ssRNA TLR8 ssRNA TLR10 ? ? Localization: Dendritic Cells, Macrophages, T Cells, B Cells, Epithelium Selected Pattern Recognition Receptors: Other Families Receptor NOD Pro teins NOD1 NOD2 CD14 C-type Lectins Macrophage Mannose Re ceptor (MMR), DC-SIGN, DEC-205 Surfactant A, D (Coll ectin Famil y) MBP/MBL Scavenger Receptors SR-A, CD36 Selected Ligands Role in Imm unit y Localization PGN (Gm- ) PGN (Gm + & -) LBP:LPS, PGN Antibacterial Antibacterial Antibacterial (wit h TLR4) Cytoplasmi c Cytoplasmi c Serum & Phagocy te Cell Surface Glycop roteins or Glyco li pids Antibacterial, Antiviral, Antif unga l Macrophage, DCs LPS, Lipop roteins, Oli gos accha rides Opsoni zation o f Bacteria, Vir us & Fung i; Cytokine Stimula tion; Apoptotic Cell Clearance Complement Activation (Antibacterial & Antivir al) Soluble in the Lungs Antibacterial; Apoptotic Cell Clearanc e Macrophages , Endoth elium Mannose group s on bacterial carbohyd rates LPS, LTA, PGN Serum Systematic Mouse ligand Human ligand Receptor name (alias) (alias) CCL1 TCA-3/I-309 I-309 CCR8 CCL2 JE/MCP-1 MCP-1 CCR2 References Bertuzzi et al., 2004; Bradley et al., 1999; Cardozo et al., 2001; Cardozo et al., 2003; Chen et al., 2001; Frigerio et al., 2002; Giarratana et al., 2004; Grewal et al., 1997; Kutlu et al., 2003; Nomura et al., 2000; Schroppel et al., 2005; Yang et al., 2004 CCL3 MIP-1 MIP-1 CCR1 & 5 Bradley et al., 1999; Cameron et al., 2000; Giarratana et al., 2004; Lohmann et al., 2002 CCL4 MIP-1 MIP-1 CCR5 Bradley et al., 1999; Cameron et al., 2000; Lohmann et al., 2002) CCL5 RANTES RANTES CCR1, 3 & 5 Bradley et al., 1999; Carvalho-Pinto et al., 2004; Frigerio et al., 2002; Weber et al., 2006 CCL6 C10 unknown CCR1 CCL7 MARC/MCP-3 MCP-3 CCR1, 2 & 3 Bradley et al., 1999; Matos et al., 2004 CCL8 MCP-2 MCP-2 CCR3 & 5 CCL9/10 MIP-1 unknown CCR1 CCL11 Eotaxin-1 Eotaxin-1 CCR3 CCL12 MCP-5 unknown CCR2 Bradley et al., 1999 CCL13 unknown MCP-4 CCR2 & 3 CCL14 unknown HCC-1 CCR1 & 5 CCL15 unknown HCC-2/MIP-1d CCR1 & 3 CCL16 unknown HCC-4 CCR1 & 2 CCL17 TARC TARC CCR4 Giarratana et al., 2004; Kim et al., 2002 CCL18 unknown PARC unknown CCL19 ELC MIP-3b/ELC CCR7 Bouma et al., 2005a; Bouma et al., 2005b CCL20 MIP-3/LARC MIP-3a/LARC CCR6 Cardozo et al., 2003 CCL21 SLC/6Ckine SLC/6Ckine CCR7 Bouma et al., 2005b; Giarratana et al., 2004 CCL22 MDC MDC CCR4 Giarratana et al., 2004; Kim et al., 2002 CCL23 unknown MIPIF-1/MIP-3 CCR1 CCL24 Eotaxin-2 Eotaxin-2 CCR3 CCL25 TECK TECK CCR9 CCL26 unknown Eotaxin-3 CCR3 CCL27 CTACK CTACK CCR10 CCL28 MEC MEC CCR3 & 10 CXCL1 KC GRO CXCR2 Cardozo et al., 2001; Matos et al., 2004 CXCL2 MIP-2 GRO CXCR2 CXCL3 unknown GRO CXCR2 CXCL4 PF4 PF4 CXCR3B CXCL5 LIX ENA-78 CXCR2 Matos et al., 2004 CXCL6 unknown GCP-2 CXCR1 & 2 CXCL7 TCK-1 NAP-2 CXCR2 CXC8 unknown IL-8 CXCR1 & 2 CXCL9 MIG MIG CXCR3 Christen et al., 2003; Frigerio et al., 2002; Matos et al., 2004 CXCL10 IP-10 IP-10 CXCR3 Baker et al., 2003a; Baker et al., 2003b; Bradley et al., 1999; Cardozo et al., 2001; Cardozo et al., 2003; Christen et al., 2004; Christen et al., 2003; Ejrnaes et al., 2005; Frigerio et al., 2002; Giarratana et al., 2004; Morimoto et al., 2004; Nicoletti et al., 2002; Rhode et al., 2005; Shimada et