Agriscience - Boone County Schools
advertisement

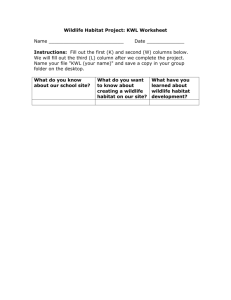
2015-2016 Larry A. Ryle High School Ms. JoAnna Heilman Agriscience Curriculum Map Unit Title SAE & SMART Goals Duration 15 Primary Standards AD 1: Perform basic and higher level math operations (e.g., addition, subtraction, multiplication, division, decimals, fractions, units of conversion, averaging, percentage, proportion, ratios) Essential Question(s) How do I make a goal that is realistic, measurable, attainable and timely? AD 3: Make reasonable estimates How can I implement an SAE at home? How can an SAE help me? AD 4: Use tables, graphs, diagrams, and charts to obtain or convey information AE 1: Locate, evaluate, and apply personal financial information AE 2: Identify the components of a budget and how one is created AE 3: Set personal financial goals and develop a plan for achieving them AE 4: Use financial services effectively Scientific Method 5 AE 5: Demonstrate ability to meet financial obligations AC 1 Utilize critical-thinking skills to determine best options/outcomes (e.g., analyze reliable/unreliable sources of information, use What are the parts of the scientific method? 2015-2016 Larry A. Ryle High School Ms. JoAnna Heilman previous experiences, implement crisis management, develop contingency planning) AC 2 Utilize innovation and problemsolving skills to arrive at the best solution for current situation AC 3 Implement effective decision-making skills Microscopes 5 Soils Plants 15-20 OA 4 Analyze site according to soil type, slope, and drainage OA 5 Differentiate the function of various growing media components Is soil and dirt the same thing? 15-20 OA 7 Describe plant responses to light color, intensity and duration OB 1 Explain systems used to classify plants OB 2 Describe the components, types, and functions of plant roots OB 3 Describe the components, types, and functions of plant stems OB 4 Describe the components, types, and functions of plant leaves OB 5 Describe the components, types, and functions of plant flowers (including seeds and fruit) OB 6 Differentiate sexual and asexual reproduction in plants What are complete flower? Profiles Horizons Ribboning Texture Color Terminology Parts of a Plant Propagation Seeds; Monocot vs. Dicot Experiment How can we measure the particles within pond scum? What are incomplete flowers? What are dicots? What are monocots? 2015-2016 Larry A. Ryle High School Ms. JoAnna Heilman The Role of Minerals in Plant Growth 10 Weed Management 10 Animal Systems 10 OB 7 Analyze the life cycle of plant growth/development from seed to seed (e.g., annual, biannual, perennial) OB 8 Explain requirements necessary for photosynthesis to occur and identify the products and byproducts of photosynthesis OB 9 Explain factors that affect cellular respiration and identify the products and byproducts of cellular respiration OC 6 Predict plant responses to plant growth regulators and different forms of tropism OC 7 Examine the importance of macronutrients and micronutrients to plant growth OC 8 Identify major local weeds, insect pests and infectious and noninfectious plant diseases in horticultural crops OC 9 Predict pest and diseases problems based on environmental conditions and life cycles OC 10 Outline pest control strategies associated with integrated pest management OC 1 Describe the anatomy and physiology of digestive systems (monogastric, ruminant, hind gut fermenters, avian) OC 2 Discuss the function of the six classes of nutrients in regards to animal nutrition OC 3 Compare common types of feedstuffs and the role they play in the diets of animals OC 4 Explain the purpose of feed additives and growth promotants in animal production OC 5 Formulate animal feeds based on nutritional requirements using feed ingredients for How are minerals and plants related? What classifies something a weed? How to we manage weeds? What is the difference between a ruminant and a monogastric? 2015-2016 Animal Reproduction Forest Ecology Aquaculture Water Chemistry Water Safety Larry A. Ryle High School Ms. JoAnna Heilman 10 10 10-15 maximum nutrition and optimal economic production OD 1 Describe the functions of major reproductive organs and hormones in the male and female reproductive systems OD 2 Contrast the processes of natural and artificial breeding methods OD 3 Infer how age, size, life cycle, maturity level, gestation, and health status affect the reproductive efficiency of male and female animals OD 4 Evaluate the use of quantitative breeding values in the selection of genetically superior breeding stock (e.g., EPD's) OD 5 Discuss the importance of efficient and economic reproduction in animals OD 6 Differentiate principles of animal genetics and heredity (e.g. homozygous, heterozygous, phenotype, genotype, dominance, recessive) OD 7 Appraise the advantages of reproductive management practices, including estrous synchronization, superovulation, flushing, and embryo transfer OF 1 Identify trees and other woody plants using morphological characteristics OF 2 Identify herbaceous plants using morphological characteristics OF 11 Identify characteristics of a healthy forest OF 12 Describe ways in which forest stands may be improved What is the difference in sexual terminology within animal species? What are the advantages vs. disadvantages between natural and artificial breeding methods? What is a woody plant? What is an herbaceous plant? What is a ‘good’ water quality standard? 2015-2016 Larry A. Ryle High School Ms. JoAnna Heilman Wildlife Habitat Suitability 10-15 Food Science Milk Dairy Products 15 Eggs (Chicken and Ducks) 10 OF 9 Describe the factors considered in stream classification OF 10 Identify indicators of the biological health of a stream OF 13 Identify characteristics of a healthy wildlife habitat OF 14 Describe methods of wildlife habitat improvement How can we help with the wildlife’s habitat? OI 1 Identify and describe foods derived from meat, egg, poultry, fish, and dairy products OI 2 Discuss desirable qualities of processed meat, egg, poultry, fish, and dairy products OI 3 Evaluate, grade, and classify processed meat, egg, poultry, fish, and dairy products What is incubation? Energy in Agriculture Biodiesel SAE Review What is pastured milk? What are the processes to pasture milk? How do you ‘grade’ an egg? What is biodiesel made out of? 15 AD 1: Perform basic and higher level math operations (e.g., addition, subtraction, multiplication, division, decimals, fractions, units of conversion, averaging, percentage, proportion, ratios) AD 3: Make reasonable estimates AD 4: Use tables, graphs, diagrams, and charts to obtain or convey information Is it sustainable? How can an SAE help me? How can I implement an SAE at home? How do I take beneficial records? 2015-2016 Larry A. Ryle High School Ms. JoAnna Heilman AE 1: Locate, evaluate, and apply personal financial information AE 2: Identify the components of a budget and how one is created AE 3: Set personal financial goals and develop a plan for achieving them AE 4: Use financial services effectively AE 5: Demonstrate ability to meet financial obligations