The Road to Revolution
advertisement

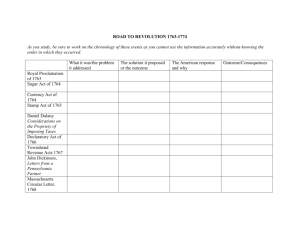
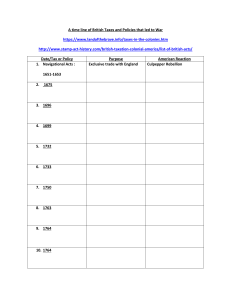
George Grenville’s Program, 1763-1765 1. Sugar Act - 1764 2. Currency Act - 1764 3. Mutiny Act - 1765 4. Stamp Act - 1765 Stamp Act Crisis * Patrick Henry - Virginia Resolves Sons of Liberty: Samuel Adams Stamp Act Congress – 1765 (NYC) * Stamp Act Resolves – James Otis Declaratory Act – 1766 Theories of Representation Q-> What was the extent of Parliament’s authority over the colonies?? Absolute? OR Limited? Q-> Representation? VIRTUAL vs. ACTUAL What was John Locke’s influence on ideal government? Townshend Duties Crisis: 1767-1770 1767 William Pitt, P. M. appoints Charles “Champagne Charlie” Townshend as Chancellor. A A External Tax on imports paper, paint, lead, glass, tea. Increase custom officials at American ports established a Board of Customs in Boston. Colonial Response to the Townshend Duties 1. Boycott British goods 2. Homespun: * “Daughters of Liberty” * spinning bees 3.Groups like the Sons of Liberty lead Riots against customs agents. 4.MA & NY Assembly voted to refuse to obey duties disbanded. The Boston Massacre (March 5,1770) Committees of Correspondence Purpose warn neighboring colonies about incidents with British broaden the resistance movement. The Gaspee Incident (1772) Providence, RI coast Tea Act (1773) 8 British East India Co.: Monopoly on Br. tea imports. Many members of Parliament held shares. Cut out colonial middlemen 8 North expected colonists to be happy - cheaper tea. Tar and Feathering Boston Tea Party (1773) The Coercive or Intolerable Acts1.(1774) Port Bill 2. Government Act 3. New Quartering Act Lord North 4. Administration of Justice Act The Quebec Act (1774) First Continental Congress (1774) 55 delegates from 12 colonies Agenda Response to the Coercive Acts & Quebec Act? 1 vote per colony represented. What 5 Decisions were made? The British Are Coming . .. Paul Revere & William Dawes make their midnight ride to warn the Minutemen of approaching British soldiers. The Shot Heard ’Round the World! Lexington & Concord – April 18,1775