Measurement and Significant Figures
advertisement
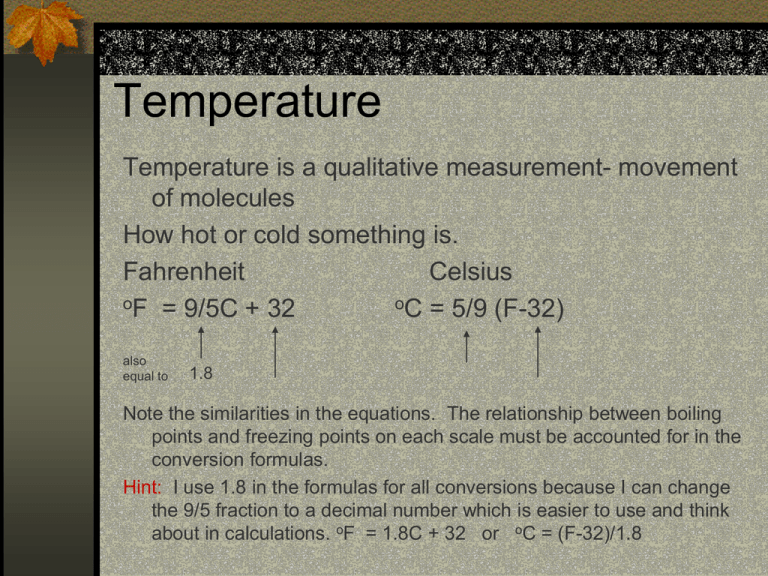
Temperature Temperature is a qualitative measurement- movement of molecules How hot or cold something is. Fahrenheit Celsius oF = 9/5C + 32 oC = 5/9 (F-32) also equal to 1.8 Note the similarities in the equations. The relationship between boiling points and freezing points on each scale must be accounted for in the conversion formulas. Hint: I use 1.8 in the formulas for all conversions because I can change the 9/5 fraction to a decimal number which is easier to use and think about in calculations. oF = 1.8C + 32 or oC = (F-32)/1.8 Comparison of Scales A) The difference between the freezing point and boiling point of water is different in each of the scales: On the Fahrenheit scale Boiling Point of water is 212oF and the Freezing Point is 32oF. The difference between the points is 180oF. On the centigrade scale, Celsius, Boiling Point of water is100oC and the Freezing Point is 0oC. The difference between the points is 100oC. The ratio between scales is thus 180/100 = 5/9 or 1.8 Fahrenheit units/ 1 Celsius unit. Another way to say it: A 10oC change is equal to 18oF This factor must be accounted for when doing a conversion between scales Comparison of Scales B) We also need to make a correction for the fact that the corresponding freezing points are not numerically equal: 0oC and 32oF Subtract 32 if going from Fahrenheit to Celsius 2) Add 32 if going from Celsius to Fahrenheit 1) Kelvin Scale We do need to mention the Kelvin scale. Sometimes chemists, most often physicists and engineers use Kelvin for temperature calculations. Kelvin is the degree unit, no degree symbol is used. The coldest possible temperature is -273oC and is considered to be absolute zero, as such it is given the value 0 on the Kelvin scale. 1K = 1oC because the difference between the boiling (373) and freezing (273) points in K is 100 units. This is the same difference on the Celsius scale. To calculate Kelvin use the following formula which accounts for the absolute zero value: K = oC + 273



![Temperature Notes [9/22/2015]](http://s3.studylib.net/store/data/006907012_1-3fc2d93efdacd086a05519765259a482-300x300.png)