tectonic plates
advertisement

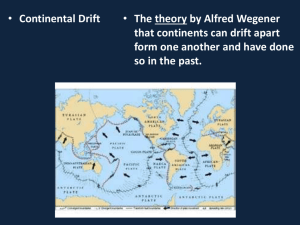
Unit 7 Lesson 2 Plate Tectonics and Landforms Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Company Unit 7 Lesson 2 Tectonic Plates and Landforms Stressed Out What does the theory of plate tectonics explain? • Earth’s outermost layer is called the lithosphere, and the layer directly below is called the asthenosphere. Both are solid layers of rock. • The lithosphere is divided into large, moving pieces called tectonic plates. • The theory of plate tectonics explains how lithospheric plates move around on the slowflowing rock of the asthenosphere. Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Company Unit 7 Lesson 2 Tectonic Plates and Landforms What are some properties of tectonic plates? • The lithosphere is broken into 15 major tectonic plates that differ in size, shape, density, thickness, and composition. • Continental lithosphere is thicker and older than oceanic lithosphere. • Tectonic plates move slowly around Earth’s surface and interact with one another. Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Company Unit 7 Lesson 2 Tectonic Plates and Landforms What types of stress are related to the movement of tectonic plates? • As tectonic plates move and interact, stress is put on rock. • This stress causes deformation, which is the bending, tilting, and breaking of rock. • Deformation changes the size and shape of features on or below Earth’s surface. Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Company Unit 7 Lesson 2 Tectonic Plates and Landforms What types of stress are related to the movement of tectonic plates? • Compression is a stress that squeezes or shortens material. • This type of stress can cause folds as rock is squeezed and shortened. • Compression can also cause breaks in rock, or faults, where Earth’s lithosphere is more rigid. Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Company Unit 7 Lesson 2 Tectonic Plates and Landforms What types of stress are related to the movement of tectonic plates? • Tension is a stress that lengthens a material or pulls a material apart. • Two plates moving away from one another cause tension. • When tension is greater than the strength of the rock, the rock break and faults form. Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Company Unit 7 Lesson 2 Tectonic Plates and Landforms What types of stress are related to the movement of tectonic plates? • Shear stress causes material to twist or become distorted. • This type of stress can occur when two tectonic plates move past one another and grind against each other. Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Company Unit 7 Lesson 2 Tectonic Plates and Landforms What are the different types of plate boundaries? • Most deformation occurs at boundaries where tectonic plates meet. • These plate boundaries may be on the ocean floor, around the edges of continents, or even within continents. • Certain landforms are formed at different types of boundaries. Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Company Unit 7 Lesson 2 Tectonic Plates and Landforms What are the different types of plate boundaries? • A convergent boundary forms when tectonic plates collide. • In oceanic-continental convergence, the denser oceanic plate sinks beneath the continental plate. • In continental-continental convergence, the plates push against each other and buckle. • In oceanic-oceanic convergence, the denser plate sinks beneath the less dense plate. Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Company Unit 7 Lesson 2 Tectonic Plates and Landforms What are the different types of plate boundaries? • A divergent boundary forms when two tectonic plates move away from one another. • Magma rises up through cracks that form when two plates move away from each other along a divergent boundary. • Most divergent boundaries are under the ocean. Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Company Unit 7 Lesson 2 Tectonic Plates and Landforms What are the different types of plate boundaries? • A transform boundary forms when two tectonic plates move past one another in opposite directions. • The plates slowly scrape against one another before shifting suddenly, which shear stress breaks or distorts rock. • The San Andreas Fault is a transform boundary, but most transform boundaries are on the ocean floor. Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Company Unit 7 Lesson 2 Tectonic Plates and Landforms Push Up What features are associated with convergent boundaries? • Compression along convergent boundaries can cause rock to be folded and move upwards, forming mountain ranges • The Appalachian Mountains formed from faulting and folding when the North American plates collided with the Eurasian and African plates. • The Himalayas formed when the Indian plate collided with the Eurasian plate. Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Company Unit 7 Lesson 2 Tectonic Plates and Landforms What features are associated with convergent boundaries? • When oceanic and continental plates collide, magma can rise to Earth’s surface and eventually form a continental volcanic arc. • Volcanoes can also form when two oceanic plates converge and one sinks beneath the other. This type of collision results in a volcanic island arc. Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Company Unit 7 Lesson 2 Tectonic Plates and Landforms What features are associated with convergent boundaries? • Ocean trenches are the deepest landforms found on the ocean floor. • They can form when a oceanic plate collides with and slides beneath an oceanic or continental plate. Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Company Unit 7 Lesson 2 Tectonic Plates and Landforms What features are associated with divergent boundaries? • Mountains may also form at divergent boundaries. • Fault-block mountains form when block of lithosphere drop down or are lifted up along faults. • Tension at diverging plates also causes rifting, where Earth’s lithosphere pulls apart to form long, narrow, faulted rift valleys. • Rifting also forms rift zones, which can form volcanic mountains and tall, flat-topped plateaus. Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Company Unit 7 Lesson 2 Tectonic Plates and Landforms What features are associated with transform boundaries? • Some chains of volcanic islands, known as hot spots, form far from plate boundaries. • At a hot spot, magma rises from deep within the Earth. Repeated lava flows form an undersea volcano that eventually reaches above the ocean’s surface to form a volcanic island. • As the oceanic plate shifts, a new island may form over the hot spot. Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Company Unit 7 Lesson 2 Tectonic Plates and Landforms What volcanic landforms occur way from plate boundaries? • Major and minor earthquakes are associated with transform boundaries • Transform boundaries can also cause mid-ocean ridges to be offset. • Offset streams and fences can be a sign of a transform boundary on land. Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Company