Genghis Khan and the Rise of the Mongols
advertisement

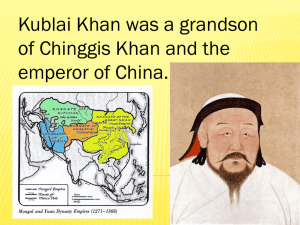
Genghis Khan and the Rise of the Mongols Chapter 12 (pp. 295 – 302) Geography O Central Asian Steppe O Dry high plains O Lack of resources Origins O Pastoral nomads O Life determined by scarcity of resources O Contact could result in alliances or warfare O Hatred for cities and all that they represented Rise of the Mongols O Belief system based on Shamanism O Beliefs and practices concerned with communication with the spirit world O Believed the tribal leader, khan, and his shamans spoke for the god of the universe O Power families had influence with the khan O This leads to intermarriage and alliances tied together via marriage O Women played an important role in negotiating these alliances Genghis Khan O Rose to power through alliances & warfare O 1206, became the supreme leader of the Mongols “Genghis Khan” O Set out to conquer other kingdoms to force them to pay tribute O Conquered northern China, but not the Song Dynasty O Turned west… Greatest Conquerors of All Time O Conquerors O 1. Genghis Khan O 2. Alexander the Great O 3. Timur O 4. Cyrus the Great O 5. Attila O 6. Adolf Hitler O 7. Napoleon Bonaparte Square Miles 4,860,000 2,180,000 2,145,000 2,090,000 1,450,000 1,370,000 720,000 Genghis Khan O “Man’s greatest joy is to crush his enemies and have them flee before him, to seize his possessions, hear the wailing of his women, and embrace his wives and daughters.” Reasons for Mongol Success O Excelled in warfare O Horse riding ability O Properties of their bows: smaller and could shoot farther O Tactics O Fear and terror O Adaptability O Adapted new weapons to suit their need O Ex. Iron & siege weapons O Inclusiveness O Would offer protection for surrenders O Would use local religions to suit the needs of their conquests O Ex. Buddhism & Islam Continued Mongol Conquests O Genghis’ son Ogodei continued the conquest of Eurasian landmass including: O Song China O The Middle East O But not Europe… O Ogodei died Results of Mongol Conquest O The empire created by terror ultimately created a region that allowed for: O Travel O Trade O Exchange of ideas O Spread of disease What happened to Mongol Culture? Compare them to the Romans… two large empires based on conquest… did the people they conquer become them or did they become the people they conquered? Pax Mongolica O Pax Mongolica O “Commerce prospered, and cosmopolitanism flourished under Pax Mongolica, the name historians give to the continual political stability brought about by the stable and harsh Mongol rule which created unprecedented commercial integration of Eurasia” O Directly connected East Asia & Europe Division of the Empire O Mongols assimilated to cultures & religions they conquered O Realms now saw themselves as autonomous of the Great Khan O Mongol empire broke into different realms of Khanates (a new form of governmental organization) Il-Khan O Located in the Middle East O Sacked Baghdad & killed last Abbasid Caliph O Eventually converted to Islam O Acted as a doorway to the West Golden Horde O Located in Russia O Russian cooperation allowed them to avoid direct subjugation Jagadai O Located in Central Asia O Led by Timur (Tamerlame) 1370-1405 O Wanted to be the next Genghis Khan O Attacked the Delhi Sultanate in northern India O Acted as a central piece in Silk Road trade O The capital of Samarkand had many scholars and artists O Helped preserve Greek/Islamic achievements O The descendants of the Timurids would later become the last Indian empire (the Mughals) The Yuan Dynasty O Located in China O Originally, Mongols ruled as foreigners – plundered the Chinese O Kublai Khan changed this by becoming an absolute Chinese emperor Kublai Khan O Understood and assimilated into Chinese culture O Chose not to impose Mongol pastoral lifestyle, social structure, or religion on the Chinese O Embraced all things Chinese O Centralized government O Chinese customs O “Conquerors grow soft…” O Kublai declares himself the next great khan – only the Il Khan recognized this O Symbolized the break between all the khanates Yuan Philosophy O This period acted as one of vital cultural transmission between China and the rest of the world O Europe formally met with China during the reign of Kublai Khan with the arrival of Marco Polo Yuan Expansion O One of the largest (but also shortest) Chinese empires O Kublai tried to extend through conquest O Failed invasion of Japan End of the Yuan O As with all Chinese dynasties, nature conspired in the downfall O Floods & famine plagued China O Rebellion finally forced the Yuan emperor back to Mongolia O Allowed for the succession of another Chinese dynasty