kopparla dps_2014_ko..
advertisement
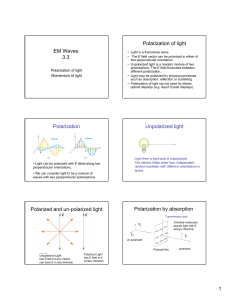
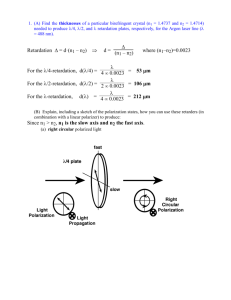
Polarized Light from Exoplanets: The Key to Clouds and Hazes? Pushkar Kopparla Vijay Natraj Yuk Yung Matthew Wilcoxson 1 Polarization and Exoplanets UNPOLARIZED POLARIZED Stam et al (2004) UNPOLARIZED 2 Model Setup From Star 1. Create a model atmosphere and perform radiative transfer (with VLIDORT*) *Spurr et al (2013) To Earth 2. Rotate polarization vectors into equatorial plane and sum over illuminated disc 3 Model Setup 3. Repeat at various phases and rotate into Earth’s sky plane Berdyugina et al (2011) 4. Compare with observations! 4 Polarimetric Observations of HD 189733b -π π 0 Observations at 0.36 and 0.44 micron wavelength -π Berdyugina et al (2011) π 0 5 Model Output: Maximum Polarization Rayleigh atmosphere Geometric albedo 0.5 Model Observations Berdyugina et al (2011) Conclusions • Polarized light from exoplanets contains information about atmospheric structure and orbital orientation. • We show that simple Rayleigh scattering comes close to but cannot fully account for the observed polarization of HD 189733b. 7 End Longitude of Ascending Node (omega) Ω star To observer