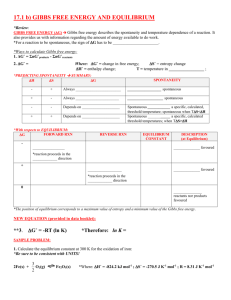
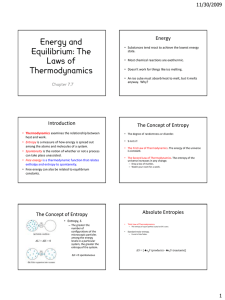
Worksheet# 1
advertisement
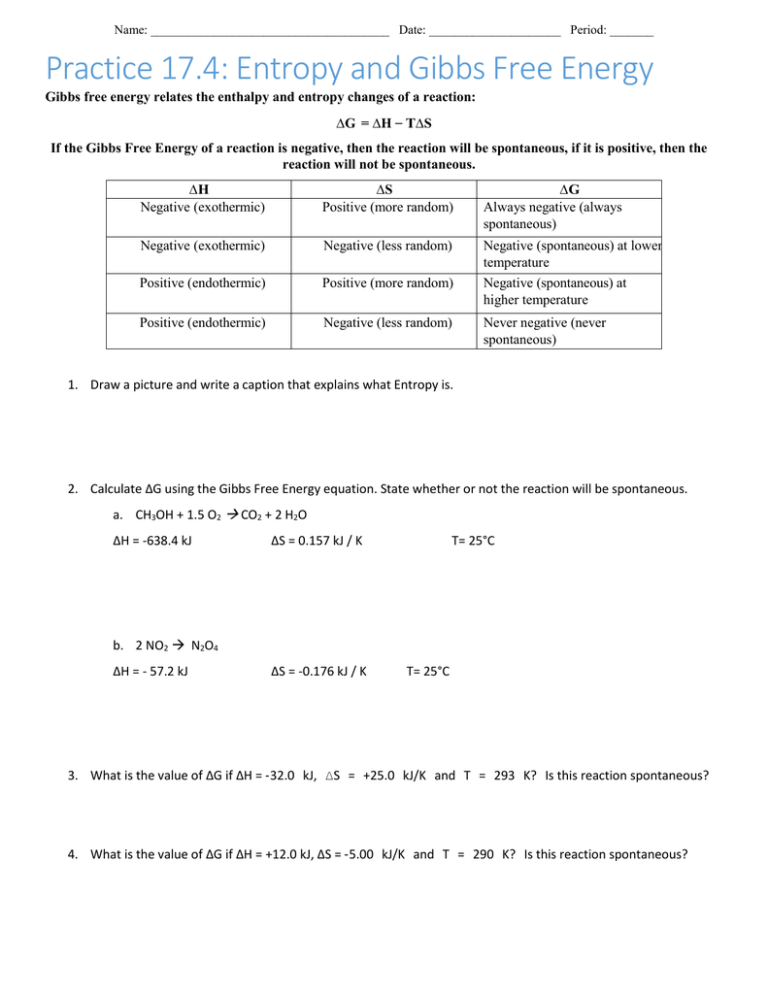
Name: ______________________________________ Date: _____________________ Period: _______ Practice 17.4: Entropy and Gibbs Free Energy Gibbs free energy relates the enthalpy and entropy changes of a reaction: ∆G = ∆H _ T∆S If the Gibbs Free Energy of a reaction is negative, then the reaction will be spontaneous, if it is positive, then the reaction will not be spontaneous. ∆H Negative (exothermic) ∆S Positive (more random) ∆G Always negative (always spontaneous) Negative (exothermic) Negative (less random) Positive (endothermic) Positive (more random) Negative (spontaneous) at lower temperature Negative (spontaneous) at higher temperature Positive (endothermic) Negative (less random) Never negative (never spontaneous) 1. Draw a picture and write a caption that explains what Entropy is. 2. Calculate ∆G using the Gibbs Free Energy equation. State whether or not the reaction will be spontaneous. a. CH3OH + 1.5 O2 CO2 + 2 H2O ∆H = -638.4 kJ ∆S = 0.157 kJ / K T= 25°C b. 2 NO2 N2O4 ∆H = - 57.2 kJ ∆S = -0.176 kJ / K T= 25°C 3. What is the value of ∆G if ∆H = ‐32.0 kJ, ∆S = +25.0 kJ/K and T = 293 K? Is this reaction spontaneous? 4. What is the value of ∆G if ∆H = +12.0 kJ, ∆S = ‐5.00 kJ/K and T = 290 K? Is this reaction spontaneous? Name: ______________________________________ Date: _____________________ Period: _______ More Le Chatelier’s Practice 1) For the reaction below, which change would cause the equilibrium to shift to the right? CH4(g) + 2H2S(g) ↔ CS2(g) + 4H2(g) ∆H= 37.2 kJ/mol (a) Decrease the concentration of dihydrogen sulfide. (b) Increase the pressure on the system. (c) Increase the temperature of the system. (d) Increase the concentration of carbon disulfide. (e) Decrease the concentration of methane. 2) What would happen to the position of the equilibrium when the following changes are made to the equilibrium system below? 2SO3(g) ↔ 2SO2(g) + O2(g) (a) Sulfur dioxide is added to the system. (b) Sulfur trioxide is removed from the system. (c) Oxygen is added to the system. 3) What would happen to the position of the equilibrium when the following changes are made to the reaction below? 2HgO(s) ↔ Hg(l) + O2(g) (a) HgO is added to the system. (b) The pressure on the system increases. 5) Predict the effect of decreasing the temperature on the position of the following equilibria. (a) H2(g) + Cl2(g) ↔ 2HCl(g) (b) 2NH3(g) ↔ N2(g) + 3H2(g) ∆ H = - 49.7 kJ ∆ H = 37.2 kJ (c) CO(g) + H2O(g) ↔ CO2(g) + H2(g) ∆ H = -27.6 kJ