Add to Table of Contents
advertisement

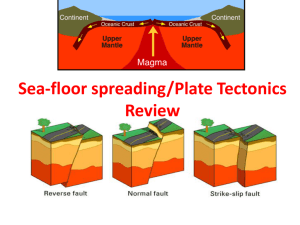
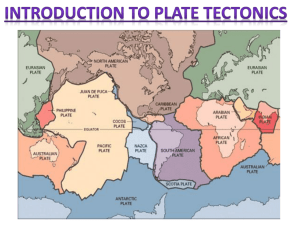
Add to Table of Contents: • Boundaries Draw-Along • Plate Tectonics Pg. 54 Pg. 55 Don’t write-Review • Prior to Alfred Wegener’s theory of continental drift geologists thought continents were fixed in their locations. In developing his theory which of the following evidence was NOT used by Wegener? a) Fossil similarities between southern continents. b) Evidence of polarity change in found along the MidAtlantic Ridge. c) Similarities in the paleoclimates of South America and Africa. d) The apparent fact the South America and Africa seemed to fit together. Plate Tectonics Lithosphere - the rigid outer layer of the Earth. •Made of the crust and the solid outer layer of mantle. Asthenosphere - the layer of “plastic” rock in the lower mantle. • Flows like a very thick liquid. Pg. 55 Lithospheric Plates • Lithospheric Plates-The rigid lithosphere is broken into plates =tectonic plates – Float on the semi rigid, moving asthenosphere. Theory of Plate Tectonics – explains how the lithospheric plates move and change shape. Tectonic Plates 1. Earth’s lithosphere is broken into 7 major(large) plates and numerous minor (smaller) ones. 2. The plates glide over the asthenosphere and produce earthquakes, volcanoes and create mountains. Convection Currents - driving forces of plate tectonics - very hot material at the deepest part of the mantle rises, then cools and sinks again, then repeating. This cycle is repeated over and over. HOT!!!! ***Remember…this heat is generated by the core!! How Plate Tectonic Works As magma heats up and rises, it exits through the rift in the middle of the mid-ocean ridge. It cools and pushes the plates apart. What is the average rate of movement from lithospheric plates? • 5cm/yr (2inches) and it is driven by unequal heating of the Earth. Plate Boundaries 1. Convergent – moving together 2. Divergent – moving apart 3. Transform – moving side by side Convergent Boundary – Oceanic & Oceanic http://pubs.usgs.gov/gip/dynamic/understanding.html & http://www.geology.com Aleutian Islands, Alaska, May 23, 2006 Convergent Boundaries Continental - Continental http://pubs.usgs.gov/gip/dynamic/understanding.html & http://www.geology.com Himalayan Mountains Convergent Boundary – Oceanic & Continental http://pubs.usgs.gov/gip/dynamic/understanding.html & http://www.geology.com Mt. St. Helen – Cascade Mtns. May 20, 1980 Divergent boundary – Continental - Continental Divergent Boundary – Arabian and African Plates Divergent Boundary Oceanic - Oceanic Transform Boundary – San Andreas Fault www.geology.com San Andreas Fault Train crossing San Andreas Fault – Cajon Pass, CA Draw – Alongs!