USING YOUR ATLAS
advertisement

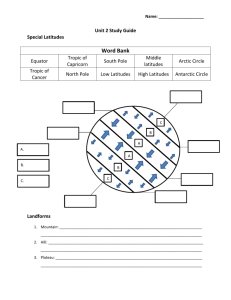
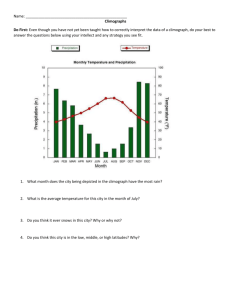
USING YOUR ATLAS ORIENTATION IN SPACE Using your atlas I. Table of contents Hungary page: ...-... Europe page: ...-... Africa page: ...-... Asia page: ...-... America page: ...-... Australia and Oceania Polar regions The Earth Index page: ...-... page: ...-... page: ...-... page: ...-... II. Legend 1. The legend explains you what all the symbols used by the map mean III. Index is the alphabetical list of all locations to be found in the atlas 1. Square grid network helps you to find any geographical location quickly - numbers representing page numbers and in case of more map per page, the number of the map - combination of letters and numbers - red letters and numbers around the frame of the map - thin blue parallels of latitudes and lines of longitudes bordering the squares 2. Exercise. Search for the item given below! Kampala – Give the country it belongs to! 3. Exercise. Answer the questions with the combination of the index and the legend! Skelleftea continent: country: altitude: raw materials(3): branches of industry(2): number of population: Main features of maps I. Definition A map is a plane representation of the proportionately reduced surface of the Earth using conventional symbols. II. Main types of maps 1. Sorted by content a, topographical maps: depicting objects on the surface in the fullest detail b, geographical maps: relief, hydrography c, thematic maps: depicting certain topics on the map, e.g.: geological, forestry, touristic, road, climatic maps 2. Sorted by scale a, large scale: 1:500 – 1:100 000 in great detail b, medium scale: 1:100 000 – 1:500 000 e.g: counties c, small scale: 1:500 000 – maps of continents Scale shows you the ratio of reduction, i.e. how long 1 cm on the map in the reality is. E.g.: if the scale of our map is 1:200 000, it means, that 1 cm is in the reality 200 000 cm (2 km). [1m=100cm; 1km=1 000m; 1km =100 000cm] III. Exercise. 1, The scale of our map is 1:50 000. There is an 8cm long highway indicated on the map. Calculate how long that section of the highway in the reality is! 2, 1:200 000, 8cm – 16 IV. Main parts of a map 1. Title 2. Frame 3. Line scale 4. Scale 5. Symbols, hue, font, etc. 6. Search engine 7. Network of latitudes and longitudes V. Exercise. Measure the distances between the following settlements in your atlas with a stripe of paper and the help of the actual line scale! 1. Solt – Kecskemét: 54 km 2. Barcelona – Pamplona: 350 km 3. Atlanta – Miami: 930 km VI . Symbols on the map 1. Depiction of relief - contour line: a line connecting points with the same altitude - hue: the larger the number (indicating depth or hight), the darker the colour - hachure: shading, the most spectacular way of depicting relief 2. Planimetry: representation of natural and artificial elements on the surface - hydrography (rivers, streams, lakes, seas, oceans) - borders - settlements (homesteads, villages, towns, cities) - roads - cables - vegetation 3. Nomination - names with different types of letters - numbers with different font types and colours - explanations Vocabulary orientation talbe of contents symbol legend square grid network represent geographical location paralell line of latitude line of longitude altitude, height above sea level branch of industry number of population definition plane representation reduced surface conventional tájékozódás tartalomjegyzék jel jelmagyarázat keresőrendszer jelez földrajzi hely párhuzamos szélességi vonal hosszúsági vonal tengerszint feletti magasság iparág lakosságszám meghatározás sík(beli) ábrázolás kicsinyített felszín egyezményes sort topographical depict in the fullest detail relief hydrography thematic topic geology climate forestry scale frame line scale hue hachure contour line planimetry settlement cable nomination csoportosít topográfiai ábrázol a legrészletesebben domborzat vízrajz tematikus téma földtan éghajlat erdőgazdálkodás (méret)arány keret vonalas aránymérték színárnyalat árnyékolás szintvonal síkrajz település vezeték névrajz Orientation in space Definitions: Horizon is the line where sky and earth seem to meet, and there are four main orientation points: north, south, west and east. To