View/Open - CSUN ScholarWorks
advertisement

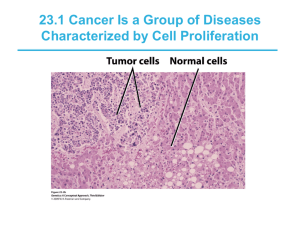
Cell Division & Cancer Song and Screencast Student Learning Outcomes and Assessment The animated song and screencast videos are intended to be used together to give students an introduction to the types of genes that regulate normal cell division and an understanding of the processes that lead to cancer. It is intended for non-biology majors (eg. CSUN BIOL100 and BIOL285) but may serve as a fun review for majors as well. After listening to the cell division song and the accompanying tutorial, students should: - appreciate that cell division is a highly regulated process. - know that oncogenes are the overactive versions of proto-oncogenes. - know that tumor suppressors police the cell cycle and can inhibit cell division. - understand the relationship between benign, malignant, and metastatic tumors. - appreciate that cancer development is a multi-step process. One way to present the material to students may be to show the song component in class (2 min long, captioned) and assign the screencast as a pre-quiz study aid. Links to both could be made available in Moodle, along with a quiz comprised of some of the questions below. Videos are also present on youtube.com and can be found using the terms "cell division cancer animation csun". Cell Division Song: 2:01 http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=qdX87vWQm_E Cell Division Screencast: 3:30 http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=SnaCvuUZoqM Any comments or questions please contact me at cheryl.vanbuskirk@csun.edu Multiple-choice Questions 1. Genes that function to promote cell division when needed are called: a) promoters b) proto-oncogenes c) oncogenes d) tumor suppressor genes 2. When a gene that normally promotes cell division gets mutated in way that causes it to be overactive (jammed on), what is the 'jammed on' version of the gene called? a) a promoter b) a proto-oncogene c) an oncogene d) a tumor suppressor gene 3. Genes that function to stop cell division are called: a) promoters b) proto-oncogenes c) tumor suppressor genes d) oncogenes 4. The primary characteristic that defines whether a tumor is benign or malignant is its: a) size and shape b) location in the body c) ability to grow d) ability to invade neighboring tissues 5. You find a strange growth on your skin and you get it checked at the doctor. Tests are performed and they indicate that you do not have cancer. What did the tests show? a) the growth is malignant b) the growth is benign c) the growth has metastasized d) all of the above 6. What is the name of the process by which cancer cells break off of tumors and spread to other parts of the body? a) mutagenesis b) metastasis c) carcinogenesis d) angiogenesis 7. The multiple hit model of cancer means that a) a person gets cancer only if both of his or her parents had cancer b) most cancers occur in many different tissues at once c) most cancer-causing mutations are passed on to future generations d) multiple mutations are required to cause most forms of cancer 8. A protein called P53 functions to monitor DNA damage. If damage is detected, it will prevent the cell from dividing, or, if the damage is severe, P53 will instruct the cell to kill itself. The gene that encodes p53 is an example of a(n) a) growth factor gene b) proto-oncogene c) tumor suppressor gene d) oncogene