Chapter 2:
advertisement

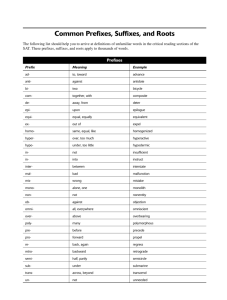
Chapter 2: Analyze Word Structure The Skill: Analyze Word Structure • Word structure analysis means using the structure (parts)of a word to figure out the word’s meaning. • The three types of word parts are prefixes, roots, and suffixes. • Like puzzle pieces, you can fit them together to get the overall “picture” (meaning). © 2008 McGraw-Hill Higher Education. Chapter 2: Analyze Word Structure 2 Prefixes • Prefixes are word parts that are added to the beginning of a base (root) word. • They add their meaning to the meaning of the base word. Example: prefix pre- (before) + fix (attach) = a word part that is attached before the root word • Prefixes can mean not, can indicate location or spatial relationships, number or amount, or have other meanings. © 2008 McGraw-Hill Higher Education. Chapter 2: Analyze Word Structure 3 Roots • Roots are base words to which other word parts (prefixes and suffixes) are added. • Each root has a specific meaning meaning. Examples: aud = to hear audible (can be heard) auditory (pertaining to hearing) • Knowing common roots can be the key to understanding entire “families” of related words. These groups of related words are called cognates. • Common roots: bio, mis, dict, and spect. © 2008 McGraw-Hill Higher Education. Chapter 2: Analyze Word Structure 4 Suffixes • Suffixes are word parts that are added at the end of a base word. • Some suffixes have a specific meaning; others change the root word’s part of speech. Examples: joyful = full of joy calmness (noun), calmer (adjective), calmly (adverb) • Common suffixes: -y, -ness, -ion, -er, -al, -able, and -ly. • Suffixes are not as helpful as other word parts. © 2008 McGraw-Hill Higher Education. Chapter 2: Analyze Word Structure 5 Memory Peg Prefixes come first, like the dinosaur’s head. The root is like the body. Suffixes, like the tail, come at the end. prefix suffix root © 2008 McGraw-Hill Higher Education. Chapter 2: Analyze Word Structure 6 The Technique Use prefixes, roots, and suffixes to unlock word meanings. Question to ask yourself: “What clues do the parts of this word give me about the meaning of the word?” © 2008 McGraw-Hill Higher Education. Chapter 2: Analyze Word Structure 7 A word can consist of • a root only (scribe) • a prefix and a root (prescribe) • a prefix + root + suffix (prescription) • a root and a suffix (scripted) © 2008 McGraw-Hill Higher Education. Chapter 2: Analyze Word Structure Scribe, script = to write 8 The Edge: Pointers • Use word structure clues to confirm guesses based on context clues. • Read the etymology at the end of a dictionary definition: It tells the word parts. • Word structure analysis is especially helpful for scientific and technical words; it doesn’t work for every word, though. • Prefixes and suffixes are usually separate syllables. © 2008 McGraw-Hill Higher Education. Chapter 2: Analyze Word Structure 9