al., 2001 CXCL11 I-TAC I-TAC CXCR3 Cardozo et al., 2003 CXCL12 SDF-1/PBSF SDF-1/ CXCR4 Dubois-Laforgue et al., 2001; Kawasaki et al., 2004; Kayali et al., 2003 CXCL13 BLC BLC/BCA-1 CXCR5 CXCL14 BRAK BRAK unknown CXCL15 Lungkine unknown unknown CXCL16 SR-PSOX SR-PSOX CXCR6 XCL1 lymphotactin SCM-1/ATAC XCR1 Bradley et al., 1999; Weber et al., 2006 XCL2 unknown SCM-1b XCR1 fractalkine fractalkine Cardozo et al., 2001 CX3CL1 CX3CR1 Table 1. T1D, chemokines and their receptors (modified after Lut et al., 2006). Chemokines with a putative role in T1D pathogenesis are identified by gray background shading. The Adaptive Immune System • Cell-mediated Immunity (Cytotoxicity) • T cells • CD4+ (Th1 & Th2) • CD8+ (Tc1 & Tc2) • Humoral Immunity (Antibody production) • B Cells BDC Th1 and Th2 CD4+ T Cells Th1 Th2 • IL-12 induces differentiation • • Cytokine Production: • Interferon- Interleukin-2 • Intracellular Pathogens • • Macrophage Activation • • Delayed Type Hypersensitivity • • IL-4 induces differentiation Cytokine Production: Interleukin-4 Interleukin-5 Interleukin-13 Extracellular Pathogens B Cell activation & IgE Eosinophil responses Immediate Type Hypersensitivity BDC T cell signaling molecules and autoimmunity Human T1D loci (Ref1) MHC : λs ≈ 3 Insulin : odds 1.9 CTLA4 : odds 1.2 PTPN22 odds 1.7 Cblb : Komeda rat (Yokoi N, Nat Genet, 2002) Pten: Cre-loxP knock-out (Suzuki A, Immunity, 2001) Zap70: Sakaguchi mice (Sakaguchi N, Nature, 2003) (Mustelin T, et al. Mol Immunol. 2004) Concannon P et al. Diabetes. 2005 Oct;54(10):2995-3001. H. Ueda B and T Lymphocyte Antigen Receptors VH VH V CH1 CH1 VL CH2 CH2 Ig/Ig CH3 CH3 e VL CL CL V z z e C C Ig/Ig fyn lck Zap 70 Blk, Fyn or Lyn 2 light chains ( or ) 2 heavy chains (5 isotypes: IgG, M, A, D, E) 2 Binding sites (Divalent) Secreted into circulation Binds Soluble Antigen 2 Chains / (95%) or / (5%) 1 Binding site (Monovalent) Membrane Bound, Not Secreted Binds Antigen Complexed with MHC BDC J. Noble HLA Human Leukocyte Antigen human MHC cell-surface proteins important in self vs. nonself distinction present peptide antigens to T cells CLASS I: A,B,C CLASS II: DR,DQ,DP DQB1*0402 -chain Leu56 -chain Asp57 BDC BDC Hahn, Wucherpfenning et al. Nature Immunology 6:490-496, 2005 Topology of Self-peptide/MHC Binding by Ob.1A12 TCR Autoimmune (MBP Peptide+DR2) Ob.1A12 Anti-viral (HA Peptide+DR1) HA1.7 Red: TCR Yellow: TCR Hahn, Wucherpfenning et al. Nature Immunology 6:490-496, 2005 Ob.1A12 HA1.7 Anti-viral (HA Peptide+D R1) Autoimmune (MBP Peptide+DR2) Red: TCR Yellow: TCR The Human Leukocyte Antigen Complex (6p21.31) Class II (1.1 Mb) DP DQ Class III (0.7Mb) DR Class I (2.2Mb) B C A Telomere Centromere Frequent Recombination Recombination is Rare Complement and Cytokines Class I-like genes and pseudogenes Recombination is Rare BDC HLA Class I and II Molecules Have a Distinct Structure and Function •Binds 8-10mers •Expressed on most Nucleated cells •Presents Cytosolic Proteins to CD8+ T cells •Binds 13-25mers •Expressed on APCs, Macs, B cells, activated T cells •Presents Vesicular Proteins to CD4+ T cells 1 2 1 1 2 3 2 2 Class I Class II BDC Cis and Trans- Class II Dimerization Maternal DQA1 DQB1 0501 0201 cis DQA1*0501/DQB1*0201 