Kublai Khan's administration
advertisement

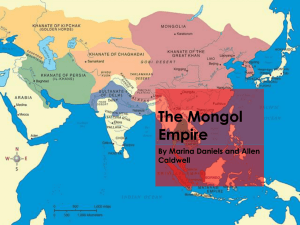
Kublai Khan Kublai Khan was the greatest of the Mongol emperors after Genghis Khan and founder of the Yüan Dynasty in China. He was a wise ruler and was able to lead a vast empire of nations by adapting different traditions to his own government. Early life Kublai Khan was the fourth son of Tulë and the grandson of Genghis Khan (c. 1165–1227), the founder of the Mongol Empire. Strong, brave, and intelligent, Kublai was Genghis's favorite grandson; he had accompanied his father, Tulë, in battles as a child. By the age of twelve he was a skilled horseman, and his reputation as a warrior grew as he became older. Kublai was seventeen when his father died. In 1251 Kublai was given control over Chinese territories in the eastern part of the empire after his brother, Möngkë, became Great Khan of the Mongol Empire. Kublai organized a group of Chinese advisers to introduce reforms in his territories. Kublai was also put in charge of expeditions with the goal of unifying China under the Mongol emperor. In 1257, unhappy with the progress of the war against the Chinese Sung Dynasty, Möngkë led an expedition into western China but was killed by the Chinese defense in August 1259. In 1260, supported by pro-Chinese groups, Kublai was elected as Möngkë 's successor, but his younger brother, Ariq Böge, disputed the election and proclaimed himself khan at Karakorum, Mongolia. In the following years Kublai fought his brother, defeating him in 1264. Kublai Khan's administration Under Kublai, the Mongols adopted divide-and-rule tactics. The Mongols and central Asians remained separate from Chinese life; in many ways life for the Chinese was left basically unchanged. Kublai was also well known for his acceptance of different religions. The rule of the Mongol minority was assured by dividing the population of China into four social classes: the Mongols; the central Asians; the northern Chinese and Koreans; and the southern Chinese. The first two classes enjoyed extensive privileges; the third class held an intermediate position; and the southern Chinese, the most numerous of all, were practically barred from state offices. Separate systems of law were maintained for Chinese and for Mongols. Kublai also reorganized the government, establishing three separate branches to deal with civilian (nonmilitary) affairs, to supervise the military, and to keep an eye on major officials. Following this reorganization, a new capital city was constructed at present-day Peking, China, in 1267. First called Chungtu, the city was renamed Ta-tu (or Daidu, "great capital") in 1272. In the eyes of Kublai, leaving some Chinese institutions and customs in place was a political decision. Outside the administration, much of the Mongol way of life still prevailed. The Mongols, especially the military, preserved their tradition as nomads (wanderers). Even within the administration, Chinese influence was controlled by the large numbers of Mongols and central Asians. Kublai Khan named his rule the Yüan Dynasty in 1271. By February 1278 he had destroyed the Sung dynasty and was the unquestioned leader of an empire that stretched across two continents. Kublai was a great supporter of trade, science, and the arts. He introduced the use of paper money for the entire empire and ordered the creation of a new alphabet for the Mongol language that closely resembled Chinese writing. Kublai also established a system of sea transport and developed inland river and canal routes to move grain from the fertile ricegrowing Yangtze River basin to provide food for the growing population. The Grand Canal system was finally extended north to Peking from the Yellow River. As emperor of China, Kublai demanded loyalty and gifts from other states within the empire. Some of these, such as Annam and Korea, cooperated. To others, Kublai sent messengers asking for payment and attacked if his demands were ignored. Many of these expeditions, however, ended in failure. Twice between 1274 and 1281 Kublai's armies against Japan were either destroyed by storm or crushed by the Japanese because of the Mongols' inability to fight sea battles and the poor quality of their naval forces. Kublai suffered a setback when he failed to conquer the Malay kingdom of Champa in Indochina after a long war (1283–87). Three expeditions to conquer Burma in 1277, 1283, and 1287 also failed. In 1293 near the end of his reign, Kublai launched a naval expedition against the Javanese kingdom of Majapahit, but the Mongol forces had to withdraw after considerable losses. Contact with the West Under Kublai, the opening of direct contact between China and the West was made possible by Mongol control of central Asian trade routes and aided by the presence of efficient postal services. In the early thirteenth century, large numbers of Europeans and central Asians made their way to China. The presence of the Mongol power also enabled many Chinese to travel freely within the Mongol Empire, all the way to Russia, Persia, and Mesopotamia. There were several direct exchanges of missions between the pope and the Great Khan. In 1266 Kublai entrusted the Polo brothers, two Venetian merchants, to carry a request to the pope for one hundred Christian scholars and technicians. The Polos met with Pope Gregory X (c. 1210–1276) in 1269 and received his blessing but no scholars. Marco Polo (c. 1254–1324), who accompanied his father on this trip, was probably the best-known foreign visitor ever to set foot in China. It is said that he spent the next seventeen years under Kublai Khan, including official service in the administration and trips through the provinces of Yunnan and Fukien. The accuracy of his descriptions of China was questioned, but the popularity of his journal generated great interest among Europeans for going east. Rabban Sauma, a monk born in Peking, crossed central Asia to the Il-Khan's court in Mesopotamia in 1278 and was one of those whom the Mongols sent to Europe to seek Christian help against Islam. Under Kublai, the first direct contact and cultural exchange between China and the West had occurred. Kublai Khan's legacy After a glorious reign of thirty-four years, Kublai Khan died in Ta-tu in February 1294. He is regarded as one of the great rulers in history. He was a shrewd and thoughtful ruler of a huge state. He was popular among the Chinese, and his achievements ranked him second to Genghis among the Mongol rulers. He showed great intelligence in using partial adoption of Chinese political traditions and divide-and-rule tactics to help in the administration of a large empire. The main problem with his reign was that as he and his successors became more involved in Chinese traditions, there was a growing conflict between the Mongol rulers of China and those of the other khanates within the Mongol confederacy. They preferred to maintain their own character instead of looking toward China for leadership.