Statistics PPT
advertisement
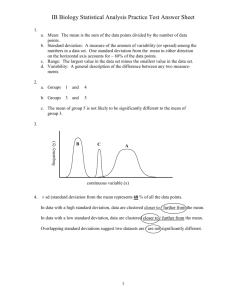
statistics Key statistics and their purposes • Chi squared test: determines if a data set is random or accounted for by an unwanted variable • Standard deviation: indicates how much variation there is from the average, or expected data value – Represented by sigma (σ) • Standard error: shows quality of data, or precision – Indicated on a histogram (bar graph) by error bars Don’t forget • Hardy-Weinberg: to look at allele frequencies in a gene pool and individual frequencies in population, assuming the population is in equilibrium Chi Squared test • Null hypothesis: there is no significant difference between observed and expected – Purpose of chi squared test is to accept/reject null hypothesis • Degrees of freedom: number of outcomes-1 • Critical value: number in a table which, if exceeded, the data is considered unreliable Chi squared test: Critical value table (we accept a 95% certainty) Chi squared test • Mission: Are dice rigged to favor a particular number? Do we have grounds to reject the null hypothesis that it is random? • Practice problems • Two practice problems Standard deviation: of normal distribution: shows how much dispersion from the average there is • In statistics, the 68–95–99.7 rule — or threesigma rule, or empirical rule — states that for a normal distribution, nearly all values lie within 3 standard deviations of the mean. Standard deviation • Try an analysis: Here are the scores on a recent test, what is the deviation? – 80, 74, 62, 91, 45, 88, 90 Standard error: Expresses the quality of data • SEx̄ = Standard Error of Mean s = Standard Deviation of Mean n = Number of Observations of Sample Standard error data set 1 data set 2 11 10 9 10.1 9.7 10.2 9.5 10.4 10.1 11.1 8.9 mean st dev st error