find the northern direction you should use a compass, a gnomon, the shadow at noon, a traditional watch or at night the Pole Star. Having identified the northern direction, you also have to determinate your position on the map by measurement or by resection. Network of latitudes and longitudes is an artificial system for orientation on the surface of the Earth. It allows you to give the exact place of any location on Earth. I. Paralleles of latitudes - the main parallel of latitude is the Equator, the longest line of latitude, its length equals to the periphery of the Earth - a parallel is expressed by degree, minute and second (1°=60’=360’’), which represent the angle of an opposite angle of a triangle described from the center of the Earth along the Equator - other notable latitudes are the Tropic of Capricorn (23,5° N), the Tropic of Cancer (23,5° S), the Arctic Circle (66,5° N), the Antarctic Circle (66,5° S) - parallels of latitudes are parallel, shrink from the Equator, and end up in a point at the poles II. Lines of longitudes - the starting line of longitudes (the Prime Meridian) is by agreement the line running through the observatory in London, Greenwich (0°) - longitudes are measured by degree, minute and second (1°=60’=360’’), 180° to the west and 180° to the east from the Prime Meridian - other notable longitude is the International Date Line (when crossing from west to east subtracts, from east to west adds one day) - longitudes cross each other at the poles and their length is equal, that is the periphery of the Earth III. Find the cities and use the legend to answer all questions! 1, 48° N, 0° 10’E continent: country: name of the city: L number of population: industry: 2, 5° S, 119° 30’ E continent: country: island: name of the city: U number of population: industry: raw material: 3, 19° S, 47 °E continent: country: name of the city: number of population: 4. Give latitudinal and longitudinal data for the following settlements or peaks! Mount Logan: Lop-nor lake: Ouagadougou: Budapest: Vocabulary horizon cardinal points artificial compass Pole Star orientation determination bisect coincide measurement resection standpoint parallel of latitude line of longitude horizontal vertical periphery diameter diagonal opposite angle horizont fő égtájak mesterséges iránytű Sarkcsillag tájolás meghatározás kettéoszt egybe esik mérés visszametszés tartózkodási hely szélességi kör hosszúsági kör vízszintes függőleges kerület átmérő átló csúcsszög notable nevezetes Tropic of Cancer Ráktérítő Tropic of Capricorn Baktérítő Arctic Circle Északi Sarkkör Antarctic Circle Déli Sarkkör Prime Meridian kezdő délkör observatory csilagvizsgáló International Date Line Dátumválasztó apperent látszólagos local time helyi idő orbit pálya zone time zónaidő Orientation in time Definition: Time is change, which started in our Universe with the Big Bang 13.7 billion years ago. Humans measure this change with units connected to the apparent movement of the Sun. I. Concepts 1. Local time - starting point is the highest position on the apparent daily orbit of the Sun - it is different on every meridian 2. Zone time - was introduced to meet the demands of economy - 24 time zones, each covering 15°(24*15°=360°) with one hour difference - Greenwhich Mean Time (GMT)(Universal Time), Central European Time (CET) II. Exercises 1. What is local and zone time in the cities with the following coordinates at 12 am GMT? a, 45° N, 65° E local time: zone time: b, 70° S, 120° W local time: zone time: Summary I. Main parts of maps II. Symbols on the map III. Main types of maps IV. Exercises 1. Measuring distance 2. Calculate with the scale 3. Use network of latitudes and longitudes 4. Use index 5. Local time and zone time V. Exercises 1. Find the cities and use the legend to answer all the questions! a, settlement: 50°N, 22°E continent: ……………………………… country: ……………………………….. name of the city: R………………………. industry: ………………………………. b, settlement: 59°N, 151°E continent: ……………………………. country: ……………………………….. name of the city: M………………………. industry: ………………………………. industry: ………………………………. 2. Look up the following cities in your atlas and give accurate latitudinal and longitudinal data for them! New Orleans, Szentpétervár, Köln, Hirosima, Sydney, Budapest