HAPPY WEDNESDAY
advertisement

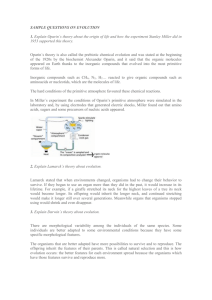
B3 Computer HAPPY THURSDAY Bellwork: Fix your Line Graphs. Look at the example provided of what it should look like. On your bellwork write “Bean Lab Line Graph”. HW: Prepare a line graph. Use a different color line for each species and provide a key. -Graph Title: “Food collecting ability of four species of bean eaters.” -Y axis: # of beans collected -X axis: Trial # (represents the generations) -Lines: The graph will have 4 lines, one for each species in different colors. -Conclusion: Based on the results, describe the change in the populations over 3 generations. Explain the relationship between ability to gather food and the ability to survive. Food Collecting Ability of Four Species of Bean Eaters 55 51 50 46 46 42 41 38 35 25 25 2 TRIA 1 TRIAL 2 John TRIAL 3 Jessica Michael Carrie Collect Today Page 88 – Evolution Bean Lab Graph Assigned Page 86 – Notecard Definitions (Monday) Evolution Quiz (Monday) Most Missed Quiz – Genetics (Wednesday) Late Family Tree Project– Include Rubric and Punnett Squares (-50 points) Page 87 – Natural Selection Video Guide (-30%) Unit 6 – Evolution Definitions Due Monday (1/11/16) All Parts Due Friday (1/15/16) 1. Adaptation 13.Evolution 2. Anatomical Homologies 14.Fitness 3. Ancestry 15.Fossil Record 4. Artificial Selection 16.Founder Effect 5. Biodiversity 17.Gene Flow 6. Biogeography 18.Gene Pool 7. Bottleneck Effect 19.Genetic Drift 8. Charles Darwin 20.Genetic Variation 9. Common Descent 21.Gradualism 10.Developmental Homologies 22.Homologous Structures 11.Disruptive Selection (Graph) 23.Homology 12.Directional Selection (Graph)24.Limiting Factor PG 86 25.Migration 26.Molecular Homologies 27.Natural Selection 28.Non-Random Mating 29.Overpopulation 30.Recombination 31.Reproductive Success 32.Speciation 33.Stabilizing Selection (Graph) 34.Stasis 35.Theory 36.Vestigial Structure Essential Question PG 89 How do adaptations affect survival? Standard B.7C - Analyze and evaluate how natural selection produces change in populations, not individuals. B.7E - Analyze and evaluate the relationship of natural selection to adaptation and to the development of diversity in and among species. What is Evolution? I. Evolution: change over time. A. Scientists involved in the Evolution theory 1. Hutton and Lyell: helped scientists realized 2 things a. Earth is millions of years old b. the processes that changed Earth in the past are the same as the present. At that time, most scientists believed that the Earth was only a few thousand years old. 2. Jean-Baptiste Lamarck: one of the first scientists to recognize that living things have changed over time. a. Lamarck proposed that by selective use or disuse of organs, organisms acquired or lost certain traits during their lifetime. b. These traits could be passed to the offspring. c. Over time, this process led to a change in a species. d. Lamarck’s theory proved incorrect because he did not know that an organism’s behavior has no effect on its heritable characteristics. 3. Malthus: contributed to Darwin’s theory of evolution by establishing the idea that population size is limited by environmental resources. 4. Charles Darwin: contributed more to our understanding of evolution than anyone else. A. Darwin traveled, made observations and collected evidence that led him to propose his revolutionary process. B. Darwin’s Finches b. Darwin published the results of his work in a book called On the Origin of Species. Summary of Darwin’s Theory: Individual organisms differ and some of these variations are heritable (passed on) Organisms produce more offspring than can survive and many that do survive do not reproduce Because more organisms are produce than can survive, they must compete for limited resources (food, shelter, etc) Each unique organism has different advantages (good) and disadvantages (bad) Individuals best suited to their environment survive and reproduce successfully These organisms that survive pass their heritable traits to their offspring Summary of Darwin’s Theory cont’d: Other individuals that are not suited for their environment die or leave few offspring This process called natural selection causes species to change over time Species alive today are descended with modification from ancestral species (their ancestors) This process by which diverse species evolved from a common ancestor unites all organisms on Earth into a single tree of life One of Darwin’s most important insights was that members of each species vary from one another in important ways. Today, we know that heritable variation in organisms is caused by variations in their genes. II. How Evolution Works A. Artificial selection: selection by humans for breeding of useful traits 1. The struggle for existence is competition among members of a species for food, living space, and the other necessities of life. 2. High birth rates and a shortage of life’s basic needs eventually forces organisms into a competition for resources. B. Fitness: the ability of an organism to survive and reproduce 1. Fitness is the result of adaptations. 2. Adaptation: any inherited characteristic that increases an organism’s chance of survival. a. Successful adaptations: - enable organisms to become better suited to their environment - increase an individual’s ability to survive and reproduce. Humans have thousands of adaptations: large brain, opposable thumbs, excellent sensory organs, light, strong skeleton, etc. C. Natural selection: the process by which individuals with characteristics that are not well suited to their environment either die or leave few offspring. 1. Also referred to as survival of the fittest. 2. It is not seen directly, but only observed as changes in a population over a long time. 3. Zombieland: The Rules