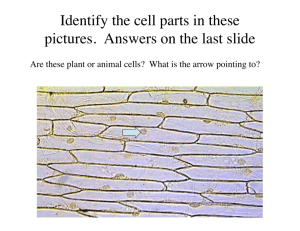
Keratinized stratified squamous epithelium
advertisement

Histology (MLHS-201) Lecture 4 Tissue types (Epithelial tissue) Dr. Afaf Mousaad • Department of Medical Laboratory Technology • Faculty of Allied Medical Sciences 1 Learning objectives • How to Identify the keratinized, basal and apical layers in stratified epithelium. • Distinguish between simple and stratified. • Describe the shapes of stratified epithelial cells. 2 All epithelial cells are in contact with the basement membrane, but not all of them reach the surface of the epithelium. The nuclei are often located at different heights give the epithelium a stratified appearance. Ciliated e.g. epithelium of respiratory tract (Nasal cavity ,larynx, trachea, bronchi,....) 3 4 5 Stratified epithelium a.keratinized stratified epithelium: The mammalian skin epidermis (cornified epithelium) : -A protective type of epithelium containing a tough, resistant keratin protein . Protects underlying tissues from, dehydration, chemicals, and bacterial invasion. 6 The outermost layers of cells are flattened squamous, filled with Keratin. -protects delicate tissues in areas subjected to abrasion. The thickness of the cornified layer of the skin varies greatly, being thickest on the soles and palms. 7 Keratinized stratified squamous epithelium e.g epidermis of the skin 8 This type of stratified epithelium is constantly renewing itself. Cells in the bottom layer divide, and the daughter cells move towards surface maturing and then degenerating. There are around 8-10 layers of cells. The cells become more flattened towards the top (apical) layer and have flattened nuclei - these cells are dying. 9 Horny cells are constantly shed from this part of the stratum corneum. Variations in the thickness of the epidermis are mainly the result of variations in the thickness of the stratum corneum(~0.1 mm in thin skin and 1 mm or more in thick skin). 10 The stratum spinosum: cells become The irregularly polygonal. The cells have spine-like cytoplasmatic extensions (hence the name of the layer and of its cells: spinous cells), which interconnect the cells of this layer. 11 Elongated keratinized structures derived from invaginations of epidermal epithelium. 12 Horny hard plates made up of cornified cells containing keratin. Nail plate is divided into: 1-The body of the nail : Broad pink part, appears pink because it is semi- transparent (blood capillaries in the dermis shows through). It shows a crescent-shaped area, Lunula best seen on the thumb and absent from the little fingers 2- The root of the nail:It lies beneath the skin (invisible part). Nails grow at a rate of 0.5 mm/week. A finger nail grows faster than toe nail 13 b.Non keratinized type: the most common stratified type consists of many layers of closely held cells with the outermost layer consisting of flattened cells . e.g. covers the tongue and lines the mouth cavity, throat, esophagus, anus, & vagina. - non-keratinized, mucousal cell layer lining the esophagus - protection of the esophagus from stomach acid, 14 Stratified squamous epithelium.There are 1020 layers of cells present, which by definition makes this a "stratified" epithelium; and that the cells at the free surface are flattened, squamous shaped ones.The cells in the deeper layers are cuboidal. The lumen of the esophagus is lined with stratified squamous epithelium. 15 Rare-found in ducts of e.g. Sweat glands which are coiled tubular glands. Their ducts consisting of two layers of small cuboidal cells 16 Stratified cuboidal epithelium is a rare type of epithelial tissue cube-shaped commonly cells make up two layers sweat glands in the skin mammary gland in the breast salivary glands in the mouth Stratified cuboidal epithelium : the ducts of the parotid gland composed of cuboidal shaped cells arranged in multiple layers. 17 Transitional epithelium: e.g. Urinary bladder , ureter, urethra . Control the amount of water and salts that are absorbed back into the blood and what is taken out as waste. 18 Transitional epithelium •Multilayered •Surface cells varying in shape from round to flat if stretched •Lines hollow organs of the urinary tract that expand 19 20 3.Transitional epithelium is a stratified epithelium in which the shape of the surface cells changes (undergoes transitions) depending on the degree of stretch. Empty:Unstretched cells :rounded superficial cells bulge out 1.When a transitional epithelium is not stretched (in an empty bladder) the cells of the surface layers are large and rounded. 2.When a transitional epithelium is stretched (in a full bladder) the cells of the surface layers are pulled into a flatter shape. 21 "transitional“ = ability to change its shape from cuboidal to squamous when stretched. e.g. Urinary bladder , ureter, urethra. Empty bladder, consists of 4 -8 layer of cells . When the bladder is distended with urine the cells at the top become flat , the number of layers is reduced to 2 3 glide on each other. 22 a. distended urinary bladder (full with urine). The epithelium is very thin with fewer layers of cells and the top layer become flattened. The cells of the intermediate Transitional layers glide on each others. depends and reduced to 2 or 3 layers . epith. thickness on the state of distension (full) or contracted (empty). 23 b. Empty urinary bladder- the epithelium consists of more than five layers of cuboidal cells.The surface cells facing the lumen of the bladder are dome- shaped which characterizes on the apical surface the transitional epithelium. on the apical surface 24 Neuroepithelial Cells The tongue is a muscular organ covered with mucosa. Tiny bumps called papillae give the tongue its rough texture. Thousands of taste buds cover the surfaces of the papillae. Taste buds contain neuroepithelial cells embedded in the stratified squamous epithelium of each papilla that are the receptors for taste. 25 We all have about 10,000 taste buds, mainly on the tongue. Most highly concentrated in certain regions of the tongue's surface. Sweet receptors on the tip of the tongue . Sour receptors occur along the sides of the tongue . Salt receptors most common in the tip and upper front portion of the tongue. Bitter receptors :located toward the back of the tongue. 26 Receptor cells live for only 1 to 2 weeks and then replaced by new receptor cells. Each receptor responds to one of the basic tastes. The four common tastes are sweet, sour, bitter, and salty. 27 Questions 1.Keratinization is a characteristic of the cells in the epidermis of the skin. 2.What type of epithelium has dome shaped cells on the apical surface? a. Epithelioid tissue b. Mesothelium c. Endothelium d. Transitional e. Pseudostratified 3.Keratinized stratified squamous epithelium forms the epidermis. 28 Assignments األسم م I.D 1 51012018 اسالم عادل رمضان ابراهيم على 2 51012019 اسالم محمد عبد السالم محمد 3 51012020 اسماء إبراهيم كمال بسيوني 4 51012021 اسماء النقراشي وادي احمد 5 51012022 الشيماء مصطفى عبد العاطي 6 51012023 امل محمد احمد احمد سويدان 7 51012024 اميرة اسعد يوسف االسكندراني 8 51012025 أميرة صالح مرشدي عبد السالم 1 51012109 محمد احمد فتوح احمد سعده 2 51012110 محمد احمد محمد قاقا 3 51012111 محمد انور عبد الغنى السيد هالل 4 51012112 محمد خالد اسماعيل عبد العال 5 51012113 محمد صالح السيد صابر سعيد 6 51012114 محمد صالح الدين جامع فتح الباب 7 51012115 محمد عادل خضر إبراهيم 8 51012116 محمد علي رمضان علي النقيب Assignment tittles Nucleus Smoking & Lung cancer 3/23/2016