Food Web Power Point
advertisement

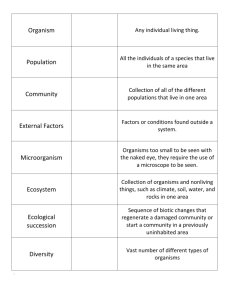
Ecology: Community Interactions Food Web Notes/2.0: Energy and feeding relationships! Terms to know….. Producers • A group of organisms that can use the energy in sunlight to make food. • Energy for all ecological systems begin with producers. • Also called Autotrophs • Ex. Plants and Algae Autotrophs Consumers • Organisms that do not make their own food • They must consume other organisms in order to live. • Also called heterotrophs. • Ex. Rabbits, Deer, Mushrooms Heterotrophs Herbivores • Consumers – 2. Herbivores – eat ONLY plants • Ex. – Cows, Elephants, Giraffes Carnivores • Consumers – 3. Carnivores – eat ONLY meat • Ex. – Lions, Tigers, Sharks Omnivores • Consumers – 4. Omnivores – eat BOTH plants and animals • Ex. – Bears and Humans Decomposers • Consumers – 5. Decomposers – absorb any dead material and break it down to return nutrients to the earth. • Ex. – Bacteria and Mushrooms Trophic (energy) Levels • Energy moves from one organisms to another when it is eaten. • Each step in this transfer of energy is know as a trophic level – The main trophic levels are producers, consumers and decomposers • Food chains show how energy moves from one level to another. Arrows show energy flow. Food Chain Food Web • Most organisms eat more the JUST one organism! When more organisms are involved it is know as a FOOD WEB. • Food webs are more complex and involve lots of organisms. Food Web examples Food Web Activity / Not in Notebook • Complete Part A of the Food Web Activity – Work as a table group. – Follow instructions on the plastic sheet. – There are LOTS of correct ways to create this food web – 25 minutes Transfer of Energy • No organism EVER receives all of the energy from the organism they just ate. Why? – Energy is lost as heat – Not all of the organism is eaten • Only 10% of the energy from one trophic level is transferred to the next – this is called the 10% law • As energy moves through a food web it ________________. Ecological Pyramid Ecological Pyramid Ecological Pyramid 5. Which level has the most energy? 6. Which level has the most organisms? 7. Which level has the least organisms? 8. Which level has the least energy? Food Web Activity • Complete Part B of the Food Web Activity – 15 minutes Symbiosis • A close and permanent association between organisms of different species (not predator /prey) • Chart – Commensalism – a relationship in which one organism benefits and the other is not affected • Example: Barnacles on a whale – Mutualism – a relationship in which both organisms benefit from each other • Example: Birds eating pest off a rhino’s back – Parasitism – A relationship in which one organism benefits and the other is harmed • Example: Ticks on a dog Cycling through the ecosystem 1. Water Cycle – 4 –tions: evaporation, transpiration, condensation, precipitation – Powered by the Sun – Abiotic Cycle Cycling of resources in an ecosystem. 2. Carbon Cycle • Write the equation for photosynthesis. • Write the equation for respiration. – How does carbon ENTER the atmosphere? – How is carbon REMOVED from the atmosphere? – Biotic Cycle Carbon Cycling of resources in an ecosystem. 3. Nitrogen Cycle All living things need nitrogen! • Lots of nitrogen is available in the air but plants cannot take it in. • Bacteria in the soil or on roots create usable nitrogen for plants. • Animals eat plants • Death and decay puts nitrogen back into the air. • Biotic Cycle Diagrams • Paste both diagrams in your notebook with the notes. • On the Carbon Cycle: – Color the arrows that PUT Carbon Dioxide into the air RED. – Color the arrows that TAKE Carbon Dioxide out of the air GREEN. – What parts of the Carbon Cycle would not have been present before the Industrial Revolution? Water Carbon Nitrogen Into the atmopshere Out of the atmosphere Biotic or Abiotic Important Organisms Color ONE of the cycles on your sheet. Predator/Prey Interactions (Homework Sheet) Cycling of resources in an ecosystem. • Water Cycle – 4 –tions: evaporation, transpiration, condensation, precipitation – Abiotic Cycle • Carbon Cycle – How does carbon enter the atmosphere? – How is carbon removed from the atmosphere? – Biotic Cycle • Nitrogen Cycle – Bacteria in the soil or on roots create usable nitrogen for plants. Biomass • The total mass of the organic matter at each trophic level is called biomass • Biomass is just another term for potential energy – energy that is to be eaten and used. • The transfer of energy from one level to another is very inefficient (10% Law) Biomass Ecological Pyramid • An ecological pyramid shows the relationship between consumers and producers at different trophic levels in an ecosystem • Shows the relative amounts of energy or matter contained at each trophic level • The Pyramid shows which level has the most energy and the highest number of organisms