Topical Anesthetics
advertisement

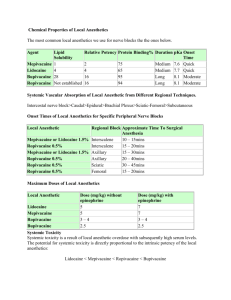
Topical Anesthetics Topical Anesthetics Can not penetrate intact skin More effective if not water soluble Higher concentrations than injectables Can cause toxicity Topical Anesthetics Concentrations are higher to facilitate diffusion; leads to a greater potential for toxicity Many injectables are not used as topical because their effective concentrations would be toxic Topical Anesthetics Only penetrate 2-3 mm, on mucous membranes or disrupted skin Smallest effective quantities, since rapidly absorbed into systemic circulation Cocaine Hydrochloride Water soluble ester, 2-4% for topical use Vasoconstrictive, potentiates adrenalin which may result in dysrythmias Onset - 1min; duration - up to 2 hrs Schedule II drug, not recommended for use in dentistry Benzocaine Ester, poorly soluble in water Available as spray, gel, ointment - 14-20% Poor CV absorption, little risk of toxicity Remains at site, increased duration Possible localized allergic reactions Can inhibit sulfonamides Lidocaine Hydrochloride Amide, 2% solution Water soluble Better penetration, greater toxicity than base Low incidence of allergic reaction Lidocaine Base Poor water solubility 5% liquid, ointment, gel Poor penetration, best on ulcerated, lacerated, or abraded tissue Low incidence of allergic reaction Dyclonine Hydrochloride Ketone, no cross-sensitization Slight water solubility, low toxicity Slow onset -to 10 mins; long duration -to 1 hr 0.5% solution Butacaine Sulfate Topical for eyes, ears, nose, throat Substitute for Cocaine 2X as potent, 2X as toxic 4% dental ointment Tetracaine Hydrochloride Ester, highly soluble in water Potency - 5-8X Cocaine, great potential for systemic toxicity 2% liquid Short Duration-5-40mins Without vasoconstrictors Lidocaine 2% Prilocaine 4% Mepivacaine 3% Intermediate Duration-45-90mins With vasoconstrictors Lidocaine 2% with epi Mepivacaine 2% with epi or levonordefrin Prilocaine 4% with epi Long Duration->90mins With vasoconstrictors Bupivacaine 0.5% with epi Etidocaine 1.5% with epi Maximum Dosage Calculated by body weight (mg/kg or lb) Arbitrary maximum usually approximately at average adult weight of 70 kg Decrease in very young, elderly, debilitated, or medically compromised Contraindications - Absolute Med problem Avoid May use Anesthetic same class different class allergy Bisulfite vasoconstrict. non-constrict. allergy anesthetics types Sulfur Articaine non-sulfur allergy types Contraindications - Relative Med problem Avoid Atypical esters cholinesterase MethemoPrilocaine, globinemia Articaine Liver disease amides (severe) May use amides others esters, or amides judiciously Contraindications - Relative (cont.) Med problems Avoid Kidney disease amides & (severe) esters CV disease excess (severe) vasoconstrictor Hyperthyroid excess (severe) vasoconstrictor May use either judiciously plain or decrease amt plain or decrease amt Selection of an Anesthetic Duration required for treatment Posttreatment discomfort Possibility for self-inflicted injury Need for hemostasis Patient’s medical status Two or more anesthetics ? Maximum total dose The total allowable dose for both local anesthetics should not exceed the lower of the two maximum doses for the individual agents.