Cellular respiration
advertisement

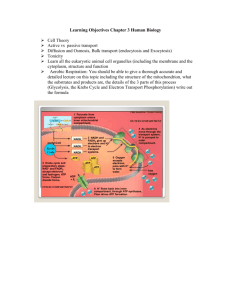
Dispatch 1) Get a book 2) Explain this diagram Intermediate Step + Krebs Cycle/ Citric Acid Cycle 1) 2) 3) 4) 5) 6) 7) 8) 9) 10) 11) 12) 13) 14) What is the starting molecule?____ Where was pyruvate made? What organelle does pyruvate enter?____ How does pyruvate cross the cell membrane?____ What does pyruvate become?_____ How many carbons atoms is acetyl-CoA?___ What 2 molecules transform pyrvate?___ What molecule is made and released through the cell membrane?___ What molecule is made and will go to the ETC?___ What does acetyl-Co A join with?_____ How many carbon atoms is citrate?_____ What gets recycled when citrate is made?___ After 1 cycle of Krebs cycle, what is made?______________ Glucose became 2 pyruvates, so from 1 glucose how many molecules are made at the end of the Krebs cycle?____________________ • http://www.science.smith.edu/departments/Biology/Bio231/krebs.html Electron Transport Chain 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. 12. Where is the location of the ETC?____ What proteinjs are involved in the ETC?____________________ When NADH drops off its e- (electrons) where do they go?____ When NADH drops off its e- (electrons) where do they end up?____ When NADH drops off its H+ (protons) where do they end up?____ What molecule is waiting at the end of the ETC to pick up electrons?___ When FADH2 drops off its e- (electrons) where do they go?____ When FADH2 drops off its e- (electrons) where do they end up?____ When FADH2 drops off its H+ (protons) where do they end up?____ What protein do the H+ (protons) pass through?____ The energy created when protons pass through ATP synthase convert __ + ___ into ____ How many ATPs are made at the end of the ETC?___ • http://www.science.smith.edu/departments/Biology/Bio231/etc.html Set up your photosynthesis boards • Walk around and look at all the boards for: -creative stationary pieces -creative moving pieces -overall display Rate your top 3 Cellular respiration C6H1206 + 6O2 6CO2 + 6H20+ ATP OIL RIG • OIL=oxidation involves losing e• RIG=reduction involves gaining e- NAD+ ---NADH • NADH--electron holder. Can hold 2 e-. Electrons lose very little energy when they are transferred from glucose to NAD+ FAD—FADH2 • FADH2 holds electrons • FADH2 carries lower energy electrons than NAD+ ATP--ADP • PHOSPHORYLATION... adding a phosphate to ADP ADP + P ------> ATP • ATP holds more energy than ADP Substrate level phosphorylation ATP synthase ATP synthase • http://www.sp.uconn.edu/%7Eterry/images /movs/synthase.mov Movie on the ETC and ATP synthase • http://vcell.ndsu.nodak.edu/animations/etc/ movie.htm • http://vcell.ndsu.nodak.edu/animations/atp gradient/movie.htm NO OXYGEN=Fermentation • In fermentation to pyruvic acid molecules are turned into some “waste” product, and a little bit of energy (only two ATP molecules per molecule of glucose – actually four are produced in glycolysis, but two are used up) is produced. • Out of many possible types of fermentation processes, two of the most common types are lactic acid fermentation and alcohol fermentation. Watch an overview of cellular respiration C=carbon 1. In what organelle is this process occurring?____ 2. How many C does the starting molecule have?_____ 3. What is the name of the starting molecule?____ 4. What is the first step called?_____ 5. What is released during the first step?____ 6. What is the second step called?____ 7. What is released during the second step?____ 8. What is recycled during the second step?____ 9. What is the third step called?___ 10. What do the 2e- do?___ 11. What picks up the 2e-?____ 12. What is made in the end of the 3 steps?____ • http://www.qcc.cuny.edu/BiologicalSciences/Faculty/DMeyer/respirat ion.html Glycolysis Animation 1) 2) 3) 4) 5) 6) 7) 8) 9) 10) 11) 12) 13) 14) 15) ATP has how many P’s?___ ADP has how many P’s?