Periodic Table
advertisement

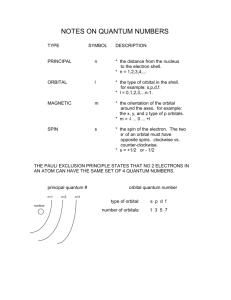
Periodic Table Quantum Numbers The Bohr model of hydrogen provided a single quantum number n. • Principal quantum number • One-dimensional solution Schrödinger’s equation for a real atom is 3-D. • Two other quantum numbers • Orbital angular momentum • Orbital magnetic number 1 2 3 Shells for the principal quantum number n Orbital Shells The orbital angular momentum l is quantized in steps of h. • Values from 0 to n-1 The values are named based on early spectroscopy. • n shells 1=K, 2=L, 3=M, 4=N, 5=O • l shells 0=s, 1=p, 2=d, 3=f, 4=g A. Clark, Chemical Computing Group Zeeman Effect Lz ml Spectral lines from atoms in a strong magnetic field are split. • Zeeman effect • Magnetic moment of orbiting electron Orbital magnetic number ml lines up with applied field. • Values from –l to l • Lz is with respect to field Spin Electrons possess intrinsic angular momentum. • Spin angular momentum s • Spin magnetic number ms No two atomic electrons can occupy the same set of quantum numbers. • Pauli exclusion principle • Applies to fermions Electron spin s can only have one value: 1/2. • ms = +1/2 or -1/2 • Spin up or spin down Photons are spin 1 Electron Configurations Electrons in atoms populate the lowest energies first. • Two electrons per state for spin Atoms have unique ground states. • • • • Hydrogen has 1 1s electron Helium adds another 1s Lithium must start 2s shell Boron starts 2p shell which holds 6 electrons H 1s He 1s 2 Li 1s 2 2 s Be 1s 2 2s 2 B 1s 2 2s 2 2 p C 1s 2 2s 2 2 p 2 N 1s 2 2s 2 2 p 3 O 1s 2 2s 2 2 p 4 Germanium Germanium (Ge) has an atomic number of 32. Find the shell configuration for the ground state. Start counting shells from the lowest state. • • • • • • • • n = 1, l = 0: 1s – 2 electrons n = 2, l = 0: 2s – 2 electrons n = 2, l = 1: 2p – 6 electrons n = 3, l = 0: 3s – 2 electrons n = 3, l = 1: 3p – 6 electrons n = 3, l = 2: 3d – 10 electrons n = 4, l = 0: 4s – 2 electrons n = 4, l = 1: 4p – 2 electrons Total 2+2+6+2+6+10+2+2=32 1s 2 2s 2 2 p 6 3s 2 3 p 6 3d 10 4s 2 4 p 2 Organized Table The periodic table was organized to explain chemical properties. • Quantum physics explained structure Energy Levels Subshell: S G F D P Period • 1 • 2 • 3 • 4 • 5 • 6 • 7 • 8 The shells don’t fill up in exact order. 1s 2s 3s 4s 5s 6s 7s 8s 3d 4d 4f 5d 5f 6d 5g 6f 7d 2p 3p 4p 5p 6p 7p 8p Energy levels are determined by quantum calculations. • General patterns exist next