Units and Quantities
advertisement

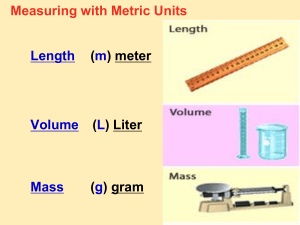
Measurement In this chapter we will explore the following concepts: 1. Measurement of a physical parameter 2. Units, systems of units 3. Basic units in mechanics 4. Changing units Stating a Measurement In every measurement there is a Number followed by a Unit from measuring device Standards of Measurement When we measure, we use a measuring tool to compare some dimension of an object to a standard. Basic & Derived Quantities Basic Quantity Must be defined in terms of a standard (meter, kilogram, second). Derived Quantity Defined in terms of combinations of basic quantities Unit of speed = meter/second = m/s International System of Units: In this system the units for the base quantities are: Parameter Length Unit Name Symbol meter m Mass kilogram kg Time second sec or s Unit of Length: the Meter A meter is a unit of length, currently defined as the distance light travels within 1/299782458th of a second. Time Unit –second (s) The time needed for a cesium-133 atom to perform 9,192,631,770 complete oscillations Volume Unit – the Liter (L) Volume is the amount of space occupied by a substance. S.I unit of volume is liter (L). The milliliter (ml) is commonly used for measuring smaller volumes of fluids. 1 gallon = 4 quarts 1 liter (L) = 1.06 quart 1 quart = 946 mL 1 L = 10 deciliters (dL) = 100 centilliters (cL) = 1000 milliliters (mL) Mass The mass of an object is a measure of the quantity of material it contains. In the SI system, the mass unit is the kilogram (kg). In the metric system, the mass unit is the gram (g). Compare to US weight units: 1 kg = 2.20 lbs 1 lb = 454 grams Temperature Scales The degree of hotness or coldness is called temperature. The S.I unit of temperature is kelvin Other Scales: 1. Celsius (C) scale 2. Fahrenheit (F) scale 1 C = 1.8 F Other Systems of Units CGS centimeter-gram-second FPS foot-pound-second Learning Check From the previous slide, state the tool (s) you would use to measure A. temperature ____________________ B. volume ____________________ ____________________ C. time ____________________ D. weight ____________________ From the previous slide, state the tool (s) you would use to measure A. Temperature B. Volume C. Time D. Weight thermometer measuring cup, graduated cylinder watch, clocks spring balance Unit conversions We will work exclusively in SI (MKS) units! Unit Conversion Learning Check What are some S.I units that are used to measure each of the following? A. length B. volume C. weight D. temperature Some possible answers are A. length inch, foot, yard, mile B. volume cup, teaspoon, gallon, pint, quart C. weight ounce, pound (lb), ton D. temperature F Units in the Metric System length meter m volume liter L mass gram g temperature Celsius °C Learning Check Identify the measurement in metric units. A. John’s height is 1) 1.5 yards 2) 6 feet 3) 2 meters B. The volume of Pepsi in a big bottle is 1) 1 liters 2) 1 quart 3) 2 pints C. The mass of a lemon is 1) 12 ounces 2) 145 grams 3) 0.6 pounds Solution A. John’s height is 3) 2 meters B. The volume of Pepsi in a big bottle is 1) 1 liter C. The mass of a lemon is 2) 145 grams Changing Units Units of Volume: • The SI unit of volume is the cubic meter (m)3. • A more convenient unit of volume for everyday use is the liter, a non-SI unit. • A liter (L) is the volume of a cube that is 10 centimeters (10 cm) along each edge (10 cm 10 cm 10 cm = 1000 cm3 = 1 L). Units and Quantities Units of Temperature Scientists commonly use two equivalent units of temperature, the degree Celsius and the kelvin. Units and Quantities The joule (J) is the SI unit of energy. One calorie (cal) is the quantity of heat that raises the temperature of 1 g of pure water by 1°C. Section Quiz. 1. Which of the following is not a base SI unit? gram meter second mole Section Quiz. 3. A temperature of 30 degrees Celsius is equivalent to 303 K. 300 K. 243 K. 247 K. THE END