Ideal Gas EOS - University of Idaho
advertisement
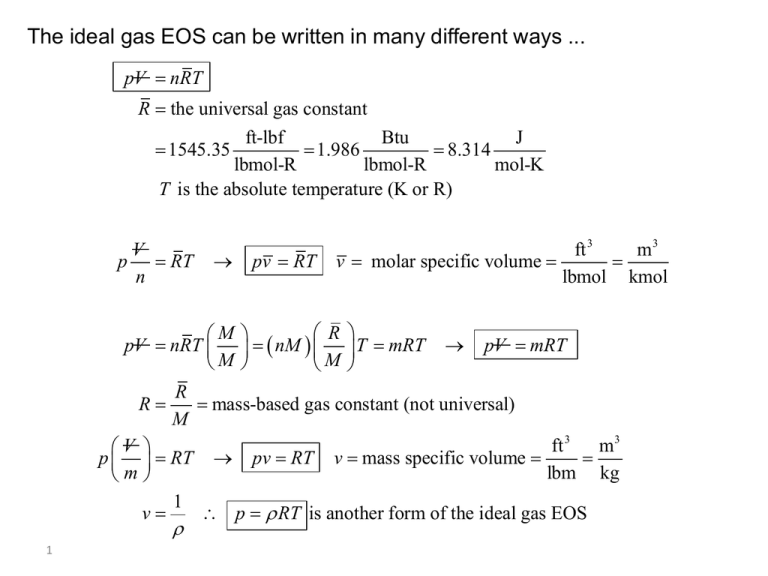
The ideal gas EOS can be written in many different ways ... pV nRT R the universal gas constant ft-lbf Btu J 1545.35 1.986 8.314 lbmol-R lbmol-R mol-K T is the absolute temperature (K or R) V p RT n M pV nRT M R pv RT ft 3 m3 v molar specific volume lbmol kmol R nM M T mRT pV mRT R mass-based gas constant (not universal) M ft 3 m3 V p RT pv RT v mass specific volume lbm kg m 1 v p RT is another form of the ideal gas EOS 1 Given: A sample of room air at 72°F and 14.0 psia Find: The specific volume and density of the air (mass-based) using the Ideal gas EOS. Critical Thinking Questions: What form of the Ideal gas EOS should you use? What temperature units should you use in the Ideal gas EOS? What pressure units should you use in the Ideal gas EOS? What is the universal molar gas constant? Which table is this in the Properties Supplement? What is the mass-based gas constant for air? Which table is this in the Properties Supplement? 2 Given: A sample of room air at 72°F and 14.0 psia Find: The specific volume and density of the air (mass-based) using the Ideal gas EOS RT p T 72 459.67 531.67 R ft-lbf 1545.35 R lbmol-R 53.34 ft-lbf R lbm lbm-R M 28.97 lbmol pv RT v Notice M ft-lbf 53.34 531.67 R ft 3 lbm-R 14.07 v 2 lbm lbf 144 in 14.0 in 2 ft 2 3 1 v 1 ft 3 14.07 lbm 0.0711 lbm ft 3 and R in Table C.13a