Document
advertisement
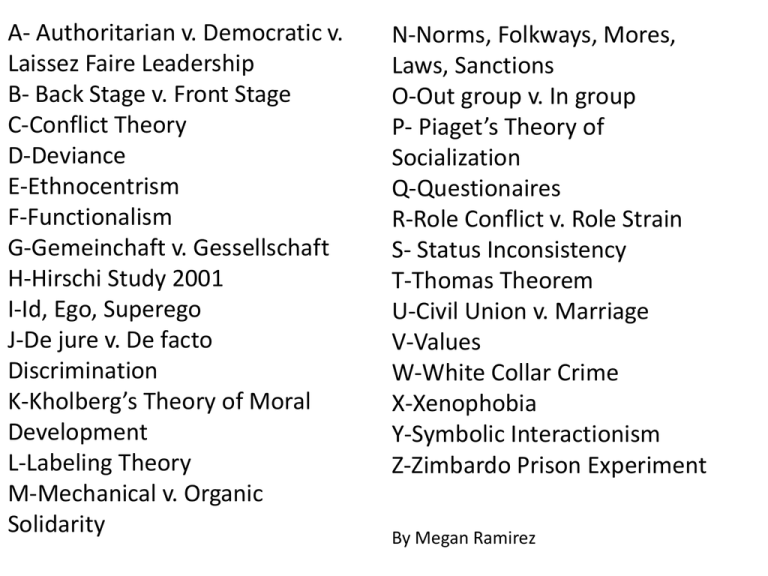
A- Authoritarian v. Democratic v. Laissez Faire Leadership B- Back Stage v. Front Stage C-Conflict Theory D-Deviance E-Ethnocentrism F-Functionalism G-Gemeinchaft v. Gessellschaft H-Hirschi Study 2001 I-Id, Ego, Superego J-De jure v. De facto Discrimination K-Kholberg’s Theory of Moral Development L-Labeling Theory M-Mechanical v. Organic Solidarity N-Norms, Folkways, Mores, Laws, Sanctions O-Out group v. In group P- Piaget’s Theory of Socialization Q-Questionaires R-Role Conflict v. Role Strain S- Status Inconsistency T-Thomas Theorem U-Civil Union v. Marriage V-Values W-White Collar Crime X-Xenophobia Y-Symbolic Interactionism Z-Zimbardo Prison Experiment By Megan Ramirez IS FOR: Authoritarian v. Democratic v. Laissez Faire Styles of Leadership Authoritarian • they lead by giving orders Democratic • they leads by trying to reach a compromise Laissez Faire • they lead by being easy going and giving people a lot of freedom (not that effective) IS FOR: Back Stage v. Front Stage Back Stage • Where you let your hair down • Ex. home Front Stage • Where we play our assigned roles • Ex. when at work, school IS FOR: Conflict Theory Conflict Theory • Key to human history is class conflict • Bourgeoisie (wealthy) v. proletariat (workers) • All about power and competition • Karl Marx! • “social living is a contest” IS FOR: Deviance Deviance • the violation of norms, rules, or expectations • The reactions to the act is what makes it deviant • Ex. Criminals IS FOR: Ethnocentrism Ethnocentrism • Use your culture to judge another (“Eating a monkey is gross • Thinking your group is better that another for no good reaso • Leads to negative feelings about “their” behavior • Gives us the right to take over other countries/ have slaves IS FOR: Functionalism Functionalism • Life is like a body • Contributions made by each part of society • Change in one part of society leads to changes in all parts of society • 4 Types • Function- positive; keeps group together • Dysfunction-negative; hurts group • Manifest- main or intended purpose • Latent- unintended outcome IS FOR: Gemeinchaft v. Gessellschaft Gemeinchaft • Intimate community • personal relationships with family and friends Gessellschaft • Impersonal association • Most time spent with strangers IS FOR: Hirschi Study 2001 Hirschi Study 2001 • Deviance depends on the bonds between society and the individual • Social bonds formed with attachment, commitment involvement, and belief IS FOR: Id, Ego, Superego Freud and Personality Id • Inborn basic drives to avoid pain, seek pleasure etc. Ego • Balancing force between the id and superego Superego • Our conscience IS FOR: De Jure v. De facto Discrimination De Jure • Discrimination “by law” • Ex. Plessy v. Ferguson • segregation in schools and other public places • ”separate but equal” De facto • Discrimination “by fact” • Ex. After Brown v. Board of Education • Segregation not constitutional but people still discriminate IS FOR: Kholberg’s Theory of Moral Development Kholberg’s Theory of Moral Development • Amoral (0-6 yrs) • Preconventional (7-10) • Conventional (10-18?) • Post Conventional (adult+) IS FOR: Labeling Theory Labeling Theory • Idea that the labels people are given affect their own and others’ perceptions of them • The result is that people channel their behavior into either deviance or conformity IS FOR: Mechanical v. Organic Solidarity What holds