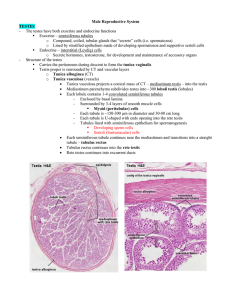
Anatomy of male reproductive system
advertisement

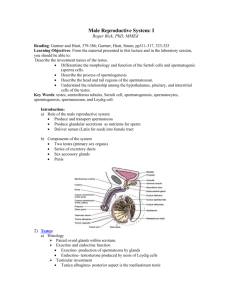
Scrotum , Testes and prostate General Histological Structure Histologic Section of Scrotum The scrotal skin is typical skin with an overlying epidermis and underlying tunica dartos, or subcutaneous layer, that contains smooth muscle which forms the scrotal septum. A-Dermis. B- Epidermis C-Separation artifact. A-Dermis. C-Hair. E-Hair follicle. G-Sweat gland. B- Epidermis. D-Hair bulb. F-Sebaceous gland. Histologic Section of Testes The testes are comprised of two main areas: 1- Connective tissue layers. 2-Vascular layers. * That associate and penetrate into the testes. The testes are comprised of two main layers A- tunica vaginalis . It is includes the parietal and visceral lamina layers . B- tunica albuginea. which is composed of dense, irregular connective tissue (DICCT) . TESTES A-Tunica albuginea. B- Tunica vasculosa. C-Tunica septulum. TESTES A- parietal lamina of vaginal tunic. B- viscral lamina of vaginal tunic. C- Tunica albuginea. The Convoluted comprised of stratified spermatogenic epithelium with two main cell- types: A- Sertoli (Sustentacular) cells. Functions : support, protect, and nourish the developing germ cells and produce androgen binding protein (ABP) and inhibin in response to Follicle Stimulating Hormone (FSH). B- spermatogenic cells . Functions: . produce the spermatozoa . ( B) A- Sertoli (Sustentacular) cells. B- spermatogenic cells . (A) Interstitial (Leydig) Cells located in the interstitium of the testis between the convoluted seminiferous tubules. Boars and stallions have the greatest number of Leydig cells compared to other domestic animal species. Functions : produce testosterone and some estrogen in adult animals. responsible to interstitial cell stimulating hormone (ICSH), Interstitial (Leydig) Cells Interstitial (Leydig) Cells Rete testes in mediastinum -. A-rete testis in mediastinum. (simple squamous to columnar) B- mediastinum. Seminiferous tubule. The Parenchyma of the Testis is made up of various tubules lobules, or ductules. which produce the spermatozoa . 225 Efferent Ductule A- Cilia Cells. B- Spermatozoa. 224 Testis A- Rete testis. B Seminiferous tubule. C- Straight tubule. D-Tunica albuginea. 224 Junction of Rete Testis and Efferent A- Cilia cells. B- Efferent ductule. C- Rete testis. D- Spermatozoa 215 Efferent Ductules, Stallion. A- Columnar epithelium. B- Pseudoslrotified epithelium. C- Spermatozoa. 224 Straight Tubule, Testis A- Seminiferous tubule. B- Sertali cell, nucleus. C- Siraight tubule. D-Tunica albuginea. 225 Vas Deferens, Distal A- Pseudostratified epithelium. B- Smooth muscle. C- Spermatozoa Cauda epididymis A- collections of spermatozoa in the ductus epididymis. B- one epididymal tubule or ductule. Head of epididymis,stallion A. loose connective tissue B. Lymphocyte, migrating C. Pseudoslrotified epithelium D. Smooth muscle Cauda epididymis. A- pseudostratifi ed columnar epithelial lining of the epididymis. B-the collection of spermatozoa in one epididymal tubule. 215at Junction of rete testis & efferent ductule ,stalion A. Cuboidal epithelium. B- Pseudostrolified epithelium, efferent ductule. C- Spermatozoa. 216 Tail of Epididymis, Stallion A- loose connective tissue. B- Pseudostratified epithelium. C- Smooth muscle. D- Spermatozoa.. E- Villus-like projection. Spermatogenic cells Spermatogonia Spermatocytes (primary and secondary) Spermatid to spermatozoa (cells are cytoplasmically connected at all stages) Histologic Section of Prostate All domestic animal species have a prostate, but the dog has the most prominent prostatic body surrounding the urethra *the prostatic tissue is disseminated within the lamina propria-submucosa of the pelvic urethra. Simple cuboidal strikingly acidophilic epithelium *Function. produce an alkaline product to neutralize the acidity of the semen, and the prostatic secretions are the bulk of the initial ejaculate. Prostatic glands - - Lined by simple cuboidal to low columnar epithelium with apical blebs . Function The alkaline product buffers the spermatozoa. Prostate glands. A- tubuloalveolar prostatic glands . 218 Body of the Prostate. A- Capsule. B- Gland. C- Trabecula. Prostate& prostatic urethra. A-uterus masculinis. B-ductus deferens. C-epithelial lining of urethra. REFERNCE 1. Comparative Reproductive Biology. (©2007 Blackwell Publishing.) 2.color atlas of veterinary histology ( © 2000 Lippincott Williams & Wilkins) 3.The anatomy of the domestic animals.