A Linear Model
advertisement

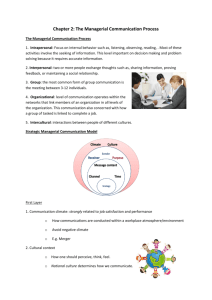
A Linear Model Source Message Contents of Messages • Information • Emotion • Combination of information/emotion A Linear Model Source Message Channel Channels • Verbal—using words or language to communicate • Nonverbal—using something other than words or language to communicate A Linear Model Source Message Channel Receiver Decoder/Receiver • Receives • Interprets • Responds • Response to a message is called feedback. An Interactional Model Source Message Channel Feedback Loop Receiver Noise Source Channel Message Context Feedback A Transactional Model Receiver Dimensions of Context • Where—physical dimension • When—temporal dimension • Why—social/psychological dimension Noise • Anything that interferes with the transmission of a message. • Internal—inside the bodies of the participants • External—outside the bodies of the participants Internal Noise • Physiological—headache, hearing loss, disabilities, etc • Psychological—religion, politics, current worries, past experiences, etc Six Types of Human Communication • Intrapersonal • Interpersonal • One person • Two people • Small Group • Public Speaking • Three to ? • One to many • Mass • One to many A Linear Model Source Message Contents of Messages • Information • Emotion • Combination of information/emotion A Linear Model Source Message Channel Channels • Verbal—using words or language to communicate • Nonverbal—using something other than words or language to communicate A Linear Model Source Message Channel Receiver Decoder/Receiver • Receives • Interprets • Responds • Response to a message is called feedback. An Interactional Model Source Message Channel Feedback Loop Receiver Noise Source Channel Message Context Feedback A Transactional Model Receiver Dimensions of Context • Where—physical dimension • When—temporal dimension • Why—social/psychological dimension Noise • Anything that interferes with the transmission of a message. • Internal—inside the bodies of the participants • External—outside the bodies of the participants Internal Noise • Physiological—headache, hearing loss, disabilities, etc • Psychological—religion, politics, current worries, past experiences, etc Six Types of Human Communication • Intrapersonal • Interpersonal • One person • Two people • Small Group • Public Speaking • Three to ? • One to many • Mass • Mediated • One to many • One to one/group