Chapter 13
advertisement
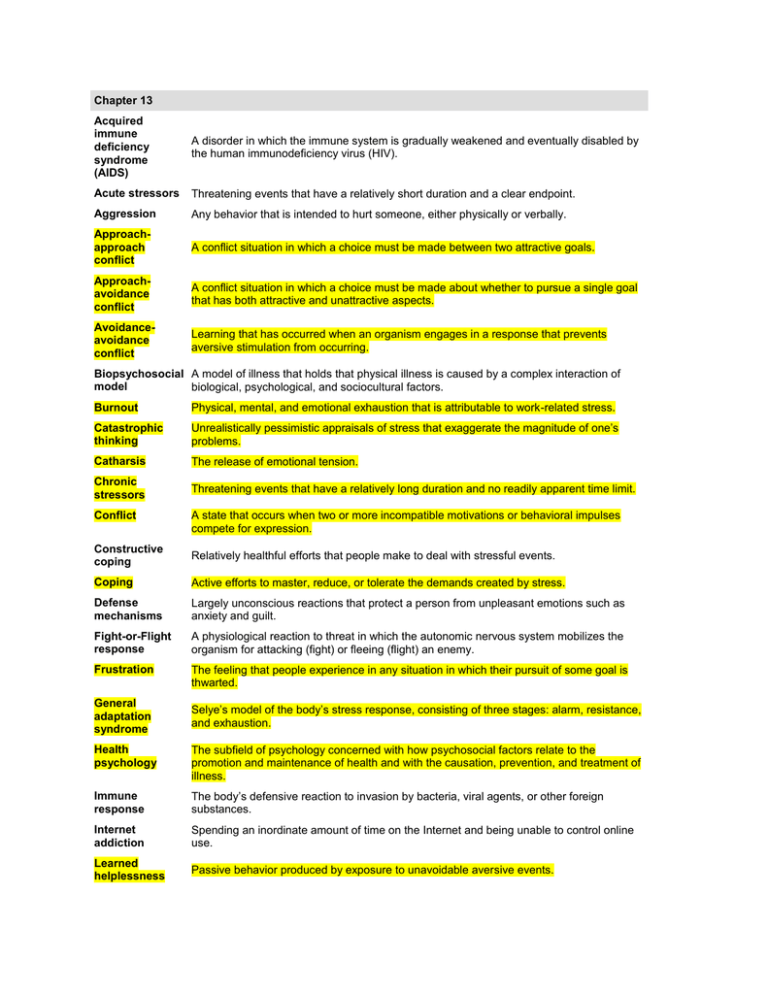
Chapter 13 Acquired immune deficiency syndrome (AIDS) A disorder in which the immune system is gradually weakened and eventually disabled by the human immunodeficiency virus (HIV). Acute stressors Threatening events that have a relatively short duration and a clear endpoint. Aggression Any behavior that is intended to hurt someone, either physically or verbally. Approachapproach conflict A conflict situation in which a choice must be made between two attractive goals. Approachavoidance conflict A conflict situation in which a choice must be made about whether to pursue a single goal that has both attractive and unattractive aspects. Avoidanceavoidance conflict Learning that has occurred when an organism engages in a response that prevents aversive stimulation from occurring. Biopsychosocial A model of illness that holds that physical illness is caused by a complex interaction of model biological, psychological, and sociocultural factors. Burnout Physical, mental, and emotional exhaustion that is attributable to work-related stress. Catastrophic thinking Unrealistically pessimistic appraisals of stress that exaggerate the magnitude of one’s problems. Catharsis The release of emotional tension. Chronic stressors Threatening events that have a relatively long duration and no readily apparent time limit. Conflict A state that occurs when two or more incompatible motivations or behavioral impulses compete for expression. Constructive coping Relatively healthful efforts that people make to deal with stressful events. Coping Active efforts to master, reduce, or tolerate the demands created by stress. Defense mechanisms Largely unconscious reactions that protect a person from unpleasant emotions such as anxiety and guilt. Fight-or-Flight response A physiological reaction to threat in which the autonomic nervous system mobilizes the organism for attacking (fight) or fleeing (flight) an enemy. Frustration The feeling that people experience in any situation in which their pursuit of some goal is thwarted. General adaptation syndrome Selye’s model of the body’s stress response, consisting of three stages: alarm, resistance, and exhaustion. Health psychology The subfield of psychology concerned with how psychosocial factors relate to the promotion and maintenance of health and with the causation, prevention, and treatment of illness. Immune response The body’s defensive reaction to invasion by bacteria, viral agents, or other foreign substances. Internet addiction Spending an inordinate amount of time on the Internet and being unable to control online use. Learned helplessness Passive behavior produced by exposure to unavoidable aversive events. Life changes Any noticeable alterations in one’s living circumstances that require readjustment. Optimism A general tendency to expect good outcomes. Pressure Expectations or demands that one behave in a certain way. Psychosomatic diseases Physical ailments with a genuine organic basis that are caused in part by psychological factors, especially emotional distress. RationalAn approach to therapy that focuses on altering clients’ patterns of irrational thinking to emotive therapy reduce maladaptive emotions and behavior. Social support Various types of aid and succor provided by members of one’s social networks. Stress Any circumstances that threaten or are perceived to threaten one’s well-being and that thereby tax one’s coping abilities. Type A personality Personality characterized by (1) a strong competitive orientation, (2) impatience and time urgency, and (3) anger and hostility. Type B personality Personality characterized by relatively relaxed, patient, easygoing, amicable behavior.











