The Great Depression
advertisement

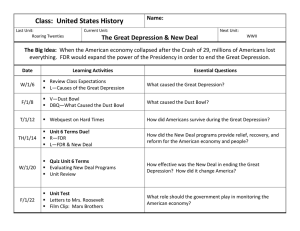
The Great Depression c/notes ERA DEFINED Depression 1929-1941: Crash of stock market Great Depression Dust Bowl New Deal Expansion of the Federal government Relief, Reform, Recovery SOLVENCY OF LONG-TERM ENTITLEMENT PROGRAMS Entitlement Programs (government programs providing benefits to members of specified groups) Solvency – (in this context this term refers to the idea that assets are greater than liabilities) Social Security – According to the Brookings Institute this entitlement program will likely run out of money sooner than expected. Medicare – According to the Brookings Institute this entitlement program will likely run out of money sooner than anticipated. IMPACT OF PHYSICAL AND HUMAN GEOGRAPHIC FACTORS The Dust Bowl Human factors – many farmers had misused the land (over planting, not rotating crops); millions of acres of farmland became useless; hundreds of thousands of people were forced to leave their homes Physical factors – years of sustained drought caused the land to dry up; great clouds of dust and sand were carried by the wind (where the name “Dust Bowl” came from) EFFECTS OF THE GREAT DEPRESSION ON THE U.S. ECONOMY AND SOCIETY Widespread unemployment – by 1933 unemployment was at 25% (according to Bureau of Labor Statistics). Deportation and repatriation of people of European and Mexican heritage – in the 1930s, the U.S. government looked for ways to ease the country's financial hardship. In order to make more jobs available, the government deported many people of European and Mexican heritage. NEW DEAL POLICIES AND ITS OPPONENTS' APPROACHES TO RESOLVING THE ECONOMIC EFFECTS OF THE GREAT DEPRESSION Roosevelt Introduced higher taxes on the rich Believed if it was good for business, then it was good for America New Deal divided into three parts (Relief, Reform, and Recovery) Opponents Believed too generous to the corporate interests Confiscate any personal fortune over $3 million and use this money to give each family in America Promised a national minimum wage, old age pensions, and cheap food for the poor (opinions of Huey Long) VARIOUS NEW DEAL AGENCIES AND PROGRAMS FDIC – Federal Deposit Insurance Corporation SEC – Security and Exchange Commission – regulate the stock markets and businesses SSA – Social Security Administration – retirement savings Expectation that government should step in during economic crises or when the people are suffering AAA – Agriculture Adjustment Act – drastic measure to raise agricultural prices by limiting the surplus/supply TVA – Tennessee Valley Authority – brings electrical power to poverty-stricken rural areas of Tennessee, Mississippi, Alabama and other states; also provided jobs to the area. CONSTITUTIONAL ISSUES RAISED BY FEDERAL GOVERNMENT POLICY CHANGES DURING TIMES OF SIGNIFICANT EVENTS Great Depression – Roosevelt’s attempt to increase the number of Supreme Court justices from 9 to 13 would have created a shift in the “separation of powers” and “checks and balances”