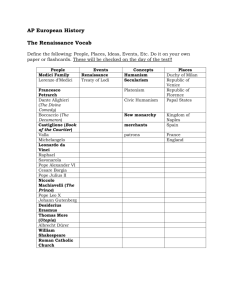
The Renaissance - Duplin County Schools
advertisement

The Renaissance Lesson 1 The Middle Ages • Lasted about 1,000 years (about 500 c.e. to about 1500 c.e. • Middle Ages also refers to what happened in Western Europe during this time period The Middle Ages • 4 key points about the Middle Ages – Feudalism – Manorialism – The role of the church – Lack of learning Feudalism • System of government during most of the 1,000 year period of the Middle Ages • Nobles who were loyal to kings fought as knights • In exchange for their loyalty, they were given pieces of land called fiefs to rule Manorialism • Most fiefs included several manors, or large farms • Serfs, or poor peasants were bound to the manor to work hard • Most manors were self-sufficient • This economic system of the Middle Ages Role of the Church • For nobles and peasants the church played an important role • Nearly every European was a member of the Roman Catholic Church • The Church was very powerful – Great influence socially, finically, and even militarily Lack of Learning • Very few people could read or write • Life was hard • Very few towns, travle between them were very dangerous • Epidemic (Black Death) killed countless numbers of people The Middle Ages • Towards the end things began to change • Trade began to increase, marketplaces and the cities built around them began to grow • More people living in towns put an end to manorialism – Feudalism began to decline The Middle Ages • Changes took place gradually • 2 things marked the end of the Middle Ages – Feudalism – Manorialism • Ended about 1500 Check for Understanding Tell if each statement below is TRUE – Feudalism was a characteristics of the Middle Ages – During the Middle Ages, most people were well educated – The Roman Catholic Church was very powerful during the Middle Ages – The economic system of the Middle Ages was called manorialism The End of the Middle Ages • No exact date for the end of the Middle Ages • 1492 Christopher Columbus sailed to the “New World” of North America • This marked the beginning of many changed in European life The End of the Middle Ages • The year 1453 • Muslim Ottoman Empire conquered the Christian Byzantine city of Constantinople • Constantinople – Great captial of the Byzantine Empire The End of the Middle Ages • 1455 • Johannes Gutenberg developed a new system for printing • Meant books could be printed quickly and easily The End of the Middle Ages • None of the date actually mark the end of the Middle Ages • 1492, change in geography • 1453, change in government • 1455, change in learning Check for Understanding • In what year did Columbus sail to North America? A. 1492 B. 1453 C. 1455 D. 1500 Check for Understanding In what years was Constantinople conquered by the Ottoman Empire? A. 1492 B. 1453 C. 1455 D. 1500 Check for Understanding In what year did Gutenberg finish developing a new system of printing? a. b. c. d. 1492 1453 1455 1500 The Renaissance • Lasted for about 300 years – Began toward the end of the Middle Ages, around 1300 to about 1600 • Means to be “reborn” • Was a great cultural movement, a great period of European history, and a great period of revival in learning Check for Understanding True or False 1. The word renaissance means “Middle Ages.” 2. The Renaissance took place between about 1300 and 1600. 3. The Renaissance was a great period of European history and a period of revival in learning. Humanism • Towards the end of the Middle Ages people began to question the authority of the church • Scholars and artists began to look at life in a new way – Instead of concentrating on the Church and religion, they began to concentrate on people and the world Humanism • Most learned people focused on theology • During the Renaissance more people focused on the study of humanity • Humanism was the most important development of the Renaissance Check for Understanding What is theology? A. B. C. D. A religion Another term for humanism The study of God A style of painting Check for Understanding What is humanism? A. B. C. D. A religion An artistic or scholary focus on humanity The study of God A style of painting Check for Understanding What was the most important development of the Renaissance? A. B. C. D. Humanism Theology Art