Introduction
advertisement
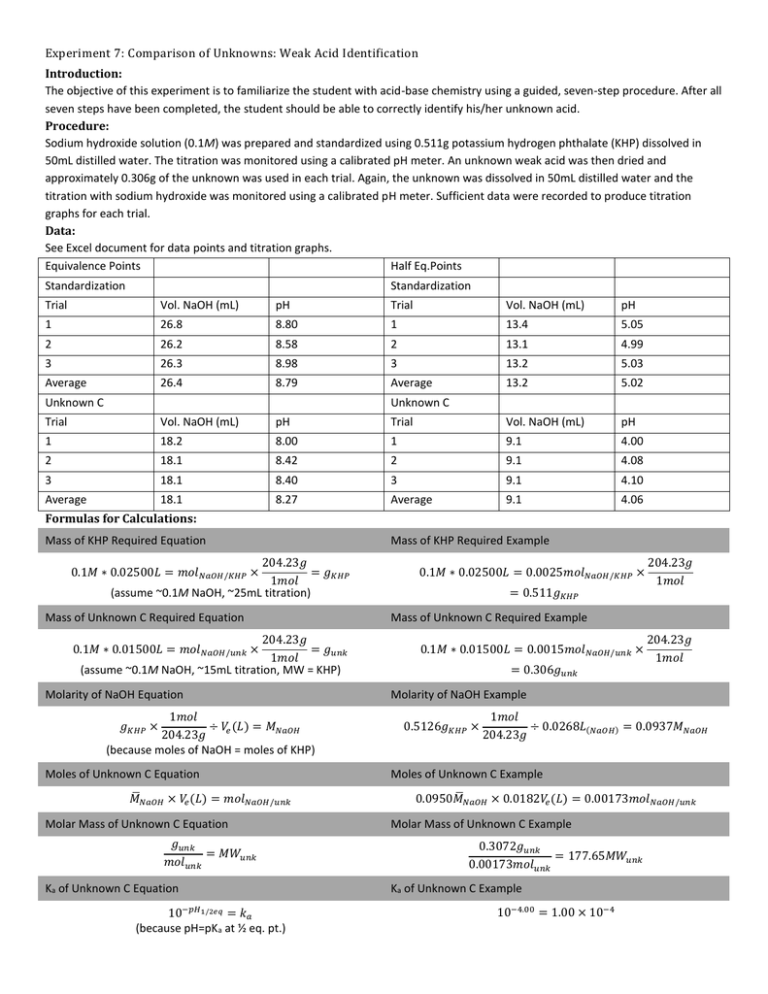
Experiment 7: Comparison of Unknowns: Weak Acid Identification Introduction: The objective of this experiment is to familiarize the student with acid-base chemistry using a guided, seven-step procedure. After all seven steps have been completed, the student should be able to correctly identify his/her unknown acid. Procedure: Sodium hydroxide solution (0.1M) was prepared and standardized using 0.511g potassium hydrogen phthalate (KHP) dissolved in 50mL distilled water. The titration was monitored using a calibrated pH meter. An unknown weak acid was then dried and approximately 0.306g of the unknown was used in each trial. Again, the unknown was dissolved in 50mL distilled water and the titration with sodium hydroxide was monitored using a calibrated pH meter. Sufficient data were recorded to produce titration graphs for each trial. Data: See Excel document for data points and titration graphs. Equivalence Points Half Eq.Points Standardization Standardization Trial Vol. NaOH (mL) pH Trial Vol. NaOH (mL) pH 1 26.8 8.80 1 13.4 5.05 2 26.2 8.58 2 13.1 4.99 3 26.3 8.98 3 13.2 5.03 Average 26.4 8.79 Average 13.2 5.02 Trial Vol. NaOH (mL) pH Trial Vol. NaOH (mL) pH 1 18.2 8.00 1 9.1 4.00 2 18.1 8.42 2 9.1 4.08 3 18.1 8.40 3 9.1 4.10 Average 18.1 8.27 Average 9.1 4.06 Unknown C Unknown C Formulas for Calculations: Mass of KHP Required Equation 204.23𝑔 = 𝑔𝐾𝐻𝑃 1𝑚𝑜𝑙 (assume ~0.1M NaOH, ~25mL titration) 0.1𝑀 ∗ 0.02500𝐿 = 𝑚𝑜𝑙𝑁𝑎𝑂𝐻/𝐾𝐻𝑃 × Mass of Unknown C Required Equation 204.23𝑔 = 𝑔𝑢𝑛𝑘 1𝑚𝑜𝑙 (assume ~0.1M NaOH, ~15mL titration, MW = KHP) 0.1𝑀 ∗ 0.01500𝐿 = 𝑚𝑜𝑙𝑁𝑎𝑂𝐻/𝑢𝑛𝑘 × Molarity of NaOH Equation 1𝑚𝑜𝑙 ÷ 𝑉𝑒 (𝐿) = 𝑀𝑁𝑎𝑂𝐻 204.23𝑔 (because moles of NaOH = moles of KHP) 𝑔𝐾𝐻𝑃 × Moles of Unknown C Equation ̅𝑁𝑎𝑂𝐻 × 𝑉𝑒 (𝐿) = 𝑚𝑜𝑙𝑁𝑎𝑂𝐻/𝑢𝑛𝑘 𝑀 Molar Mass of Unknown C Equation 𝑔𝑢𝑛𝑘 = 𝑀𝑊𝑢𝑛𝑘 𝑚𝑜𝑙𝑢𝑛𝑘 Ka of Unknown C Equation 10−𝑝𝐻1/2𝑒𝑞 = 𝑘𝑎 (because pH=pKa at ½ eq. pt.) Mass of KHP Required