Native American Movement
advertisement

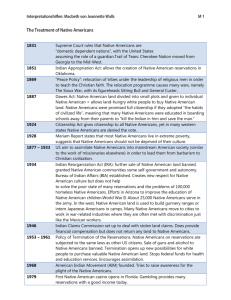
Sports Mascots Do Now: Read the Upfront Article “Insult or Honor?” Do you think sports teams should be forced to change their mascots and names? WHY? Fight for Rights Native American Movement & Chicano Movement Questions: Are Native Americans citizens of the U.S.? Should they have the same rights that other Americans have? Honor or Insult? http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=UI0inlNffA8&feature=related Well, What Would You Think of These? Stereotypes http://www.youtube.com /watch?v=_hJFi7SRH7Q& feature=related Savage Uncivilized What stereotypes have you seen or heard about Native Americans? In 1999, the crayon was changed to chestnut. Was the issue of the name Indian Red racist? Is the Use A Civil Rights Issue? http://www.youtube.com/ watch?v=RVo0fuspW3M&fea ture=related Do you think the use of these mascots gives children the wrong impression? http://www.youtube.com/ watch?v=pROGfJ4qcmQ&fe ature=related Native Americans faced segregation discrimination and marriage discrimination like African Americans Station Activity 8 minutes at each station Read passage Discuss with group and answer all questions on graphic organizer Native Americans: Whose Land is It Anyway? Under the Northwest Ordinance land was not suppose to be taken Under President Andrew Jackson tribes were moved to reservation Indian Removal Act 1830westward expansion forces Native Americans to move west Fair?????? Dawes Act (1871) Stopped signing treaties with Native Americans. US government to divide up land in allotments. Allowed government to purchase Indian land which opened it up to settlement. The RESULT Assimilation Forced Assimilation Make natives more like mainstream America. Sent to boarding schools to learn English Must cut their hair Converted to Christianity 1924 Indian Citizenship Act They are U.S. citizens Vote in elections Right to due process Termination Policy (1953-1968) Survey on Indian Reservations show horrible conditions US government terminates-> Policy that divides property among tribes which ends federal responsibility and social services (health, education, welfare) Now subject to taxation Reduced self-government of tribal communities Relocation to cities Jurisdiction left up to states The American Indian Movement (AIM) Founded 1968 Fought for land rights, against poverty, harassment, better conditions on reservations The Longest Walk of 1978 3600 mile walk to DC to protect rights NCRSM- Fights racism in sports and media today Native American Tribes Today Over 500 reservations Considered same as an independent country when dealing with federal government They have their own court system and governments on their reservations Today: High levels of Poverty Massive alcoholism, diabetic, and obesity rate from government subsidized foods High school drop out rate Many reservations lack running water and have poor conditions Underrepresented in government Fighting Environmental rights Mexican Americans: Chicano Movement Minority group pushed for rights and social change in 20th century. Restoration of land grants, farm workers' rights, enhanced education, voting and political rights, Socially, the Chicano Movement addressed what it perceived to be negative ethnic stereotypes of Mexicans in mass media and the American consciousness Caesar Chavez A Mexican American best known as Latino Civil Rights activist Co-founded the National Farm Workers Association, which later became the United Farm Workers (UFW) Approach: Unionism and Aggressive but nonviolent tactics Dolores Fernandez Huerta She left teaching when “I realized I couldn’t do anything for the kids who came to school hungry and barefoot.” Helped found NFWA with Chavez in 1962 with grape pickers strike. Also- Feminist who strove for women’s rights. Awards with NOW and NAACP Today she continues to work as activist for farmworkers and women. Raza Unida Party Founded in 1970 by youth group Centered on Chicano nationalism Influence spread, and in late 1970s focused on seeking unity with all Chicano, Latino and Native Americans. Today: The National Council of La Raza (NCLR) is the largest national Hispanic civil rights and advocacy organization in the United States and works to improve opportunities for Hispanic Americans.