Mythology-Presentation
advertisement

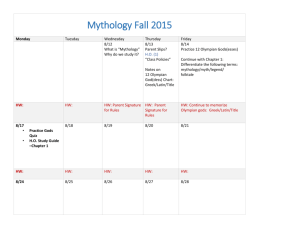
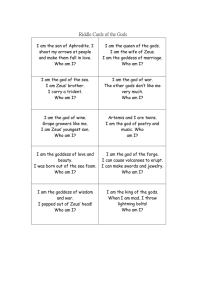
Greek Mythology: Gods & Goddesses Standards ELAGSE6W7 – Conduct short research projects to answer a question, drawing on several sources and refocusing the inquiry when appropriate. ELAGSE6W8 – Gather relevant information from multiple print and digital sources; assess the credibility of each source; and quote or paraphrase the data and conclusions of others while avoiding plagiarism and providing basic bibliographic information through the selection, organization, and analysis of relevant content. ELAGSE6W2 – Write informative/explanatory texts to examine a topic and convey ideas, concepts, and information through the selection, organization, and analysis of relevant content. I CAN…statements!! I can conduct research on a specific topic and present the information. ELAGSE6W7 I can introduce a topic of my text. ELAGSE6W2 I can develop the topic with relevant facts, definitions, concrete details, and quotations. ELAGSE6W8 What are myths? • The ancient Greeks told stories about their gods. These stories are called myths (short for mythology, or stories about gods.) Stories about the ancient Greek gods are still told today. • Each storyteller told the stories in their own way, but whatever power and personality a god had was consistent from story to story. For example, Zeus was the king of all the gods, and only Zeus could throw lightning bolts. The magical world of the ancient Greek gods was a world full of bickering and fights and wars and compromise and fear and fun and punishment and love. Many myths were based on the fact that gods, like mortal men, could be punished or rewarded for their actions. Mythology Ancient cultures used mythology belief systems much the same way that people use modern religion. 1. to explain the world 2. to instruct or guide proper behavior 3. to give a sense of community hyperlink Origins of Mythology Ancient mythology belongs to the oral tradition (folklore, legends, etc.) 1. stories passed orally appealed to the non-literate 2. these stories were a form of entertainment 3. the stories enabled the passing of history and culture from one group to the next Greek Mythology 1. The Greeks were the earliest people to give their gods human forms H y 2. The Greeks also p gave the gods e r human qualities l and emotions i n 3. Greeks were able to k determine proper behavior based on what would “anger the gods” or “please the gods.” Greek Myth Categories The Greek myths fall into the following categories: a. Explanatory (Pyramus and Thisbe) b. Instructional (Daedalus and Icarus) c. Entertainment Remember the Titans? • Gaea: Earth Goddess; made the rest of the Titans by mating with her son, Uranus. • Uranus: Sky god; first ruler. Dethroned by Cronus. • Cronus: Fathered the first of the Olympians. Swallowed his children except for Zeus. • Prometheus: “Forethought” ; Protector of man; inventor of fire. • Atlas: Punished by having to hold the world on his back. Who Were the Olympians? • The offspring of the Titans • Overthrew the Titans in a war to control the universe. • Led by Zeus, the god of the other gods. • Zeus and his brothers split territory (Zeusearth/sky, Poseidon- the seas, Hades- the underworld) The Twelve Olympians • Aphrodite: goddess of love and beauty. Her symbols were the dove, and myrtle, a type of evergreen shrub. Her Latin name was Venus. • Apollo: god of the sun and of music. His symbols were the lyre, the chariot, and the laurel tree. His Latin name was Apollo. • Ares: god of war. His symbols were armor, dogs, and vultures. His Latin name was Mars. • Artemis: goddess of the hunt and of the moon. Her symbols were hunting, weapons, stags, and the crescent moon. Her Latin name was Diana. • Athena: goddess of wisdom and war. Her symbols were the owl, the olive tree, and two types of armor—the breastplate and the aegis, a shield. Her Latin name was Minerva. • Demeter: goddess of agriculture. Her symbols were sheaves of wheat, and the poppy. Her Latin name was Ceres. • Dionysus: god of wine and revelry. His symbols were grapes and other crops. His Latin name was Bacchus. • Hephaestus: god of fire and of the forge. His symbols were the anvil and the hammer. His Latin name was Vulcan. • Hera: queen of the gods. Her symbols were the peacock and the pomegranate. Her Latin name was Juno. • Hermes: messenger of the gods. His symbols were the caduceus, and a winged cap and sandals. His Latin name was Mercury. • Poseidon: god of the sea. His symbols were the trident, a three pronged spear, and dolphins. His Latin name was Neptune. • Zeus: king of the gods. His symbols were the thunderbolt, the eagle, and the oak tree. His Latin name was Jupiter. Family Tree Other Gods and Goddesses Eris - Goddess of Discord. Eros - God of Love. Helios - Personification of the Sun. Heracles - Greatest hero of the Greek myths. Iris - Personification of the Rainbow, also the messenger of Olympus along with Hermes. Morpheus - God of Dreams. Muses - Nine ladies of science and arts. Nemesis - Greek goddess of retribution. Nike - Goddess of victory. Can you label the Gods and Goddesses on Mount Olympus?