society together? Mechanical • People perform similar tasks • Shared values and beliefs • Ex. Farmers-hard work, religion? Organic • Interdependence in an industrial society • No shared values—might not have anything in common except that they need each other to work • Ex. Factory workers—assembly line, need everyone to make a specific part IS FOR: Norms, Folkways, Mores, Laws, Sanctions Norms-specific guideline for behavior (no smoking) Folkways-everyday habits/manners (don’t talk with full mouth) Mores- norms vital to well being of society and to our values (no incest) Laws- government’s rules (murder) Sanctions- punishment for violating norms/ reward for following them (jail, honor roll) IS FOR: Out group v. In group In group • a group you are part of • Ex. VHHS students, share school pride, classes, and clubs Out group • a group you are not a part of • For every in group there is an out group IS FOR: Piaget’s Theory on Socialization Piaget’s Theory on Socialization • Well accepted • Stages are fluid • 4 stages • Sensory Motor Stage (0-2 yrs) • Pre-Operatinal Stage (2-7) • Concrete Operationl Stage (7-12) • Formal Operational Stage (12+) IS FOR: Questionnaires=Surveys Questionnaires=Surveys • Most common for reasearch • Sample=number of people or types of people picked to answer questions • Random= Ex. People on street • Representative= Ex. 50% of VHHS IS FOR: Role conflict v. Role strain Role conflict • Too many things to do/expectations and not enough time in the day!!!! • Ex.—come home and study? Prep for club? Talk with family? Role strain • More of a moral dilemma • Ex. Lance Armstrong—do drugs and win dishonestly or no drugs and don’t win? IS FOR: Status Inconsistency + Status Inconsistency • Have some status characteristics that are relatively high and some that are relatively low • Ex. A poor person wins the lottery IS FOR: Thomas Theorem Thomas Theorem • what you think is real is real IS FOR: Civil Union v. Marriage Different kinds of families Marriage • Legal union with mutual rights and obligations • Ex. Tax and insurance benefits; if one dies, other still has to pay the mortgage • • • • Civil Union Recognition of association by state Also includes things like tax and insurance benefits and DNR But! Not all states recognize civil unions so have to stay in state where it is recognized or lose these benefits IS FOR: Values Hard work Values • General idea that people share about what is good or bad • Ex. Civil rights, hard work • 5 elements important to Americans • Leisure • Self-fulfillment • Physical fitness • Youthfulness • Concern for environment IS FOR: White Collar Crime White Collar Crime • Crimes high status people commit usually as they do their jobs • Ex. Insider trading, tax evasion, embezzement • These money crimes lead to less jail time than people crime IS FOR: Xenophobia Xenophobia • irrational dislike or fear of people from other countries IS FOR: SYmbolic Interactionism SYmbolic Interactionism • Cooley and Meade • Symbol=stands for something that has agreed meaning (Ex. Love, flag) • Defines what one should and shouldn’t do • Defines oneself and others IS FOR: Zimbardo Prison Experiment Zimbardo Prison Experiment • Experiment where some college students played the role of guards while others played the role of prisoners • Not long after the experiment started, the “gaurds” were psychologically torturing the “prisoners” • The experiment had to be stopped after just six days