note taking guide
advertisement

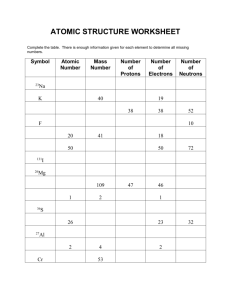
Name: _____________________________________________ Date: ___________________ Period: ________ Isotope PPT note taking guide 1. Protons define the element _______________ that have the _______________ number of _______________ are _______________ atoms of a _______________ element. 2. Neutrons can vary BUT _______________ can have _______________ numbers of _______________ and still be an _______________ of a _______________ element. 3. Isotopes This is because _______________ can have _______________ (basically _______________ of the same element with a _______________ number of _______________ in their _______________). 4. Dalton was wrong When Dalton stated his atomic theory in the early 1800’s, he _______________ that all of the atoms of a given element were _______________. 5. James Chadwick Over 100 years after Dalton, James Chadwick _______________ that the _______________ of most _______________ contains _______________ as well as protons. 6. Dalton’s Theory Changes Dalton’s theory now states: - All atoms of the same element contain the same number of protons and electrons, but atoms of a given element may have different numbers of neutrons. 7. The Isotopes of Hydrogen Hydrogen – 1 - Also written _______________ - Also known as _______________ - Hydrogen has an _______________ _______________ of _____, so it has _____ proton - The hyphen notation above tells us that the mass number of H-1 is _____ o Number of neutrons = mass number – atomic number o So H-1 must have _____ neutrons Hydrogen – 2 - Also written _______________ - Also known as _______________ - Hydrogen has an _______________ _______________ of _____, so it has _____ proton - The hyphen notation above tells us that the mass number of H-2 is _____ o Number of neutrons = mass number – atomic number o So H-2 must have _____ neutron Hydrogen – 3 - Also written _______________ - Also known as _______________ - Hydrogen has an _______________ _______________ of _____, so it has _____ proton - The hyphen notation above tells us that the mass number of H-3 is _____ o Number of neutrons = mass number – atomic number o So H-3 must have _____ neutron 8. Calculate the number of neutrons For chlorine found on the periodic table (the most common form of chlorine that is found in nature) Chlorine-35 For Chlorine-37 Chlorine-35 = _____ neutrons, Chlorine-37 = _____ neutrons For Cobalt found on the periodic table Cobalt-59 For Cobalt-60 Cobalt-59 = _____ neutrons, Cobalt-60 = _____ neutrons 9. Calculating Average Atomic Mass Average _______________ mass is the atomic _______________ that _______________ on the _______________ table. For example – Copper has an _______________ atomic _______________ of _______________ amu. Yet, in _______________, most elements are _______________ as _______________ of two or more _______________. For example, copper consists of 69.17% copper-_____ which has a _______________ atomic _______________ of 62.94 amu AND 30.83% copper-_____ which has a _______________ atomic _______________ of 64.93 amu To find the _______________ atomic _______________, multiply the _______________ equivalent of the _______________ (for example 69.17% = 0.6917) of each _______________ by the respective _______________ atomic _______________ and _______________ the _______________. Isotope Copper – 63 Copper – 65 Relative abundance in nature Relative atomic mass (_______________ X _______________) + (_______________ X _______________) = 63.55 amu 10. Practice Calculating Average Atomic Mass Boron – _____ is _______________ 19.9% of the _______________ in _______________ and has a _______________ atomic _______________ of 10.013 amu Boron – _____ is _______________ 80.1% of the _______________ in _______________ and has a _______________ atomic _______________ of 11.009 amu Calculate the _______________ _______________ _______________ of Boron Isotope Boron – 10 Relative abundance in nature Relative atomic mass (_______________ X _______________) + (_______________ X _______________) = Boron – 11 11. Practice Calculating Average Atomic Mass Magnesium – _____ is _______________ 78.99% of the _______________ in _______________ and has a _______________ atomic _______________ of 23.985042 amu Magnesium – _____ is _______________ 10.00% of the _______________ in _______________ and has a _______________ atomic _______________ of 24.985837 amu Magnesium – _____ is _______________ 11.01% of the _______________ in _______________ and has a _______________ atomic _______________ of 25.982593 amu Calculate the _______________ _______________ _______________ of Magnesium Isotope Magnesium – 24 Magnesium – 25 Magnesium – 26 23.985042 amu 24.985837 amu 25.982593 amu Relative abundance in nature Relative atomic mass (_______________ X 23.985042) + (_______________ X 24.985837) + (_______________ X 25.982593) =