Paternal 0301 0302 cis trans DQA1*0301/DQB1*0302 DQA1*0301/DQB1*0201 DQA1*0501/DQB1*0302 BDC HLA-Peptide: TCR 2 Helix NH3+ 1 Helix TCR alpha TCR beta COO- BDC “Tetramer” for T Cell Analysis DQ DQ PEPTIDE DQ Avidin DQ BDC HLA Class II tetramer ( DR0401-hGAD555-567) streptavidin Leucine zippers MHC spacers peptide W.W.Kwok & G.T.Nepom, Benaroya Research Institute at Virginia Mason T cell Recognition of Antigen on an APC Antigen Endocytosis CD4+ T cell T Cell Receptor APC Peptide MHC II T cell Activation by an Activated APC IL-1 IL-6 IL-12 IL-12 Receptor CD28 “Signal 3” B7 CD4+ T cell LPS T Cell Receptor “Signal 2” TLR4 “Signal 1” Peptide MHC II Signal 1: Specificity Signal 2: Activation Signal 3: Differentiation Antigen Presenting Cell (APC) The 2-Signal Model of Lymphocyte Activation Absence of Signal 2 T Cell APC TCR MHC Tolerance Clonal Anergy or Deletion Signal 1 + Signal 2 CD28 T Cell B7 APC TCR MHC cytokines Activation BDC APC and T cell Interactions CTLA-4 B7 (CD80/86) B7 (CD80/86) CD28 Activation Recognition TCR MHC II Activation APC CD58 (LFA-3) Activation CD40 CD2 Adhesion CD40L CD4+ T Cell Molecular Interactions of Helper T Cells and APC CD4+ T Cell CTLA-4 CD28 p56 lck CD3 e CD40L C C V CD2 z zh h TCR V CD45 LFA-1 VLA-1 peptide B7 B7 CD80/CD86 CD4 CD40 MHC II LFA-3 ICAM-1 Collagen APC/ B cell L. Chess 2002 T cell activation is regulated by signals derived from the TCR /CD3/CD4 complex and the CD40L and CD28/CTLA-4 co-stimulatory molecules CD4+ T Cell Antigen specific TCR signals Co-stimulatory signals (- ) / [+] lck e CD3 z z hh C C CD28/ CTLA4 V CD40L [+] , TCR Peptide antigen CD40 CD80 (B7.1)/ CD86 (B7.2) V CD4 MHC class II signal Antigen Presenting Cell (APC) L. Chess 2002 TCR CD4 TCR signaling CD45 CD28 PLC1 Zap70 Lck Fyn Tec Lck Shc PTK Grb2 PIP2 (ION) SOS (PMA) Ras IP3 + DAG Ca++ PKC MAPK calcineurin NFB NFAT activation Fathman T cell activation induces expression of functional T cell surface molecules Activated CD4+ T cell MHC/peptid e Induction and activation of B cells APCs CD40L TCR APC TCR Resting CD4+ T cell Late Activated CD4+ T cell TCR CD25 (+) Qa-1/V (-) VLA-1 Collagen TCR (anti-Qa-1/V) Activated CD8+ T cell Regulatory CD8+ T cell Down-regulation of Activated CD4+ T Cells Migration of sites of inflammation L. Chess 2002 Immunological tolerance • Definition: – specific immune unresponsiveness to an antigen that is induced by exposure of lymphocytes to that antigen (tolerogen vs immunogen) • Significance: – All individuals should be tolerant of their own antigens (self-tolerance); breakdown -->autoimmunity – The induction of tolerance could be exploited to treat autoimmune diseases – Mechanisms of tolerance must first be understood Fathman Mechanisms of unresponsiveness to self antigens • Central tolerance – Immature self-reactive T lymphocytes that recognize self antigens in the thymus undergo negative selection (deletion) • Peripheral tolerance – Mature self-reactive T lymphocytes that escape central tolerance and recognize self antigens in peripheral tissues can be inactivated (anergy), killed (deletion) or regulated (suppressed) • “Clonal ignorance” – Mature self-reactive lymphocytes do not respond to self antigens