Example 0.1𝑀 ∗ 0.02500𝐿 = 0.0025𝑚𝑜𝑙𝑁𝑎𝑂𝐻/𝐾𝐻𝑃 × = 0.511𝑔𝐾𝐻𝑃 204.23𝑔 1𝑚𝑜𝑙 Mass of Unknown C Required Example 0.1𝑀 ∗ 0.01500𝐿 = 0.0015𝑚𝑜𝑙𝑁𝑎𝑂𝐻/𝑢𝑛𝑘 × = 0.306𝑔𝑢𝑛𝑘 204.23𝑔 1𝑚𝑜𝑙 Molarity of NaOH Example 0.5126𝑔𝐾𝐻𝑃 × 1𝑚𝑜𝑙 ÷ 0.0268𝐿(𝑁𝑎𝑂𝐻) = 0.0937𝑀𝑁𝑎𝑂𝐻 204.23𝑔 Moles of Unknown C Example ̅𝑁𝑎𝑂𝐻 × 0.0182𝑉𝑒 (𝐿) = 0.00173𝑚𝑜𝑙𝑁𝑎𝑂𝐻/𝑢𝑛𝑘 0.0950𝑀 Molar Mass of Unknown C Example 0.3072𝑔𝑢𝑛𝑘 = 177.65𝑀𝑊𝑢𝑛𝑘 0.00173𝑚𝑜𝑙𝑢𝑛𝑘 Ka of Unknown C Example 10−4.00 = 1.00 × 10−4 Summary of Calculations: Trial Molarity NaOH Moles Unk. C Molar Mass Unk. C pH @ V1/2 (pka) Ka Unk. C 1 0.093653556 0.001729212 177.6532001 4.00 0.0001 2 0.095816982 0.001719711 178.9836054 4.08 8.31764E-05 3 0.095564365 0.001719711 178.8673067 4.10 7.94328E-05 Average 0.095011634 0.001722878 178.5013707 4.06 8.75364E-05 Mass KHP Req’d : 0.511g Mass Unk. C Req’d : 0.306g Conclusions: The calculated molar mass of unknown C was 178.50 g/mol. The pka value was 4.06, and the ka value was 8.754E-5. The unknown was known to be a monoprotic organic acid. Two monoprotic organic acids with similar molecular weights, pka and ka values to those that were calculated from this experiment are 1-naphthoic acid (172.18g/mol, 3.70, 2.1E-4) and acetylsalicylic acid (180.157g/mol, 3.50, 3.3E-4). Further experimentation would be necessary to determine which of the two weak acids is unknown C. The first fits more closely to the pka value whereas the second fits more closely to the molecular weight. One possible reason for not obtaining a clear-cut identity for the acid is that using a titration curve is inexact unless the first and second derivatives are utilized to determine the exact equivalence point. As this was not the case with this experiment, the determinations of the equivalence and half-equivalence points are very inexact, leading to an unclear identity of the unknown. Further experimentation may include NMR or IR analysis to determine which of the two possible compounds is, in fact, unknown C.