____ Glucose has how many carbon atoms?_____ Glycolysis occurs outside the _________ What is needed to start glycolysis?____ What does ATP do to glucose?____ Glucose is split into ___ molecules of ___C each. What happens to ATP?_____ What happens to glucose next?_____ After glucose is split, which molecule adds P?___ NAD+ becomes________ At the end of glycolysis, what molecule has glucose been transformed into?______ How many net ATP’s have been made?____ How many NADH have been made?_______ Where will NADH go after it is made?_______ http://www.science.smith.edu/departments/Biology/Bio231/glycolysis.html Intermediate Step + Krebs Cycle/ Citric Acid Cycle 1) 2) 3) 4) 5) 6) 7) 8) 9) 10) 11) 12) 13) 14) What is the starting molecule?____ Where was pyruvate made? What organelle does pyruvate enter?____ How does pyruvate cross the cell membrane?____ What does pyruvate become?_____ How many carbons atoms is acetyl-CoA?___ What 2 molecules transform pyrvate?___ What molecule is made and released through the cell membrane?___ What molecule is made and will go to the ETC?___ What does acetyl-Co A join with?_____ How many carbon atoms is citrate?_____ What gets recycled when citrate is made?___ After 1 cycle of Krebs cycle, what is made?______________ Glucose became 2 pyruvates, so from 1 glucose how many molecules are made at the end of the Krebs cycle?____________________ • http://www.science.smith.edu/departments/Biology/Bio231/krebs.html Electron Transport Chain 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. 12. Where is the location of the ETC?____ What proteins are involved in the ETC?____________________ When NADH drops off its e- (electrons) where do they go?____ When NADH drops off its e- (electrons) where do they end up?____ When NADH drops off its H+ (protons) where do they end up?____ What molecule is waiting at the end of the ETC to pick up electrons?___ When FADH2 drops off its e- (electrons) where do they go?____ When FADH2 drops off its e- (electrons) where do they end up?____ When FADH2 drops off its H+ (protons) where do they end up?____ What protein do the H+ (protons) pass through?____ The energy created when protons pass through ATP synthase convert __ + ___ into ____ How many ATPs are made at the end of the ETC?___ • http://www.science.smith.edu/departments/Biology/Bio231/etc.html ETC Song • http://www.nclark.net/ElectronTransportCh ain.mp3 ETC Song • http://www.nclark.net/ElectronTransportCh ain.mp3 Dispatch 1) Graph Time Number of birds 8:00 am 23 9:00 am 51 10:00 am 44 2) In general, an independent variable is__________ 3) In general, a dependent variable is__________ Draw out steps in cellular respiration • Stool Game starts at 1:17 pm Seat 1 •What are 2 events that occur in the Calvin Cycle? Seat 2 •What is the function of the smooth ER? Seat 3 •NAD+ is oxidized or reduced? Seat 4 (double points) •Which process occurs in aerobic cellular respiration and fermentation? Seat 1 •What is the function of FADH2? Seat 2 •What occurs in glycolysis? Seat 3 •Why is ATP such a great energy source? Seat 4 •Why do plants need water? Seat 1 Double points •Compare ATP to GTP. Seat 2 •Write the equation for cellular respiration. Seat 3 (double points) •Describe the process of chemiosmosis. Seat 4 • To make 1 glucose you need to go through Calvin ___times Seat 1 •What is the active site of an enzyme? Seat 2 double points • FADH2 makes ___ATPs while NADH makes __ ATPs Seat 3 •What are the products of the light reaction? Seat 4 •C12H24O12 would be a______________ Seat 1 •Water molecules are held together by_______bonds. Seat 2 •Mitochondria are found in________ cells Seat 3 •What are the products of the Kreb’s cycle? Seat 4 •What are the byproducts of cellular respiration? Early morning dispatch 1. What is in respirometer 1, 2, and 3? 2. What is the purpose of the lab? 3. What are the independent and dependent variables?