Carbohydrates
advertisement
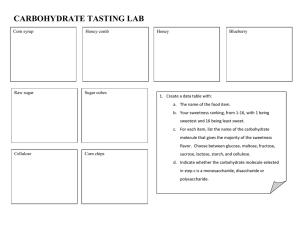
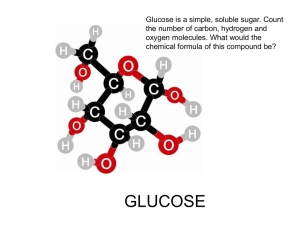
BIOMOLECULES Carbohydrates Carbohydrates (cont.) • Can be divided into 3 groups based on their size: – Monosaccharides: simple sugars like glucose, galactose and fructose – Disaccharides: double sugars like sucrose, lactose and maltose – Polysaccharides: chains of sugars like starch, glycogen, cellulose and chitin Monosaccharides • Glucose - "Blood sugar" is the immediate source of energy for cellular respiration. It is a moderately sweet sugar found in vegetables and fruit. • Galactose - Galactose is not normally found in nature, but is mostly hydrolyzed from the disaccharide lactose, which is found in milk. • Fructose - Fructose is also called the fruit sugar. Fructose is found in fruits, honey, and the sole sugar in bull and human semen. Disaccharides • Lactose is the second most common double sugar and is found in milk. It is a combination of glucose and another small sugar called galactose. • Maltose is the third most common double sugar. It is not found in the foods that we eat. Instead, the body makes it when a person eats foods that contain starches such as potatoes and bread. • Sucrose is the most common double sugar that people eat in common foods. It is found in fruits, potatoes, pasta, breads, cereals and other common foods. Polysaccharides • Starch: a storage polysaccharide in plants • Glycogen: a highly branched storage polysaccharide in animals. • Cellulose: a structural polysaccharide in plants. Cellulose is a major component of plant cell walls. • Chitin: a structural polysaccharide in fungi and animals. Chitin stiffens the cell walls of fungi and some algae and is an important component of the exoskeletons of insects and crustaceans.