Feudalism PEOPLE TO KNOW The Medicis • The most famous ruling family of the Italian Renaissance • Prominent in late 1300s • Ruled city of Florence for almost 400 continuous years The Medicis • Extremely wealthy and powerful • Supported great Renaissance thinkers and artist – Michelangelo Giovanni de’ Medici • 1st great Medici (1360-1429) • Made money from banking and trade Cosimo de’ Medici • Giovanni’s son (1389-1464) • Controlled the government of Florence • Even today he is called “the father of his country” • Gave great amounts of money to support the arts and was a strong ruler in Italy Lorenzo the Magnificant • Most famous Medici (1449-1492) • Poet, politician • Under Lorenzo, Florence became the most powerful city-state in all of Italy The Medicis • 2 Medicis women became queens of France • 2 other men became popes • Most remembered for their support of the artists, writers, and others who promoted humanism • Most important ruling family of the Italian Renaissance Check for Understanding Match the term with the description below a. Giovanni de’ Medici b. Cosimo de’ Medici c. Lorenzo the Magnificent 1. The most famous Medici 2. The first powerful and wealthy Medici 3. Also called “the father of his country” Petrarch (1304-1374) • great humanists writer of Italian Renaissance • Rediscovered the works of the great Romans, Cicero and Livy – Their documents had been hidden away in monastery libraries • Tried to copy the style of the ancient writings he discovered Petrarch (1304-1374) • Most famous writings are love poems written as sonnets – Book of Songs • Speak of human love and love for God • Inspired writers such as Shakespeare Sonnet 12 [Alas, so all things now do hold their peace] Alas, so all things now do hold their peace, Heaven and earth disturbèd in no thing; The beasts, the air, the birds their song do cease; The nightes car the stars about doth bring. Calm is the sea, the waves work less and less. So am not I, whom love, alas, doth wring, Bringing before my face the great increase Of my desires, whereat I weep and sing In joy and woe, as in a doubtful ease. For my sweet thoughts sometime do pleasure bring, But by and by the cause of my disease Gives me a pang that inwardly doth sting, When that I think what grief it is again To live and lack the thing should rid my pain. Giovanni Boccaccio • Humanists writer • Wrote in prose – Ordinary language people use when speaking and writing, as opposed to poetry • Most famous work The Decameron Giovanni Boccaccio • Decameron means “10” • The Decameron is a collection of 100 stories told by characters over a period of 10 days • Give insight into life during this time – Express many ideas about love, conflict, and human personalities In the summer of 1348, with the plague ravaging Florence, ten young men and women take refuge in the countryside, where they entertain themselves with tales of love, death, and corruption, featuring a host of characters, from lascivious clergymen and mad kings to devious lovers and false miracle-makers. Named after the Greek for “ten days,” Boccaccio’s book of stories draws on ancient mythology, contemporary history, and everyday life, and has influenced the work of myriad writers who came after him. Check for Understanding Match the term and description below a. “the first humanists” b. Boccaccio c. Petrarch 1. Author of the Book of Songs 2. Author of The Decameron 3. A term used to describe Petrarch & Boccaccio Gitto • About (1267-1337) • First humanists painter in Florence • First to paint nature as it really appeared – Painted real, flesh-and-blood human beings – Figures showed genuine emotion Donatello • 1386-1466 • Sculptor – Portrayed the human body realistically Raphael • 14-83 – 1520 • 1508, pope summoned him to paint for him • The School of Athens – Marks him as a humanists artists for realistically portraying the figures in the painting Michelangelo (1475 to 1564) • Greatest artists of the Renaissance • Accomplished painter, architect, poet • Works of art are very large in size • Best known for the ceiling of the Sistine Chapel and the David Leonardo da Vinci • Name means “genius” • The Last Supper & Mona Lisa • Work influenced art, study of anatomy, warfare, botany, geology, and engineering • Sketched his ideas in his famous notebooks