review for test 1
advertisement
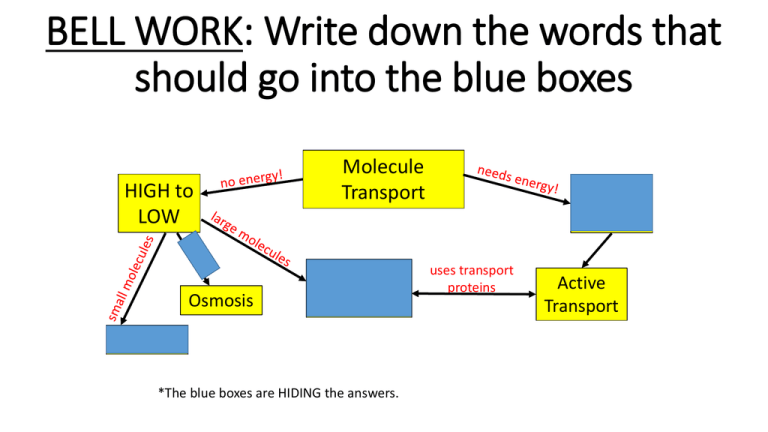
BELL WORK: Write down the words that should go into the blue boxes HIGH to LOW Molecule Transport Facilitated Osmosis Diffusion Diffusion *The blue boxes are HIDING the answers. LOW to HIGH uses transport proteins Active Transport Open journals to page 21 •We will finish our Egg Lab today. QUESTION 1 What will happen to a cell if it were placed in an isotonic solution? A) Get Bigger B) Get smaller C) No change in size Why? Equal water concentrations inside and outside the cell QUESTION 2 What will happen to a cell if it were placed in a hypertonic solution? A) Get Bigger B) Get smaller C) No change in size Why? Water will leave the cell QUESTION 3 What will happen to a cell if it were placed in a hypotonic solution? A) Get Bigger B) Get smaller C) No change in size Why? Water will enter the cell QUESTION 4 Which one requires energy? A) B) C) D) diffusion facilitated diffusion Osmosis Active transport Why? Large molecules are moving AGAINST the concentration gradient Question 5 What is the specific type of diffusion, that involves water? A) Diffusion B) Facilitated diffusion C) Osmosis D) Active Transport Does this process require energy? No this type of diffusion DOES NOT require energy Question 6 What are the 3 organelles responsible for the direct production of the protein? A) centriole, mitochondria, ribosome B) Ribosome, Endoplasmic Reticulum, Golgi apparatus A) Vacuole, cell membrane, ribosome B) Ribosome, Endoplamsmic Reticulum, mitochondria Question 7 Which organelle lets things in and out of the cell? A) B) C) D) Ribosome Mitochondria Golgi Apparatus Cell Membrane Question 8 What is the “BASIC UNIT” of life? A) B) C) D) Atoms Cells Molecules Compounds Atoms are smaller than cells but they are NOT alive Question 9 The diagram to the right shows that…. A) B) C) D) That 2 prokaryotes made 2 eukaryotic cells That 2 eukaryotic cells made 2 prokaryotic cells That 2 prokaryotic cells made 1 eukaryotic cell That 2 prokaryotic cells broke apart to form a eukaryotic cell Question 10 When you see the words…..”maintain a stable internal environment”, you should think? A) Active transport B) Concentration gradient C) permeability D) homeostasis (a state of balance) Question 11 What component of the cell membrane helps communicate the most with other cells? A)The proteins B)The carbohydrates C)The lipids D)They don’t communicate Question 12 What is the final goal of diffusion? A) B) C) D) Cells like to move around stuff To move as much stuff as possible To reach a concentration equilibrium To move from Low to High concentration Question 13 Facilitated diffusion is a process that involves the movement of? A) Water molecules B) Stuff from Low to High concentrations C) small molecules through the proteins D) LARGE molecules though the proteins Question 14 What is a selectively permeable membrane? A) A membrane that NOTHING can get in B) A membrane that everything can get in C) A membrane that only some things can get in Question 15 (What is at A? The Golgi Apparatus Question 16 (What is at D? ) The Nucleus Question 17 (What is at E? ) The Ribosomes 18. The picture below represents a container separated by a membrane. The black dots represent glucose molecules. According to the diagram, in which direction will osmosis occur if the membrane is impenetrable to the glucose. This question is asking about the direction of osmosis (water). The side marked A has more pure water than side B, therefore Osmosis will occur to the right. In this question we are NOT focusing on the particles, we are looking at WATER concentration. 19. A lab technician needs to determine whether cells in a test tube are prokaryotic or eukaryotic. The technician has several dyes she could use to stain the cells. Four of the dyes are described in the table below. Which dye could the technician use to determine whether the cells are prokaryotic or eukaryotic? Since the nucleus is a distinctive feature then “Nile Blue” is the dye the technician should use to determine if it’s prokaryotic or eukaryotic 20. What type of transport is being used to move the top H+ molecule? The example in the box is Active Transport. There is ATP present and the molecule is moving from LOW to HIGH concentratio n through the protein. 21. What type of transport is being used to move the sucrose molecule? The example in the box is Facilitated Diffusion. The molecule is moving through a protein and NO ATP is needed. *Hint…what process do you know it is NOT 22. What is part D in the diagram? What does it do for the cell? “D” is the protein component of the cell membrane. It allows LARGE molecules to pass in and out of the cell. A kidney consists of a large number of very small tubes called kidney tubules. Some of the cells which line these tubules are able to absorb glucose. The diagram shows how these cells absorb glucose from the contents of the tubule and secrete it into the blood. The actual 23. Inside of kidney tubule Cell Blood Glucose moves into cell by Glucose secreted from cell facilitated diffusion by active transport Organelle A question is boxed below. Always find the question first. Difference 1: Osmosis only deals with WATER Difference 2: Facilitated Diffusion requires a Protein channel Glucose moves into the cell by facilitated diffusion. Osmosis also takes place across the plasma membrane. Give two differences between facilitated diffusion and osmosis.