in non-inflamed settings Fathman The Control of Activated CD4+ T Cells by Regulatory T cells NKT cells/ CD4+CD25+ cells CD4+CD25- cells Apoptosis peptide/APC (- ) TH1 CD4+ cells IL-12/ IFN- (- ) IL-10 IL-4 Resting CD4 T cells IFN- (- ) Activated CD4 T cells (- ) TH2 CD4+ cells Regulatory immunity CD4/CD8 interactions CD8 or CD4 CD8 or CD4 suppressor suppressor effector precursor L. Chess 2002 Regulatory T Cell Subsets Regulatory T cell Suppressor Cell Murine Markers Proposed Mechanisms of Inhib ition CD8+ Recogn ition of Qa-1:peptide on ac tivated CD4+ T cells indu ction of cytotoxicity Natural Treg CD4+, CD25+ Cell-contact dependen t but no t antigen- specifi c; CTLA-4+, Ligation of B7 on effector cells; IL-2 GITR+, Foxp3+ sequestration; CTLA-4 interaction w ith IDO (intracellula r) tolerogen ic DCs; IL-10 & TGF-beta produc tion Adaptive Treg CD4+, CD25 -, Cell-contact dependen t but no t antigen- specifi c Foxp3inhibition Tr1 CD4+, CD45Rb lo Cell-contact independen t; IL-10 & IL-4 secretion Th3 CD4+, CD45Rb lo Cell-contact independen t; TGF-beta secretion Invariant NKT cell Invar ia nt TCR CD1d:glyco lipid complex recogn iti on; IL-10 secretion (V14-J281), CD4+, CD8-, NK1.1+ Regulatory T Cells in Autoimmunity CD4+CD45RBlo TGF, IL10 Th3 TGF,+/IL10,IL4 TR1 IL10, normal TGF,no IL4 CD4+CD25+ CTLA4 (? =TR1) Other CD4+ IL2, IFN CD8+ CD4-CD8-TCR Fas Gamma/Delta NKT IL4,IL10,IFN, TGF BDC Colitis by CD45RBhi EAE, glomeruloneph, MG, clone DM IBD by CD45RBhi , Respond IL-15 Thymectomy autoimmune Constituitive CTLA4 MBP EAE model Oral tolerance intestine Skin Allograft Gut, Nasal Insulin CD1 Activated Roncarolo et al. Curr Opinion Immunol 2000 XPID: X-linked Polyendocrinopathy, Immune dysfunction and Diarrhea Foxp3 Gene Essential CD4-CD25 T Reg • XLAAD: Autoimmunity Allergic Dysregulation • Defect in scurfin protein (gene = Foxp3/JM2) or “scurfy mouse” • Immunopathogenesis relates to a deficiency of T regulatory cells -Scurfy x Nude: No Autoimmunity -CD4+ T cells into Nude: Disease -Bone Marrow into irradiated: No Disease -Mixed Chimera: No Disease BDC Requirements for the development of an autoimmune disease Nature Immunology (9): 759-761 (2001) Fathman Immunopathophysiology of Diabetes Dendritic cell/ APC CD2 CD4+ Cell (TH0 ) DR3, DR4,,DQ8/insulin peptide IL-12 ,, TCR IFN- CD40L CD40 IL-4 CD4+ Cell (TH2 ) Macrophage/dendritic cell Fc R FasL perforin CD40L Activated TH1 CD4+ T Cell CD8+ CTL IL-1, TNF, LT, NO, PGE-2 IL-4 CD40L B Cell ?anti-insulin, GAD ab antiMog ?Antibody mediated injury cell death islet cells L. Chess 2002 Induction of CD4+ TH1 mediated autoimmunity: A paradigm for the pathogenesis of rheumatoid arthritis, multiple sclerosis and type I diabetes (1) expansion of CD4+, autoreactive TH1 cells specific for autoantigens MHC/self-peptide CD4 TCR Vx CD4 MHC/V TCR Vx CD4+ Vx T cell APC Activated autoreactive CD4+ TCR Vx TH1 cell (2) migration and infiltration of these self reactive CD4+ TH1 cells into tissues and induction of inflammation and autoimmunity (3) induction of regulatory cells which control the growth and activation of the pathogenic autoreactive repertoire of CD4+ T cells L. Chess 2002 1984:Subset Participants Immunology in Diabetes Rome