male reproductive system - Delmar
advertisement

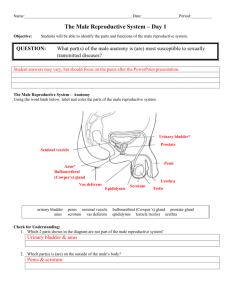
CHAPTER 16 Male Reproductive System Male Reproductive System Overview • Functions of male reproductive system – Produce, sustain, and transport sperm – Propel sperm during sexual intercourse • Copulation – Produce testosterone 2 Male Reproductive Primary Organs • Testicles = male gonads – Small ovoid glands – Responsible for production of sperm • Seminiferous tubules – Responsible for secretion of testosterone • Scrotum – Sac located posterior to the penis • Suspended from the perineum – Houses the testicles 3 Male Reproductive Accessory Organs • Epididymis – Tightly coiled tubule that resembles a comma – Sperm mature in the epididymis, becoming fertile and motile • Mature sperm are stored in lower portion of epididymis 4 Male Reproductive Accessory Organs • Vas Deferens – Also called the ductus deferens – Straight tube continuous with the epididymis • Enlarges to form an sacklike dilation (ampulla) near prostate gland • Merges with the seminal vesicle to form ejaculatory duct 5 Male Reproductive Accessory Organs • Seminal vesicles – Secrete a thick, yellowish fluid known as seminal fluid – Constitutes a large part of the volume of the semen 6 Male Reproductive Accessory Organs • Prostate gland – Lies just below the urinary bladder • Surrounds the base of the urethra as it leaves the bladder – Transports thin, milky colored, alkaline secretions that enhance the motility of the sperm • Secretion also helps neutralize the secretions within the vagina – Muscular action of gland aids in expelling semen from the body 7 Male Reproductive Accessory Organs • Urethra – Serves both urinary system and male reproductive system – Transports urine from the bladder and semen when ejaculated, to the outside of the body • Bulbourethral Glands (Cowper’s Glands) – Secrete alkaline, mucous-like fluid that provides lubrication during sexual intercourse 8 Male Reproductive Accessory Organs • Penis – Male organ of copulation – Tip of penis called the glans penis – Prepuce or Foreskin • Retractable fold of skin that covers the glans penis – Urethra extends the length of the penis and ends as an opening at the tip of the glans penis • Opening is called the urinary meatus 9 PATHOLOGICAL CONDITIONS Male Reproductive System Anorchism • Pronounced – (an-OR-kizm) • Defined – Absence of one or both testicles 11 Balanitis • Pronounced – (bal-ah-NYE-tis) • Defined – Inflammation of glans penis and mucous membrane beneath it 12 Benign Prostatic Hypertrophy • Pronounced – (bee-NYEN pross-TAT-ik high-PER-trohfee) • Defined – Benign enlargement of prostate gland – Creates pressure on upper part of urethra or neck of the bladder, causing obstruction to flow of urine 13 Carcinoma of the Prostate • Pronounced – (car-sin-OH-mah of the PROSS-tayt) • Defined – Malignant growth within prostate gland – Creates pressure on upper part of urethra 14 Carcinoma of the Testes • Pronounced – (car-sin-OH-mah of the TESS-teez) • Defined – Malignant tumor of testicle that appears as a painless lump – Also called testicular cancer 15 Cryptorchidism • Pronounced – (kript-OR-kid-izm) • Defined – Condition of undescended testicle(s) – Absence of one or both testicles from scrotum 16 Epispadias • Pronounced – (ep-ih-SPAY-dee-as) • Defined – Congenital defect in which urethra opens on the upper side of the penis at some point near the glans 17 Hydrocele • Pronounced – (high-DROH-seel) • Defined – Accumulation of fluid in any saclike cavity or duct – Particularly the scrotal sac or along the spermatic cord 18 Hypospadias • Pronounced • (high-poh-SPAY-dee-as) • Defined – Congenital defect in which the urethra opens on the underside of the penis instead of at the end 19 Impotence • Pronounced – (IM-poh-tens) • Defined – Inability of a male to achieve or sustain an erection of the penis 20 Inguinal Hernia • Pronounced – (ING-gwih-nal HER-nee-ah) • Defined – Protrusion of a part of the intestine through a weakened spot in the muscles and membranes of inguinal region of the abdomen • Intestine pushes into, and sometimes fills, the entire scrotal sac in the male 21 Orchitis • Pronounced – (or-KIGH-tis) • Defined – Inflammation of the testes due to a virus, bacterial infection, or injury • Condition may affect one or both testes • Typically results from the mumps virus 22 Phimosis • Pronounced – (fih-MOH-sis) • Defined – Tightness of the foreskin (prepuce) of the penis that prevents it from being pulled back • Opening of the foreskin narrows due to the tightness and may cause some difficulty with urination 23 Premature Ejaculation • Pronounced – (premature ee-jak-yoo-LAY-shun) • Defined – Discharge of seminal fluid prior to complete erection of the penis or immediately after the penis has been introduced into the vaginal canal 24 Prostatitis • Pronounced – (pross-tah-TYE-tis) • Defined – Inflammation of the prostate gland • May be acute or chronic • May be due to bacterial invasion 25 Varicocele • Pronounced – (VAIR-ih-koh-seel) • Defined – Abnormal dilation of the veins of the spermatic cord leading to the testicle 26 SEXUALLY TRANSMITTED DISEASES Male and Female AIDS • Pronounced – (Acquired Immunodeficiency Syndrome) • Defined – Deadly virus that destroys the body’s immune system by invading the helper T lymphocytes (T cells) – T cells play an important part in the body’s immune response • Human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) replicates itself within the T cells, destroys the lymphocyte, and then invades other lymphocytes 28 Chlamydia • Pronounced – (klah-MID-ee-ah) • Defined – Sexually transmitted bacterial infection that causes inflammation of the cervix in women and inflammation of the urethra and the epididymis in men 29 Genital Herpes • Pronounced – (JEN-ih-tal HER-peez) • Defined – Highly contagious viral infection of the male and female genitalia, caused by herpes simplex virus (HSV-2) – Also known as venereal herpes • Differs from other sexually transmitted diseases in that it can recur spontaneously once the virus has been acquired 30 Genital Warts • Pronounced – (JEN-ih-tal warts) • Defined – Small, cauliflower-like, fleshy growths usually seen along the penis in the male and in or near the vagina in women • Caused by human papillomavirus (HPV) • Transmitted from person to person through sexual intercourse 31 Gonorrhea • Pronounced – (gon-oh-REE-ah) • Defined – Sexually transmitted bacterial infection of the mucous membrane of the genital tract in men and women, caused by Neisseria gonorrhoeae • Spread by sexual intercourse with an infected partner • Can be passed from infected mother to her infant during the birth process 32 Syphilis • Pronounced – (SIF-ih-lis) • Defined – Sexually transmitted disease characterized by lesions that may involve any organ or tissue • Spread by sexual intercourse with an infected partner • If left untreated, disease passes through three stages, each with characteristic signs and symptoms 33 Syphilis • Primary syphilis – Characterized by appearance of a small, painless, red pustule on the skin or mucous membrane • Known as a chancre • Develops on the penis of the male and the labia of the vagina in females • Appears within 10 days to a few weeks after exposure 34 Syphilis • Secondary syphilis – Occurs approximately two months later if primary phase is left untreated – Dominant sign is non-itching rash on the palms of the hands and soles of the feet • May also experience headache, sore throat, fever, malaise, anorexia, and bone and joint pain 35 Syphilis • Secondary syphilis – Disease is still contagious during second stage • Can be treated effectively with penicillin – Dormant period follows secondary stage • For 5 to 20 years before reappearing in its final stage 36 Syphilis • Tertiary syphilis – Final and most serious stage of the untreated disease – By third stage, lesions have invaded body organs and systems • Lesions of tertiary syphilis are not reversible, do not respond to treatment with penicillin and can lead to life-threatening disorders of the brain, spinal cord, and heart 37 Syphilis Primary Syphilis: Male 38 Trichomoniasis • Pronounced – (trik-oh-moh-NYE-as-sis) • Defined – Sexually transmitted protozoal infection of the vagina, urethra, or prostate – Causative organism is Trichomonas vaginalis • Women will experience itching and burning, and a strong-smelling vaginal discharge that is greenishyellow 39 DIAGNOSTIC TECHNIQUES, TREATMENTS AND PROCEDURES Male Reproductive System Diagnostic Techniques, Treatments, and Procedures • Castration – Surgical removal of the testicles in the male (or the ovaries in the female) – Known as an orchidectomy or orchiectomy in the male – Known as an oophorectomy in the female 41 Diagnostic Techniques, Treatments, and Procedures • Cystoscopy – Process of visualizing the urinary tract through a cystoscope that has been inserted in the urethra • Circumcision – Surgical procedure in which the foreskin (prepuce) of the penis is removed 42 Diagnostic Techniques, Treatments, and Procedures Circumcision (A) Before (B) After procedure 43 Diagnostic Techniques, Treatments, and Procedures • FTA-ABS Test – Fluorescent Treponemal Antibody-Absorption Test – Serological test for syphilis (performed on blood serum) 44 Diagnostic Techniques, Treatments, and Procedures • Intravenous Pyelogram (IVP) – Radiographic procedure that provides visualization of the entire urinary tract • Contrast dye is injected intravenously and multiple x-ray films are taken as the medium is cleared from the blood by the glomerular filtration of the kidney – Also known as intravenous pyelography or excretory urogram 45 Diagnostic Techniques, Treatments, and Procedures • Orchidectomy – Surgical removal of a testicle – Also called orchiectomy • Orchidopexy – Surgical fixation of a testicle – Also called orchiopexy 46 Diagnostic Techniques, Treatments, and Procedures • Semen analysis – Assessment of a sample of semen for volume, viscosity, sperm count, sperm motility, and percentage of any abnormal sperm • Radical prostatectomy – Surgical removal of the entire prostate gland as a treatment for cancer • Suprapubic prostatectomy – Surgical removal of the prostate gland by making an incision into the abdominal wall, just above the pubis 47 Diagnostic Techniques, Treatments, and Procedures • Transurethral resection of the prostate (TUR or TURP) – Surgical removal of prostate gland by inserting a resectoscope through urethra and into bladder to remove small pieces of tissue from prostate 48 Diagnostic Techniques, Treatments, and Procedures • Vasectomy – Surgical cutting and tying of the vas deferens to prevent passage of sperm, consequently preventing pregnancy – Male sterilization 49 Diagnostic Techniques, Treatments, and Procedures • VDRL test – Serological test for syphilis widely used to test for primary and secondary syphilis • Performed on blood serum – VDRL = Venereal Disease Research Laboratory 50 Diagnostic Techniques, Treatments, and Procedures • Wet mount; Wet prep – Microscopic examination of fresh vaginal or male urethral secretions to test for presence of living organisms 51